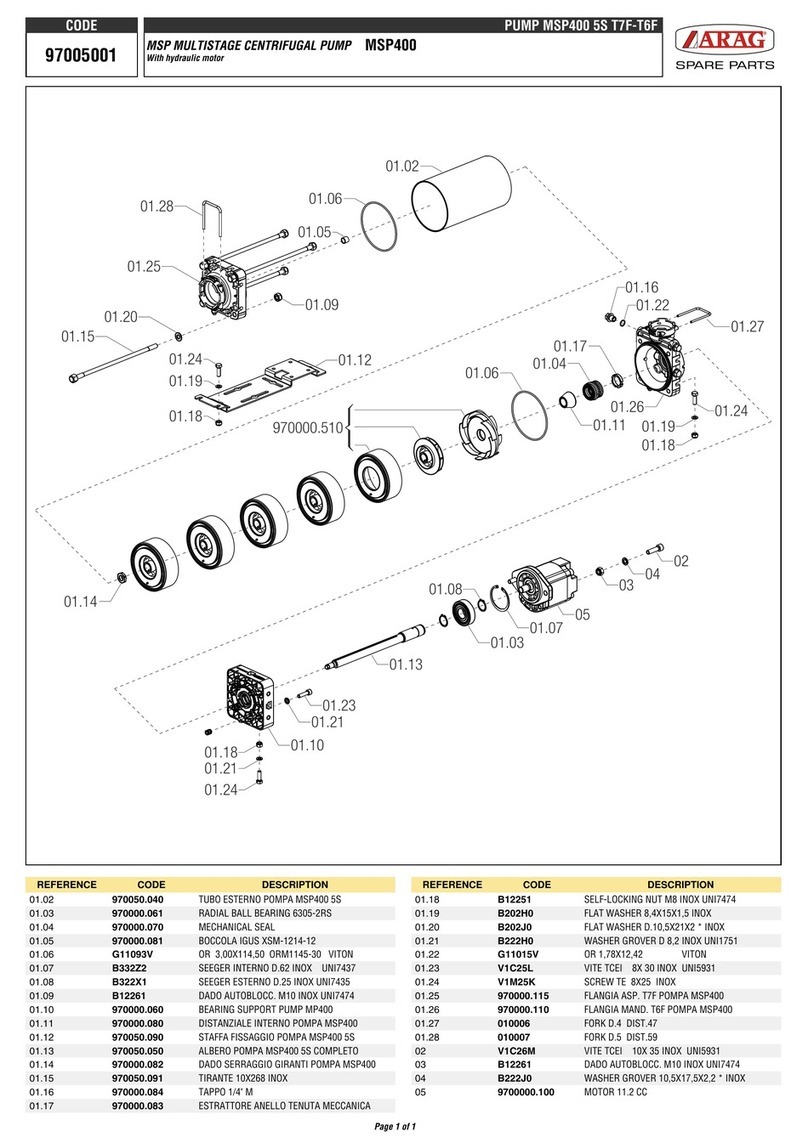
SERFILCO EFB Series Operation manual

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 1 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
⚠CAUTION
It is important that the entire contents of this booklet
be studied before installation.
All parts of the pump below the mounting plate are
constructed of corrosion resistant non-metallic
materials except the pump shaft. The shaft is stainless
steel encased in a CPVC sleeve. The major parts are
made from CPVC. These parts have been carefully
designed to safely handle all operating loads
anticipated. They should still be treated with care, to
avoid damage to the pump. All piping must be
independently supported and all temporary external
loads on the pump must be avoided. Be careful not to
over-tighten the fasteners used on the pump. Please
pay strict attention to the maximum torque values listed
below for the various fasteners.
Auxiliary connections (Bearing lubrication lines):
Do not install metal pipe fittings directly onto pipe
connections on non-metallic parts. These items are
polypropylene and included with pump.
Pump bolting: All plastic bolting below mounting
plate not to exceed 10 foot-pounds torque. All metal
bolting at underside of mounting plate not to exceed 20
foot-pounds torque.
SAFETY
This manual contains instructions for installation,
operation and maintenance of your Series 'EFB'
centrifugal pump. It has been designed to provide safe
and reliable service. However, it is both a pressure
vessel and a piece of rotating machinery. Therefore, the
operator(s) must exercise good judgment and proper
safety practices to avoid damage to the equipment and
surroundings and prevent personal injury. The
instructions in this manual are intended for personnel
with a general training in operation and maintenance of
centrifugal pumps.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND
MAINTENANCE
In these instructions you will encounter the words
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE. These are intended to
emphasize certain areas of personal safety and
satisfactory pump operation and maintenance. The
definitions of these words are as follows:
⚠WARNING: An operating procedure, practice, etc.
which, if not correctly followed, could result in personal
injury, or loss of life.
⚠CAUTION: An operating procedure, practice, etc.
