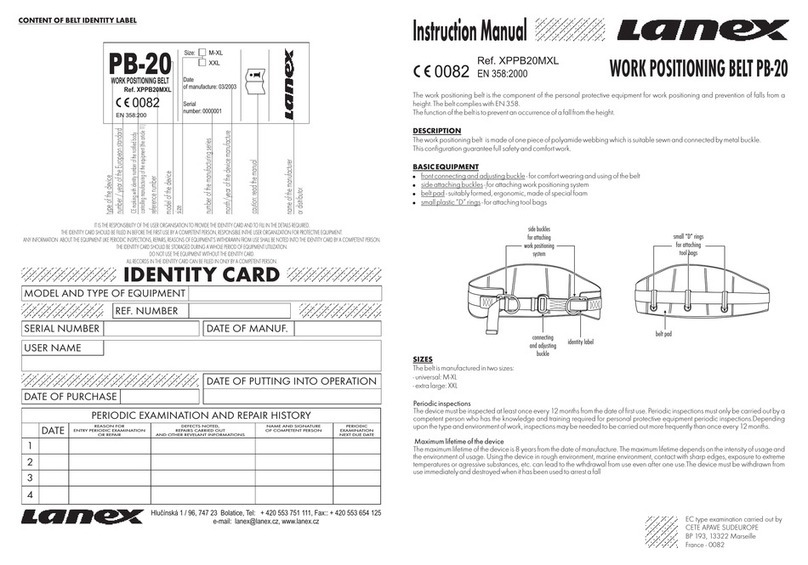
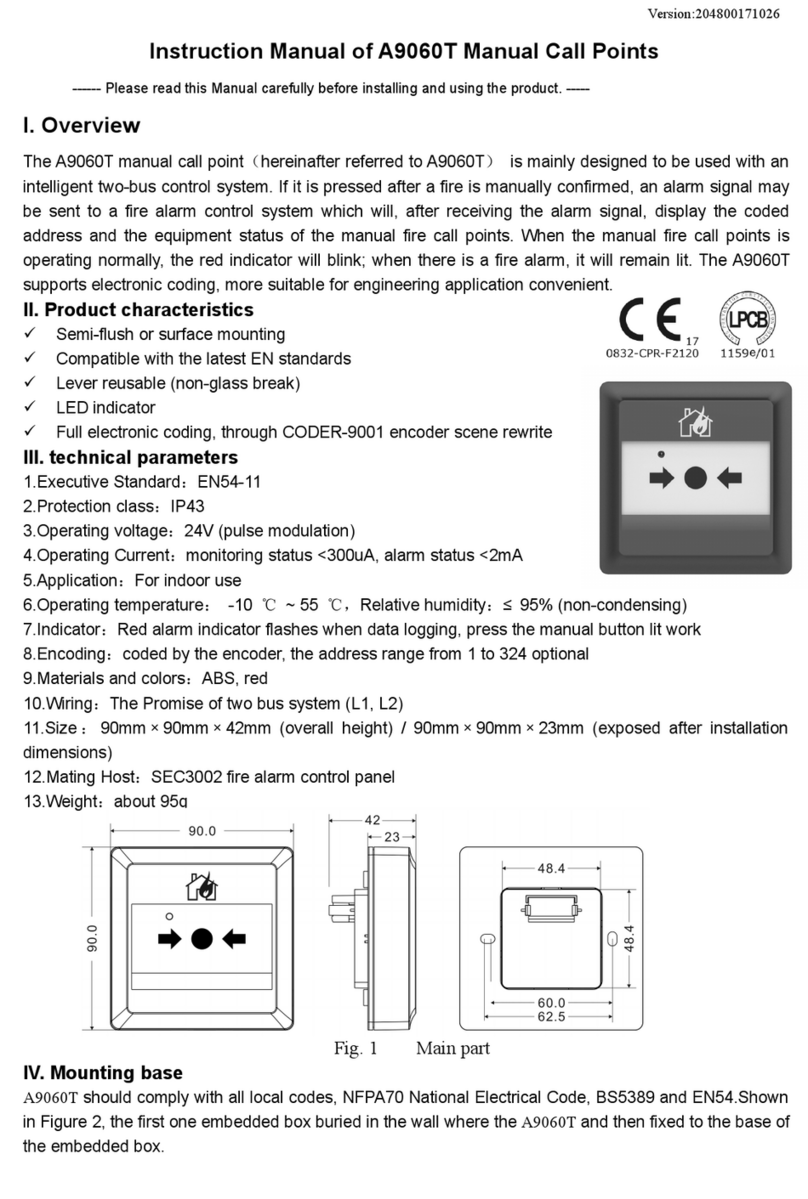
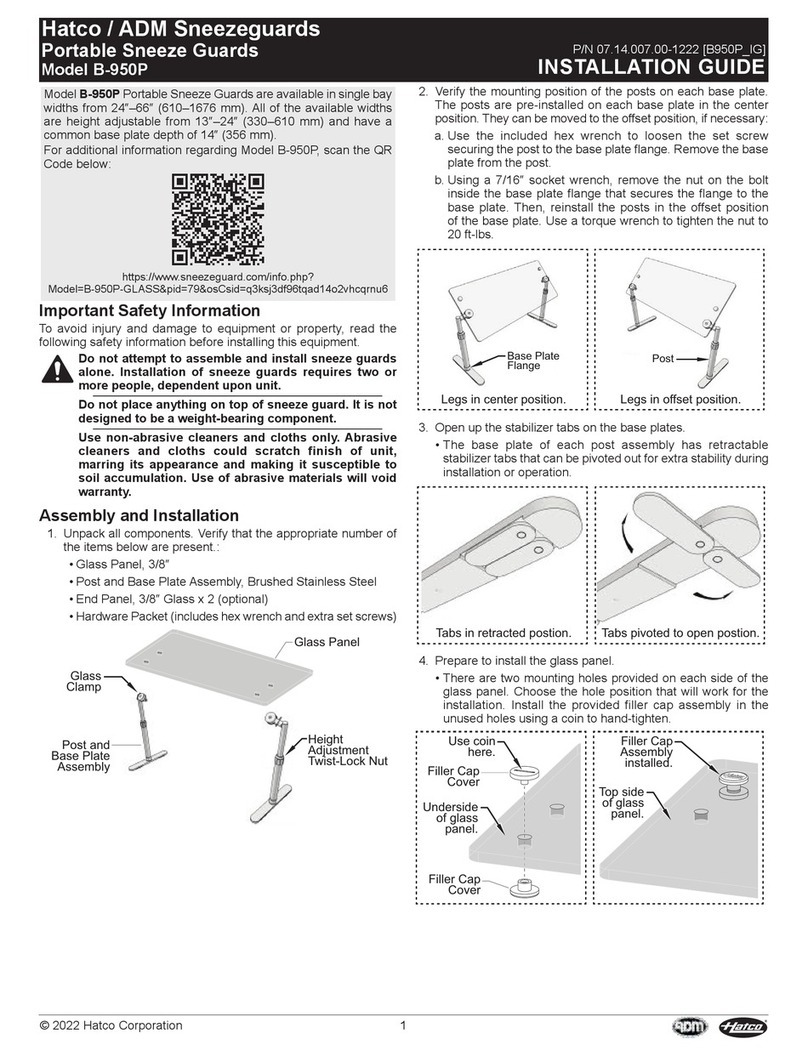
Chapter 1
Introduction and Safety
Edit: Stevens Art.#.: 86 -----, Version: 1.02 Datum:13.12.2017
1-6
Full documentation that would be needed by maintenance personnel is available
through Scheidt & Bachmann. The manual assumes that comprehensive repair
procedures will be performed by fully trained contractor technicians.
This manual reflects Scheidt & Bachmann’s commitment to providing our cus-
tomers with comprehensive technical documentation, along with training guide-
lines to augment our customer training program.
PLEASE READ THIS MANUAL AND ALL REFERENCED DOCUMENTS
CAREFULLY BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO INSTALL THIS AFC EQUIPMENT.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL AND THE
INSTRUCTIONS OR NOTES IN THE INSTALLATION DRAWINGS MAY
CAUSE INJURY TO YOURSELF OR DAMAGE TO THE EQUIPMENT AND
MAY ULTIMATELY COMPROMISE THE OPERABILITY OF THE
EQUIPMENT!
All Automated Fare Collection (AFC) equipment is TÜV-SÜD-NRTL listed. To
continue to be compliant with TÜV-SÜD-NRTL requirements, please note that
the following items need to be performed during installation:
The equipment will remain TÜV-SÜD-NRTL compliant only if the mounting and
wiring are also TÜV-SÜD-NRTL compliant. Please take great care during instal-
lation to comply with TÜV-SÜD-NRTL and NEC requirements.
Ensure compliance with all Safety Regulations and Safety Recommendations.
