2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
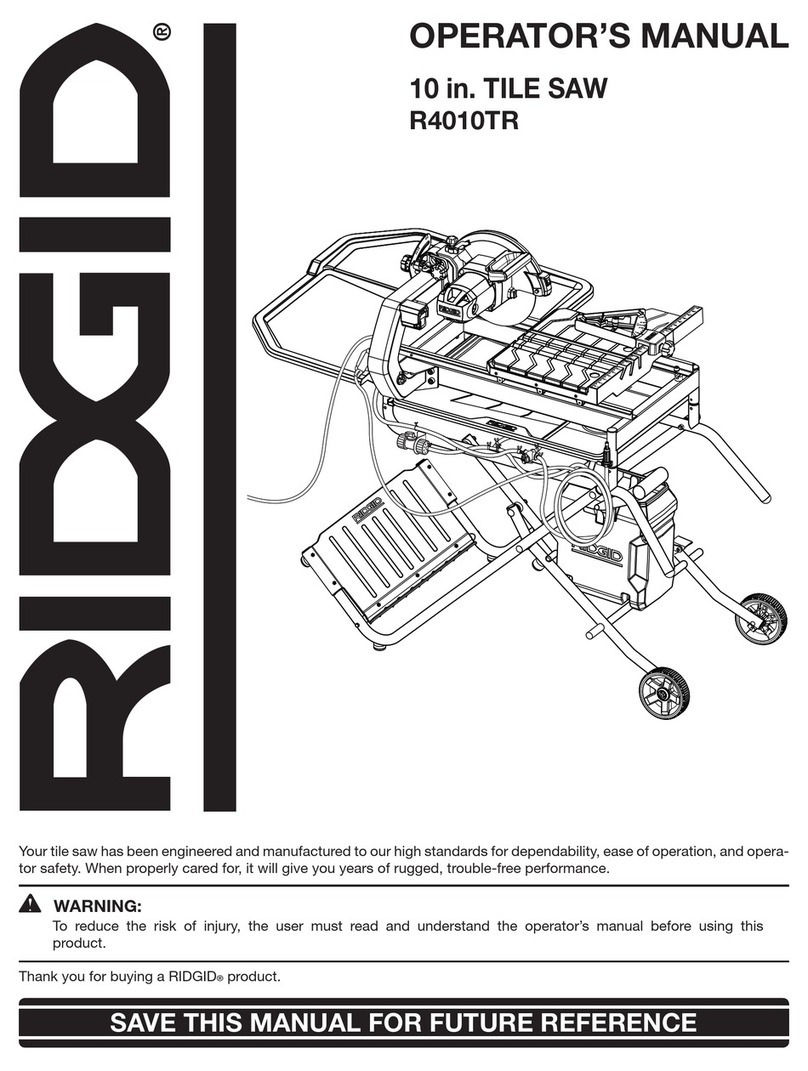
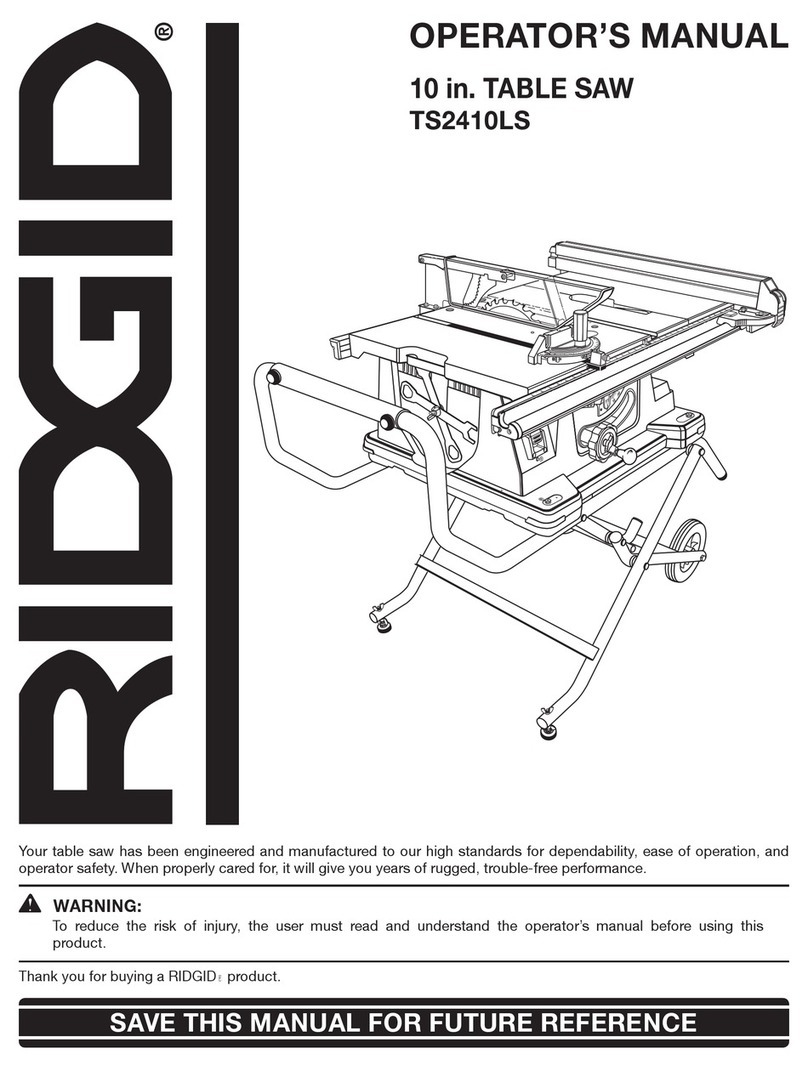
NOTE: The manual cover illustrates the current production model. All other illustrations contained in the manual are representative
only and may not be exact depictions of the actual labeling or accessories included. They are intended for illustrative purposes only.