which, if not strictly observed, could result in damage to,
or destruction of, equipment.
⚠NOTE: - An operating procedure, condition, etc. which
is essential to highlight.
Safety precautions before starting pump
1. Read operating instruction and instructions supplied
with chemicals to be used.
2. Refer to a chemical resistance data chart for
compatibility of materials in pump with solution to
be used.
3. Note temperature and pressure limitations.
4. Personnel operating pump should always wear
suitable protective clothing: face mask or goggles,
apron and gloves.
5. All piping must be supported and aligned
independently of the pump.
6. Always close valves slowly to avoid hydraulic shock.
7. Ensure that all fittings and connections are properly
tightened.
Before changing application or performing
maintenance
1. Wear protective clothing as described in Item 4
above.
2. Flush pump thoroughly with a neutralizing solution
to prevent possible harm to personnel.
3. Verify compatibility of materials as stated in Item 2,
Safety Precautions above.
4. Shut off power to motor at disconnect switch.
⚠Important:
1. Even though you have determined that CPVC is
chemically compatible with the solution, care should
be taken to protect the pump components against
unnecessary wear and physical abuse.
2. Record all models and serial numbers for future
reference. This information will be required when
contacting the Application Engineering Department.
3. Pump should be handled with care when removing
from shipping crate, or when placing pump in tank
or sump.
APPLICATION
The pump has been designed to operate safely and
reliably under normal service conditions. It is extremely
important that the pump be used within the limits
specified in the following sections of this instruction
book: The corrosion-resistant nonmetallic "wet-ends" of
the pump were designed to handle a wide variety of
liquids; however, do not use this pump on any other
service than that for which it was intended without first
checking a chemical resistance data chart and other
appropriate sources to determine its applicability and
suitability for any change in service.
Materials in solution contact
CPVC: Pump column, Shaft sleeve, Casing, impeller,
Discharge pipe, Casing bolts
EPDM or Viton: O-Ring
Alumina: Bearing Liner
Graphite (160°F)or Rulon (140°F): Bearing
Polyethylene: Suction strainer
Polypropylene: Bearing cooling lines

