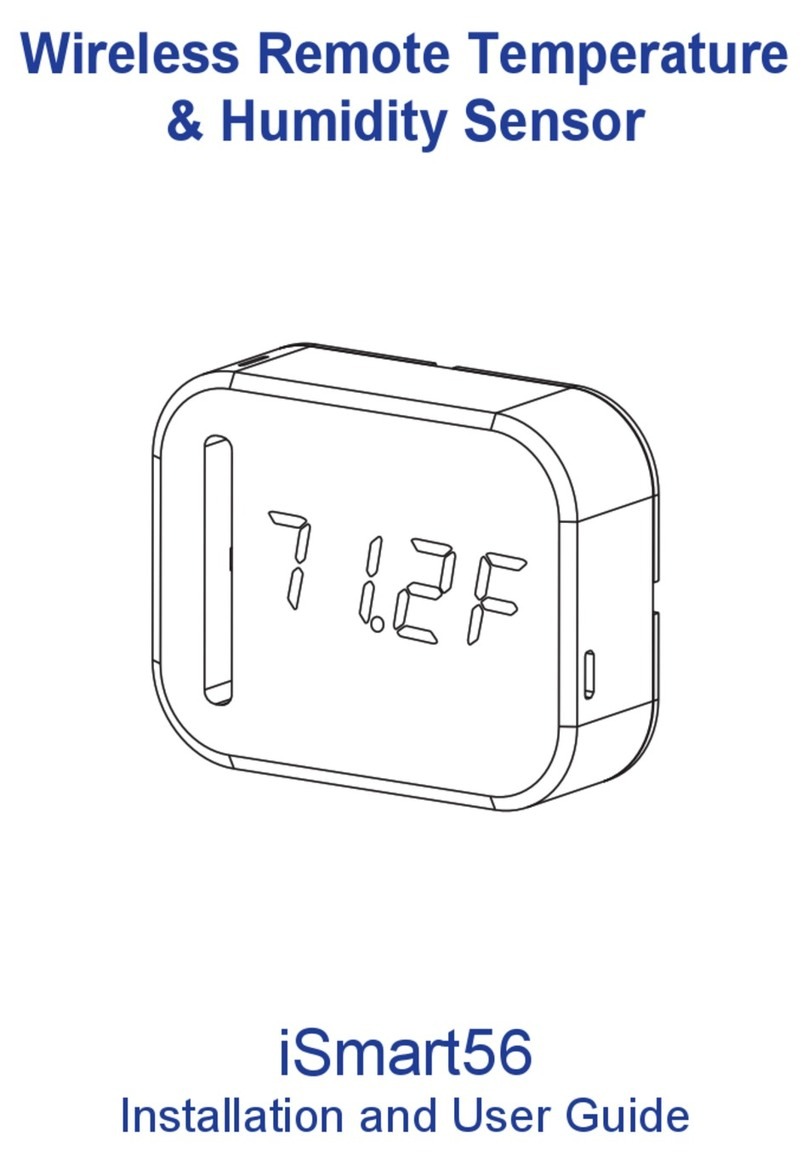
6
Operating instructions
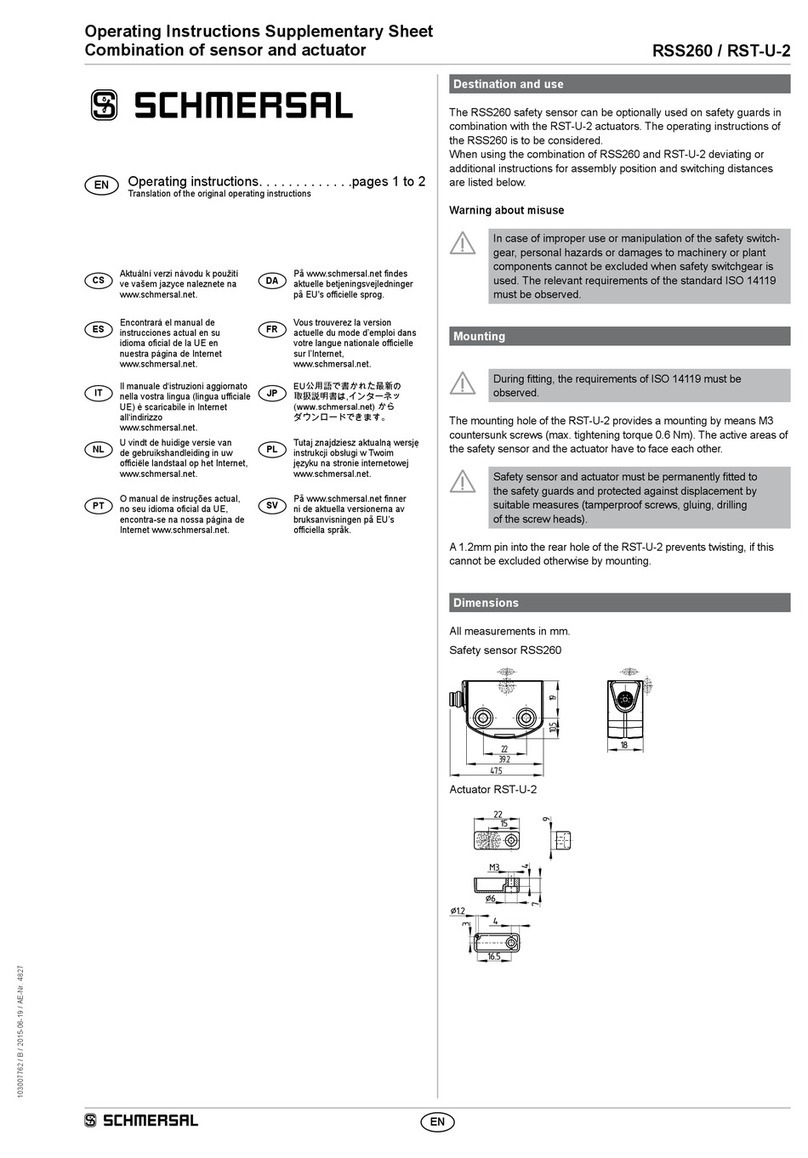
Safety sensor RSS260
EN
4. Electrical connection
4.1 General information for electrical connection
The electrical connection may only be carried out by
authorised personnel in a de-energised condition.