FEATURES ......................................................................2
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS........................................... 2
KNOW YOUR COMPOUND MITER SAW ...........................5
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS......................6
SAFETY LOGOS..............................................................6
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY WARNINGS......... 7
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FOR MITER SAWS............8
PROPOSITION 65 WARNING.....................................9
POWER CONNECTIONS............................................. 10
DOUBLE INSULATION.................................................. 10
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION.......................................... 10
POLARIZED PLUGS...................................................... 10
EXTENSION CORDS .................................................... 10
UNPACKING................................................................. 11
REMOVING CONTENTS FROM PACKING........................ 11
PACKAGED CONTENTS LIST ........................................ 11
ASSEMBLY.................................................................... 12
TOOLS NEEDED.......................................................... 12
WORK CLAMP............................................................. 13
DUST BAG.................................................................. 13
INSTALL/REMOVE/REPLACE THE BLADE....................... 14
ADJUSTMENTS............................................................ 15
ALIGN THE BLADE TO TABLE....................................... 15
ALIGN THE BLADE TO FENCE ...................................... 16
DEPTH STOP ADJUSTMENT ......................................... 17
FENCE EXTENSION ..................................................... 17
BEVEL LOCK TENSION ADJUSTMENT .......................... 17
SLIDE RESISTANCE..................................................... 18
MITER LOCK ADJUSTMENT.......................................... 18
THROAT PLATE........................................................... 19
MOUNTING AND TRANSPORTATION..................... 20
PREPARATIONS FOR TRANSPORTATION....................... 20
MOUNTING SAW TO STABLE SURFACE......................... 21
OPERATION................................................................. 22
CUTTING WARPED MATERIAL...................................... 23
CLAMPING WIDE WORKPIECES ................................... 23
SUPPORTING LONG WORKPIECES ............................... 24
POWER SWITCH LOCK................................................ 24
NON-SLIDING CUTS.................................................... 25
FOR MITER CUTS........................................................ 25
FOR BEVEL CUTS........................................................ 26
FOR COMPOUND MITER CUTS..................................... 27
SLIDE CUTS................................................................ 28
TIPS FOR CUTTING CROWN MOLDING......................... 29
AUXILIARY FENCE....................................................... 30
EXPAND WORKTABLE AREA......................................... 31
MAINTENANCE............................................................ 32
KEEP MACHINE CLEAN................................................ 32
GENERAL MAINTENANCE............................................. 32
BRUSH REPLACEMENT ................................................ 32
LUBRICATION............................................................. 32
TROUBLE SHOOTING................................................. 33
FAILURE TO START..................................................... 33
ACCESSORIES ............................................................. 33
PARTS, SERVICES OR WARRANTY ASSISTANCE. 34
FEATURES
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
Cutting Capacity
(Maximum nominal
lumber sizes)
0° Miter/0° Bevel: 4 inch x 10 inch
(2 x 12 inch Extended Capacity)
45° Miter/ 0° Bevel: 4 inch x 6 inch
0° Miter/45° Bevel: 2 inch x 10 inch
(Left & Right 45° Bevel:1 inch x 10
inch)
45° Miter/45° Bevel: 2 inch x 6 inch
(Left & Right 45°Bevel: 1 inch x 6
inch)
Baseboard (Vertical) 6 inch
Crown (Vertically Nested) 7.5 inch
Net Weight 57 lbs
Input 120 V~, 60hz, 15 Amps
Blade Arbor Hole 1 inch
Blade Diameter 12 inch
No Load Speed 4,000 r/min (RPM)
Blade Max Speed Rating 5,500 r/min (RPM)
Number of Teeth 40
Blade Thickness 0.079 inch (2mm)
Blade Kerf 0.11 inch (2.8mm)
BLADE DESCRIPTIONS
APPLICATION DIAMETER TEETH
Construction Saw Blades
(thin kerf with anti-stick rim)
General Purpose 12 inch (305mm) 40
Fine Crosscuts 12 inch (305mm) 60
Woodworking Saw Blades
(provide smooth, clean cuts)
Fine crosscuts 12 inch (305mm) 80
NOTE: ONLY use blades that are marked for speeds of
4,000 r/min (RPM) or higher. NEVER use a smaller diameter
blade. It will not be guarded properly. Use crosscut blades
only. DO NOT use blades designed for ripping, combination
blades or blades with hook angles in excess of 7°.