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 2 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
CHECK UPON ARRIVAL
The unit should be inspected immediately upon
arrival, and any irregularities arising due to shipment
should be reported to the carrier.
Care should be taken when unpacking pumps (see
Uncrating and Handling). A copy of this instruction
book as well as instruction sheets for other various
components (such as driver) will be included in the
shipment. Put these papers in a safe, accessible place
for ready reference when required. It is important that
the entire contents of this booklet be studied before
installation.
Pump parts and accessories may be packed inside
shipping containers, or attached to skids in individual
packages. Inspect all containers, crates and skids before
discarding.
Storage
The pump is protected against contamination for the
period of shipment and installation only.
If the pump is not to be installed at once, find a
clean, dry location for storage. Unit should be stored in
an approximately level position with no strains applied.
Protective coverings should be left in place. The pump
should be left in its shipping container or skid for
storage.
Pumps are furnished with a corrosion-resistant shaft
material and CPVC sleeved so no special preservation
measures are required.
Uncrating
1. Raise shipping skid/crate into vertical position
(driver end up) before uncrating and removing
pump. Do not sling on the pump column or motor
support to raise into the vertical position. Sling on
either the shipping skid itself or the pump mounting
plate.
2. Remove only enough of the skid/crate to allow
access to all the foundation holes on the pump
mounting plate. Install eyebolts in 3 or 4 of the
foundation holes in the pump mounting plate. Use
large flat washers on both sides of the mounting
plate when installing eyebolts. Carefully sling pump
using these eyebolts. Use a spreader between slings
to prevent damage to the motor support when
lifting.
3. Remove rest of shipping crate.
Handling
Pump should be handled only in the vertical position.
Use care when moving pumps. Rough handling of
the pump can cause breakage or permanent
misalignment.
Take care that bearing lubrication lines will not be
bent or damaged when handling.
Do not handle the pump by using the motor support.
Use the pump mounting plate, whether lifting the pump
alone or the pump/motor combination. The motor
eyebolts should be used only to lift the motor by itself.
Make sure that any equipment used to lift the pump
or any of its components is capable of supporting the
weights encountered. Make sure that all parts are
properly rigged before attempting to lift.
Cleaning the pump
Before putting the pump into operation, the liquid
end of the pump should be flushed out with water to
remove any foreign matter which may have
accumulated during shipment, storage, or installation.
If pump has been in storage over 6 months, it should
be inspected and cleaned as required before putting
into service.
Location
In the initial consideration of sump pump location,
attention should be paid to room and facilities to lift and
install the pump, plus access to auxiliary sources such
as electrical power, air and water, if required.
Also important, especially in the larger-flow units, is
proper sump design. Liquid velocity approaching the
pump should be one foot per second or less. When
more than one pump is installed and used at the same
time in the same sump, the location and spacing of the
pumps is important.
The guidelines for sump design and pump placement
as outlined in "Hydraulic Institute Standards" are
recommended.
Proper pump submergence will prevent pumping
troubles due to air or gas being drawn into the pump or
vortexing of the liquid as it enters the pump. Minimum
liquid level should not be confused with NPSH, since in
some cases the NPSHR of the pump could be greater
than the pump submergence.
Pumps furnished with suction extensions should be
used only on draw-down and stop service with optional
level control.
⚠CAUTION: Liquid level in sump must be above pump
casing whenever pump is started.
FACTORY ASSEMBLY AND TEST
All Series 'EFB' Pumps are factory checked and tested
for alignment, free rotation, flow, TDH and current draw,
to assure the assembly meets performance
specifications.
Handling during shipment, storage, or preparation
for installation could have caused distortions resulting
in pump shaft binding or disabling damage. If either
situation occurs, do not install or operate until
corrected.
When installing auxiliary equipment on the pump
(such as float controls) or while lowering the pump into
the pit, check all bolts and nuts for tightness. Check to
see that the discharge pipe is not causing any
distortions to the pump or column which could cause
shaft binding.