The safety outputs can be integrated into the safety circuit of the control
system. For applications of PL e / control category 4 to ISO 13849-1,
the safety outputs of the safety sensor or sensor of the chain must be
wired to a safety monitoring module of the same control category .
Protection is not required when pilot wires are laid. The cables however
must be separated from the supply and energy cables. The max. fuse
rate for a sensor chain depends on the section of the connecting cable
of the sensor.
Requirements for the connected safety-monitoring module
• Dual-channel safety input, suitable for p-type sensors with NO function
Information for the selection of suitable safety-monitoring
modules can be found in the Schmersal catalogues or in the
online catalogue on the Internet: products.schmersal.com.
As an alternative to a safety-monitoring module, the safety sensors of
the CSS 34F0 or CSS 34F1 series can also be used as first sensor
of a series-wired chain for the direct control and monitoring of safety
contactors (refer to operating manual of CSS 34F0 / CSS 34F1).
If the safety sensor is wired to relays or to non-safety relevant control
components, a new risk analysis must be carried out.
The sensors cyclically switch off the safety output to test them. The safe
The switch-off times must be tolerated by the safety-monitoring module.
The switch -off time of the safety sensor is additionally extended
depending on the cable length and the capacity of the cable used.
Typically, a switch-off time of 250 μs is reached with a 30-m connecting
cable.
Configuration of the safety-monitoring module
If the safety sensor is connected to electronic safety-
monitoring modules, we recommend that you set a
discrepancy time of min. 100 ms.
The safety inputs of the safety-monitoring module must be
able blanking a test impulse of approx. 1 ms.
The safety-monitoring module does not need to have a cross-
wire short monitoring function, if necessary, the cross-wire
short monitoring function must be disabled.
4.2 Serial diagnostic -SD
(only 8-pin version)
Cable design in case of serial diagnostics
On wiring SD devices, please pay attention to the voltage
drop on the cables and the current carrying capacity of the
individual components.
The wiring capacitance of the connecting cable of the safety sensor
must not exceed 50 nF.
Depending on the strand structure, normal unshielded 30 m long control
cables LIYY 0.25 (0.14) mm2to 1.5 mm2have a wiring capacitance of
approx. 3 - 7 nF.
Accessories for the series-wiring
For convenient wiring and series-wiring of SD components,
the SD junction boxes PFB-SD-4M12-SD (variant for the
field) and PDM-SD-4CC-SD (variant for control cabinet on
carrier rail) are available along with additional comprehensive
accessories.
Detailed information is available on the Internet, products.
schmersal.com.
5. Operating principles and coding
5.1 Mode of operation of the safety outputs
The safety outputs can be integrated into the safety circuit of the control
system. The opening of a safety guard, i.e. the actuator is removed
out of the active zone of the sensor, will immediately disable the safety
outputs of the sensor (switching distances refer to technical data).
Any error that does not immediately affect the functionality of the safety
sensor (e.g. too high the ambient temperature, interference potential
at a safety output, cross-wire short) will lead to a warning message,
the disabling of the diagnostic output and the delayed shut-down of the
safety outputs. safety outputs are disabled if the error warning is active
for 30 minutes.
The signal combination, diagnostic output disabled and safety channels
still enabled, can be used to stop the production process in a controlled
manner.
After fault rectification, the error message is reset by opening and re-
closing the corresponding safety guard. The safety outputs enable and
allow a restart.
For devices with serial diagnostic, a bit can be set/deleted in the call
telegram to reset the fault.
5.2 Coding
Safety sensors with standard coding are ready to use upon delivery.
Individually coded safety sensors and actuators will require the
following "teach-in" procedure:
1. Switch the safety sensor's voltage supply off and back on.
2. Introduce the actuator in the detection range. The teach-in procedure is
signalled at the safety sensor, red LED on, yellow LED flashes (1 Hz).
3. After 10 seconds, brief cyclic flashes (3 Hz) request the switch-off
of the operating voltage of the safety sensor. (If the voltage is not
switched off within 5 minutes, the safety sensor cancels the "teach-
in" procedure and signals a false actuator by 5 red flashes).
4. After the operating voltage is switched back on, the actuator must be
detected once more in order to activate the taught actuator code. In
this way, the activated code is definitively saved!
For ordering suffix -I1, the thus executed allocation of safety sensor and
actuator is irreversible.
For ordering suffix -I2, the "teach-in" procedure for a new actuator can
be repeated an unlimited number of times . When a new actuator is
taught, the code, which was applicable until that moment, becomes
invalid. Subsequent to that, an enabling inhibit will be active for ten
minutes, thus providing for an increased protection against tampering.
The green LED will flash until the expiration of the time of the enabling
inhibit and the detection of the new actuator.
The 10-minutes protection time will subsequently restart in case of a
power failure during the lapse of time.