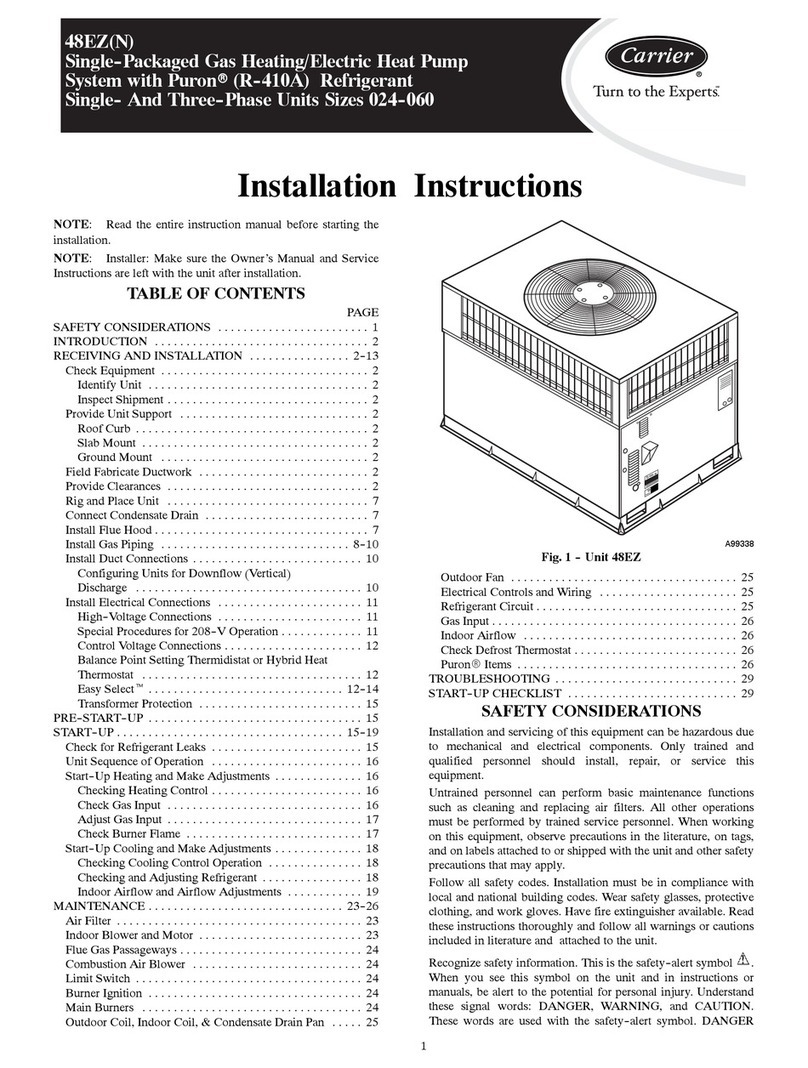
08
Manifold Sets:
-Up to 800 PSIG High Side
-Up to 250 PSIG Low Side
Manifold Hoses:
-Service Pressure Ratiing of 800 PSIG
Recovery Cylinders:
-400 PSIG Pressure Rating
3.3.1 SPECIFICATION OF R-410A:
Application: R-410A is not a drop-in replacement for R-22 ; equipment designs
must accommodate its higher pressures. It cannot be retrofitted into R-22 condens-
ing units.
Physical Properties:R-410A has an atmospheric boiling point of -62.9°F and its
saturaton pressure at 77°F is 224.5 psig.
Composition: R-410A is an azeotropic mixture of 50% by weight difluoromethane
(HFC-32) and 50% by weight pentafluoroethane (HFC-125).
Pressure: The pressure of R-410A is approximately 60% (1.6 times) greater
than R-22. Recovery and recycle equipment, pumps, hoses and the like need to
have design pressure ratings appropriate for R-410A. Manifold sets need to range
up to 800 psig high-side and 250 psig low-side with a 550 psig low-side retard.
Hoses need to have a service pressure rating of 800 psig. Recovery cylinders need
to have a 400 psig service pressure rating. DOT 4BA400 or DOT BW400.
Combustibility: At pressures above 1 atmosphere, mixture of R-410A and air can
become combustible. R-410A and air should never be mixed in tanks or supply
!CAUTION
R-410A systems operate at higher pressures than R-22 systems. Do not use
R-22 service equipment or components on R-410A equipment.
lines, or be allowed to accumulate in storage tanks . Leak checking should
never be done with a mixture of R-410A and air.Leak checking can be per-
formed safely with nitrogen or a mixture of R-410A and nitrogen.
3.3.2 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE FOR R-410A
•R-410A refrigerant operates at approximately 60% higher pressure (1.6 times)
than R-22. Ensure that servicing equipment is designed to operate with R-410A.
•R-410A refrigerant cylinders are pink in color.
•R-410A, as with other HFC’s is only compatible with POE oils.
•Vacuum pumps will not remove moisture from oil.
•R-410A systems are to be charged with liquid refrigerants. Prior to March 1999,
R-410A refrigerant cylinders had a dip tube. These cylinders should be kept
upright for equipment charging. Post March 1999 cylinders do not have a dip tube
and should be inverted to ensure liquid charging of the equipment.
• Do not install a suction line filter drier in the liquid line.
•A liquid line filter drier is standard on every unit. Only manufacturer approved liq-
uid line filter driers can be used. These are Sporlan (CW083S) and Alco
(80K083S) driers. These filter driers are rated for minimum working pressure of
600 psig.
•Desiccant (drying agent) must be compatible for POE oils and R-410A.
3.3. Information on R410a & Tools