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 3 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
Pump mounting
The pump may be mounted directly on the pit using
the pump mounting plate or in conjunction with a pit
cover.
Carefully lower the assembled pump into the pit,
taking care not to damage lube lines. Make sure that
any equipment used to lift the pump or any of its
components is capable of supporting the weights
encountered. Make sure that all parts are properly
rigged before attempting to lift.
Pump mounting plate and/or pit cover must be level,
and supported evenly at all points before being bolted
down.
The foundation for the mounting plate or pit cover
must be sufficiently rigid to prevent vibration.
Supporting members must be sufficiently strong to
prevent spring action and /or lateral movement.
Electrical
With power off and solution in sump and water in
bearing cooling lines:
Rotate the motor shaft by hand to make sure it is
free to rotate when energized.
Connect the motor terminals to the leads from the
starter panel.
Start the motor, immediately hit the stop button, and
check for proper rotation which should be clockwise
when looking down on top of the motor. If rotation is
wrong, interchange any two motor connections on
three-phase motors. On single phase motors, follow the
motor manufacturer's instructions. After changing the
connections, again check the rotation.
Motors are suitable for VFD operation.
⚠CAUTION: Failure to follow this instruction can result
in serious damage to pump and driver if rotation is
wrong.
Piping
⚠NOTE: The design of piping systems, foundations and
other areas of system design is the responsibility of the
customer. This data and comments are offered as an
aid, but we cannot assume responsibility for the
installation design and operation.
We recommend that the customer consult a
specialist skilled in the design of piping, sumps and
related systems so as to supplement and interpret the
information and ensure a successful installation.
Discharge piping should be connected to the pump
such that no strain or weight of the piping is carried by
the pump. Check pump shaft for freedom of rotation by
hand to make sure discharge piping strain is not causing
binding.
A check valve is required to prevent back-flow
through the pump on shut-down. Manufacturer will not
be responsible for damages resulting from failure to
install a check valve.
⚠NOTE: If quick-closing valves are installed in the
discharge piping system, protection MUST be provided
to ensure that no surge or water hammer is transmitted
to the pump.
PRE-STARTING CHECKS
Motor preparation
Prepare the driver for operation as instructed by the
driver manufacturer. Re-check all connections to the
motor and control with the wiring diagram. Make sure
voltage and frequency on the motor and control
nameplates correspond with the line voltage.
If the driver has not been checked for rotation, it
must be done now.
Pre-start-up
1. Verify that materials of construction are compatible
with solution being pumped. Refer to ‘Materials in
Solution Contact’ table Page 1.
2. Verify that operating temperature is not in excess of
maximum recommended. Refer to ‘Materials in
Solution Contact’ table Page 1.
3. Carefully place pump into sump or tank and secure
in position using bolts, clamps, etc. Check alignment
and position of level controls as instructed above.
4. Connect electrical supply to motor starter.
A Soft Starter is recommended to prolong the
life of the pump. If starter is furnished, verify that
starter and motor are wired for the correct
operating voltage, and the starter contains the
correct overload heaters. It is recommended that a
motor starter be installed if one was not provided
with the pump assembly.
5. If mounting plate bolts or pump-motor lock nuts are
loosened, pump alignment must be checked.
6. Do not energize motor until pump is immersed
in liquid and then follow startup no.1.
7. Secure the assembly, complete all piping and firmly
support.
8. Check for correct high-low operation of level control
by manually positioning float rod or a current check
of conductivity level controls.
9. Check for correct operation of motor starter and
Dri-Stop when included.
Product flush lubricated pump bearings
Check to see that the product flush lines are
connected to the pump discharge elbow. Check that no
damage has occurred to the lubrication lines during
shipment or installation.
⚠NOTE: If solution being pumped crystalizes when
exposed to air and bearings are not always submerged
in solution, pump bearing lubrication with water is
recommended.
Water-lubricated pump bearings
Clean water from an external source must be used
when pumps are furnished with bearings for which
water lubrication is required. Check to see that
connections are made to bearing lubrication fittings on
pump mounting plate, and that 0.5 GPM of water per
bearing at 10 PSIG is available. Do not install metal pipe
fittings directly onto pipe connections on non-metallic
parts. Check to see that no damage has occurred to the
lubrication lines during shipment or installation.