Although this manual has been prepared with great care, some information may
seem unclear. If so, please feel free to contact us with your remarks or ques-
tions.
Scheidt & Bachmann USA
781 272-1664
DISCLAIMER
Scheidt & Bachmann USA INC. IS NOT LIABLE FOR INJURIES TO ANY
PERSON OR DAMAGE TO THE EQUIPMENT RESULTING FROM FAILURE
TO COMPLY WITH THE MANUFACTURER’S INSTRUCTIONS OR
DOCUMENTATION. THIS DISCLAIMER INCLUDES ALL THIRD PARTY
DOCUMENTATION PREPARED BY OEMS AND PROVIDED AS A
COURTESY BY Scheidt & Bachmann USA INC. TO ITS CUSTOMERS.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW MANUFACTURER’S INSTRUCTIONS MAY
INVALIDATE ANY OR ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
NOTE: NOT ALL OF THESE WARNING LABELS OR HAZARDS MAY EXIST IN ALL
AFC DEVICES. ONLY THOSE LABELS THAT APPLY TO THE STATION
FARE TRANSACTION PROCESSOR, AND ARE REQUIRED TO MEET UL
CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS, WILL BE FOUND IN THE STATION
FARE TRANSACTION PROCESSOR. BE CAUTIOUS AND OBSERVANT,
AND LOOK FOR SUCH WARNING LABELS AND POTENTIAL HAZARDS.
ANY TECHNICIAN OR PERSON ACCESSING THE INTERIOR OF ANY AFC
DEVICE SHOULD USE COMMON SENSE AND EXERCISE EXTREME CAU-
TION.
1.3 Safety
Features
Safety engineering is an integral part of Scheidt & Bachmann’s designs. Mainte-
nance technicians must perform maintenance and repair in accordance with
industry safety standards including Federal, Provincial, and Local codes and
regulations.