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 4 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
OPERATION & START-UP
After all pre-starting checks have been performed,
the pump is ready to start. Observe the following
procedure to put the pump into operation:
1. Rotate the pump shaft by hand through at least one
complete revolution to see that there is no rub or
bind.
2. Leave open very slightly, the control valve in the
discharge line.
3. Start the motor.
4. As soon as the pump is up to rated speed, slowly
open the discharge valve to desired capacity or
pressure.
Operating checks
Costly shut-downs will be avoided by making routine
checks on pump operation.
1. Check to see if liquid is being discharged. A
discharge pressure gauge is an easy way to check
whether or not the liquid is being pumped.
Compare discharge pressure to pump flow curve to
determine flow rate. If, at any time, the gauge
should drop to zero, or register an abnormally high
pressure, shut down the pump immediately.
2. Observe pump for any abnormal noise or vibration.
Any CHANGE in pump noise or vibration will require
shut down and inspection.
3. At maximum flow conditions, measure amperage on
all lines. If in excess of motor nameplate ratings,
stop and consult Application Engineering Dept.
Stopping the pump
Normal operation of level controls will stop and start
the pump when MANUAL-OFF-AUTO motor starter is at
AUTO position. When performing maintenance, turn
starter to OFF, disconnect electrical supply and follow
standard safety procedures.
⚠CAUTION: When operating for some time at reduced
capacity, much of the pump horsepower will go into the
liquid in the form of heat. A bypass must be provided
under these conditions to prevent the liquid in the
pump from becoming hot enough to vaporize. Damage
to pump may result from prolonged operations at
reduced capacities. See Minimum flow.
⚠WARNING: In the interest of operator safety, the unit
must not be operated above the nameplate conditions.
Such operation could result in unit failure causing injury
to operating personnel. Consult instruction book for
proper operation and maintenance of the pump and its
supporting components.
Minimum flow
Always maintain sufficient flow through the pump to
prevent flashing of the liquid passing through the pump.
At low flows, a large proportion of the horsepower input
is absorbed by the liquid as heat, so the flow must be
maintained at a point sufficient to keep the temperature
rise through the pump within a safe limit.
⚠CAUTION: Damage to pump may result from
prolonged operations at reduced capacities.
In addition to heat rise considerations for minimum
flow, there is also a minimum flow requirement for
mechanical protection of the pump. Damage to the
pump may occur at reduced capacities due to increased
hydraulic thrust loads. These higher loads cause
increased vibration and shaft deflection, and decreased
bearing life. Also encountered at low flows is the
damage which could be done by erosive swirl. At low
flows, much of the pumped liquid is recirculated
through the pump. This can result in localized damage
to the pump by erosive action particularly when
pumping light slurries or "dirty" liquids.
Both heat rise and mechanical protection must be
considered when determining correct minimum flow.
The pump has been designed to operate at low flows
without problems due to hydraulic thrust; however, a
minimum flow of 50 GPM is required for satisfactory
operation and pump life.
TROUBLE CHART
If any of the following troubles are encountered, they
may be due to the causes listed below.
No liquid delivered:
1. Liquid level in sump too low (pump casing not
submerged).
2. Speed too low - check motor voltage.
3. Air or gas in liquid.
4. Strainer clogged.
5. Impeller clogged.
6. Casing or discharge line clogged.
7. Wrong direction of rotation.
8. Discharge valve closed; check valve installed
backwards (or stuck)
9. Not enough NPSH available
Not enough pressure:
1. Liquid level in sump too low (pump casing not
properly submerged)
2. Speed too low - check motor voltage
3. Air or gas in liquid
4. Wrong direction of rotation
5. Impeller partially clogged or damaged
6. Excessive impeller running clearance
7. Liquid vortexing in sump
Not enough liquid delivered:
1. Liquid level in sump too low (pump casing not
properly submerged)
2. Speed too low- check motor voltage
3. Air or gas in liquid.
4. Strainer partially clogged.
5. Impeller partially clogged or damaged.
6. Casing or discharge line partially clogged.
7. Wrong direction of rotation.
8. Discharge valve partially closed.
9. Not enough NPSH available.
10. Discharge head too high.
11. Excessive impeller running clearance.
12. Liquid vortexing in sump.

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 5 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
Pump uses too much power:
1. Speed too high
2. Head lower than rating (allows pump to handle too
much liquid)
3. Liquid heavier and more viscous than rating.
4. Rotor binding.
5. Impeller dragging.
6. Wrong direction of rotation.
Excessive vibration:
1. Air or gas in liquid.
2. Badly worn bearings.
3. Bent shaft.
4. Pump running backwards.
5. Impeller plugged or damaged.
6. Pump foundation not rigid.
7. Liquid level in sump too low (pump casing not
properly submerged).
8. Not enough NPSH available.
9. Pump and driver shafts misaligned.
10. Liquid vortexing in sump.
MAINTENANCE
⚠WARNING: Do not attempt any maintenance,
inspection, repair or cleaning in the vicinity of rotating
equipment. Such action could result in personal injury
to operating personnel.
Before attempting any inspection or repair of the
pump, the driver controls must be in the "OFF" position,
locked and tagged to prevent injury to personnel
performing service on the pump.
Preventive maintenance
Pumps are ruggedly constructed, and with proper
care will give years of satisfactory service. It is
recommended that operating personnel become
familiar with "Operating Checks" described previously in
this book, and that these checks be made as a matter of
routine.
Periodically, depending upon your service schedule,
the unit should be dismantled, and all internal parts and
passages cleaned and inspected for wear. Any foreign
matter found in the pump should be removed, and all
excessively worn parts replaced.
Manufacturer assumes no responsibility or liability
for improper start-up, unattended pump operation or
routine inspection performance checks or maintenance.
The following is a list of normal maintenance
procedures that might be performed between major
overhauls:
Pump bearing lubrication - 'Product'
Pumps furnished with pumped-product bearing
lubrication need no maintenance checks other than
observing that product is flowing to bearings when
motor is energized. If there is no flow to bearings then
immediately de-energize motor, clean and flush bearing
tubing and fitting.
Pump bearing lubrication - 'Water'
Check frequently to see that water is flowing to
pump bearings. Water lubrication is needed to dissipate
heat and abrasives. Some bearings may always or
temporarily be above solution level. Flow of water
lubrication must be checked. To prevent motor from
being energized without proper and adequate water
lubrication to bearings, a DRI-STOP 2 flow switch can be
installed in the water to manifold. If this pump protector
device was included with pump assembly, then refer to
Operating Instructions and Service Guide O-1685, which
is included with the DRI-STOP.
⚠WARNING: Operation of the unit without proper
lubrication can result in overheating of the bearings,
bearing failures, pump seizures and actual breakup of
the equipment exposing operating personnel to
personal injury.
Overhaul instructions
Use extreme care in removing and dismantling
pump. Refer to pump assembly drawing for part
nomenclature.
1. Close control valve in discharge line.
2. Lock out power supply to driver.
3. Disconnect all electrical connections.
4. Disconnect any external auxiliary piping
connections.
5. Disconnect discharge piping from pump.
6. Unbolt pump support plate and lift pump from pit
(let casing drain thoroughly before removing pump
completely).
7. Remove liquid level controls (if any).
8. Lay pump horizontally on supports.
⚠IMPORTANT: These models have pressure lubricated
bearings, whereby the bearing cooling / lubricating
solution enters the pump column equidistant between
each pair of bearings.
Cleaning and inspection
All parts should be clean for inspection and
reassembly. Wash all parts and spread them out in a
clean area.
Dry the parts with compressed air or lint-free cloths
and carefully inspect them as described below. Discard
O-Ring and gaskets, as new ones should be used during
reassembly.
1. Inspect impeller for excessive wear and etching due
to corrosion. Large nicks and deep pits will
unbalance the impeller and cause vibration and
wear in other parts of the pump. Be sure O-Ring
sealing surfaces are clean.
2. Check pump shaft for straightness. Inspect the
surface of the shaft in the bearing areas to make
sure it is smooth. It must be free of grooves,
scratches, corrosion or wear. Check ends of shaft for
burrs. Make sure that shaft threads are clean.
3. Inspect casing thoroughly, removing all burrs and
foreign matter. Check hydraulic passages for
cleanliness.

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 6 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
4. Check all other parts for burrs, wear, damage or
corrosion.
5. Inspect inside diameter or bearings. Check for
cracks uneven or excessive wear scoring or heat
discoloration, and corrosion. Bearings should be
replaced in accordance with the instructions given.
PUMP SERVICE
Refer to parts list P-3180 (Single Bearing Pump) or
parts list P-3182 (Double Bearing Pump). The only parts
considered for normal replacement are the ceramic
casing liner and the rotating bearings (2) (Rulon or
graphite) for each bearing assembly. Under abnormal
conditions of service these components, the impeller,
the impeller sleeve assembly and even the stainless
steel drive shaft may fail prematurely. Major causes for
premature failure are:
1. Clogged suction strainer.
2. Clogged cooling/lubricating lines to bearings when
product flushed.
3. Failure of water supply to bearings when water
lubricated
4. Motor energized before suction casing is immersed
in solution.
5. Incorrect direction of rotation.
Before proceeding with pump service, be sure the
assembly is disconnected from piping and electrical,
drained and flushed.
Replace impeller and bearing bushings
1. Loosen and remove casing bolts and lock nuts.
Remove suction casing and O-Ring. Note correct
position of suction casing for reassembly.
2. With vise grips or channel lock pliers, hold pump
shaft just below motor (or hold motor armature at
fan blade). With a chain wrench around the impeller,
turn the impeller-sleeve-bearing assembly in a
counterclockwise direction until the assembly is
unscrewed from the pump shaft, and remove with
care.
3. With vise grips or channel lock pliers now on the
sleeve assembly (above bottom bearing), the
impeller may be turned in a Clockwise Direction
(Left Hand Thread) to remove from sleeve.
4. Note position angle of grooves and slide old
bearings off sleeve. Replace with new bearings,
noting correct angle of grooves, and new bearing
spacer.
5. If pump has only a single pair of bearings, then
proceed to step 9.
6. Second set of bearing rings are removed by turning
top shaft sleeve from bottom shaft sleeve in a
Clockwise Direction (Left Hand Thread) to loosen.
7. Replace with new bearings, noting correct angle of
grooves, and new bearing spacer.
8. Replace or inspect shaft sleeve O-Ring then thread
top shaft sleeve to bottom shaft sleeve in a Counter
Clockwise Direction to tighten.
9. Replace or inspect impeller O-Ring, thread new
impeller to sleeve Counter Clockwise Direction
tighten.
10. Replace impeller-sleeve-bearing assembly to drive
shaft.
11. Replace or inspect suction casing O-Ring.
12. Reassemble suction casing and if removed, fan
blade and fan housing.

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 7 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
Replace lower ceramic liner
1. Refer to: "Replace impeller and bearing
bushings", steps 1 and 2 to remove impeller sleeve-
bearing assembly.
2. Remove Support Casing by unscrewing the (6) Cap
Nut Studs.
3. Remove Pin Holder Ring by spreading it apart to
slide over inside pins. Remove the two Liner Lock
Pins. Remove ceramic liner by sliding it out of the
Column.
4. Install new liner into Column and lining up holes.
Insert the two Liner Lock Pins. Longer part of the pin
goes in first.
5. Replace Pin Holder Ring by spreading it apart to
slide over inside pins.
6. Replace the Support Casing with the (6) Cap Nut
Studs. Make sure to replace the (2) O-Ring at each
Cap Nut Stud.
7. Replace impeller-sleeve-bearing assembly to drive
shaft.
8. Replace or inspect suction casing O-Ring.
9. Reassemble suction casing and if removed, fan
blade and fan housing.
Replace upper ceramic liners
1. Refer to: "Replace impeller and bearing
bushings", steps 1 and 2 to remove impeller sleeve
bearing assembly.
2. Remove lubrication hose from upper bearing.
3. Unscrew 3/4NPT Column Locking bushing from
column coupling.
4. With strap wrench, securely hold column above
bearing assembly and using second strap wrench,
unscrew lower column from bottom of bearing
assembly.
5. Remove the two pins in the ceramic liner. Note the
position of the flush hole in ceramic liner Remove
ceramic liner by sliding out.
6. Install new liner making sure flush hole is in same
position and secure using the two pins.
7. Tighten lower column into upper column, making
sure you see ceramic flush hole through coupling.
8. Replace 3/4NPT Column Locking Bushing into
column coupling
9. Install impeller-sleeve-bearing assembly. View
through flush hole in bearing housing to verify that
bearing spacer is in view. Then reinstall lubrication
hose.
REFERENCE DOCUMENTS:
Product Bulletin
Series 'EFB' Sump Pumps P-318
Technical Bulletin
Series 'EFB' Sump Pumps T-P-318
Parts List
Series 'EFB' Single Bearing Sump Pump P-3180
Series 'EFB' Sump Pumps Double Bearing P-3182

WWW.SERFILCO.COM 2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 (800) 323-5431
Operation and Service Guide
O-3180 - Page 8 of 8
03/05/21
© 2021 Serfilco Ltd, All Right Reserved.
®
2900 MacArthur Blvd. Northbrook, IL. USA 60062 WWW.SERFILCO.COM (800) 323-5431
Series 'EFB' | Sump Pumps
TABLE OF CONTENTS
⚠Caution ............................................................................1
Auxiliary connections......................................................1
Pump bolting: .................................................................1
Safety..................................................................................1
Installation, operation and maintenance ............................1
Safety precautions before starting pump ..........................1
Before changing application or performing maintenance .1
⚠ Important: ......................................................................1
APPLICATION ......................................................................1
Materials in solution contact ............................................. 1
Check upon arrival ..............................................................2
Storage ...............................................................................2
Uncrating............................................................................2
Handling .............................................................................2
Cleaning the pump .............................................................2
Location..............................................................................2
Factory assembly and test...................................................2
Pump mounting..................................................................3
Electrical ............................................................................. 3
Piping..................................................................................3
PRE-STARTING CHECKS .......................................................3
Motor preparation .............................................................3
Pre-start-up ........................................................................3
Product flush lubricated pump bearings............................ 3
Water-lubricated pump bearings.......................................3
Operation & start-up ..........................................................4
Operating checks................................................................4
Stopping the pump............................................................. 4
Minimum flow .................................................................... 4
Trouble chart ......................................................................4
No liquid delivered: ............................................................4
Not enough pressure:......................................................... 4
Not enough liquid delivered:..............................................4
Pump uses too much power: .............................................5
Excessive vibration: ............................................................ 5
Maintenance.......................................................................5
Preventive maintenance .................................................... 5
Pump bearing lubrication - 'Product' ................................. 5
Pump bearing lubrication - 'Water' ....................................5
Overhaul instructions .........................................................5
Cleaning and inspection ..................................................... 5
Pump service ......................................................................6
Replace impeller and bearing bushings ............................. 6
Replace lower ceramic liner ...............................................7
Replace upper ceramic liners .............................................7
Reference documents: ........................................................7
Product Bulletin..................................................................7
Technical Bulletin ...............................................................7
Parts List ............................................................................. 7
Table of Contents................................................................8
Table of contents
Popular Water Pump manuals by other brands

Grizzly
Grizzly GP 2736 K Translation of the original instructions for use

Franklin Electric
Franklin Electric FLS-400 manual

Oase
Oase AquaMax Eco Classic 3600 operating instructions

Salamander Pumps
Salamander Pumps CTFORCEU manual

Xylem
Xylem Lowara Ecocirc Premium Series manual

Crane
Crane burks pumps WB4 Installation and operation manual

emaux
emaux SPV Series user manual

Alemite
Alemite 7886-S5 Service guide

Pentair
Pentair Sta-Rite DMC Series Installation and operation manual
Spirax Sarco
Spirax Sarco APT10-2 Installation and maintenance instructions

Grundfos
Grundfos GT-C Installation and operating instructions

DROPSA
DROPSA 3414 Series User and maintenance manual