2.4
GHz
Spectrum
Overview
--
-~-
·
·
·
··
·
--·
··
··
-•
" ""
·
~·
·
··
··
·"'""
"
~·
--·
··
·
~·
~
-~
-
~
..~
..
..
......
..
-·~-
·
-
-
·
"'
"
"
'~
··
··~
·".
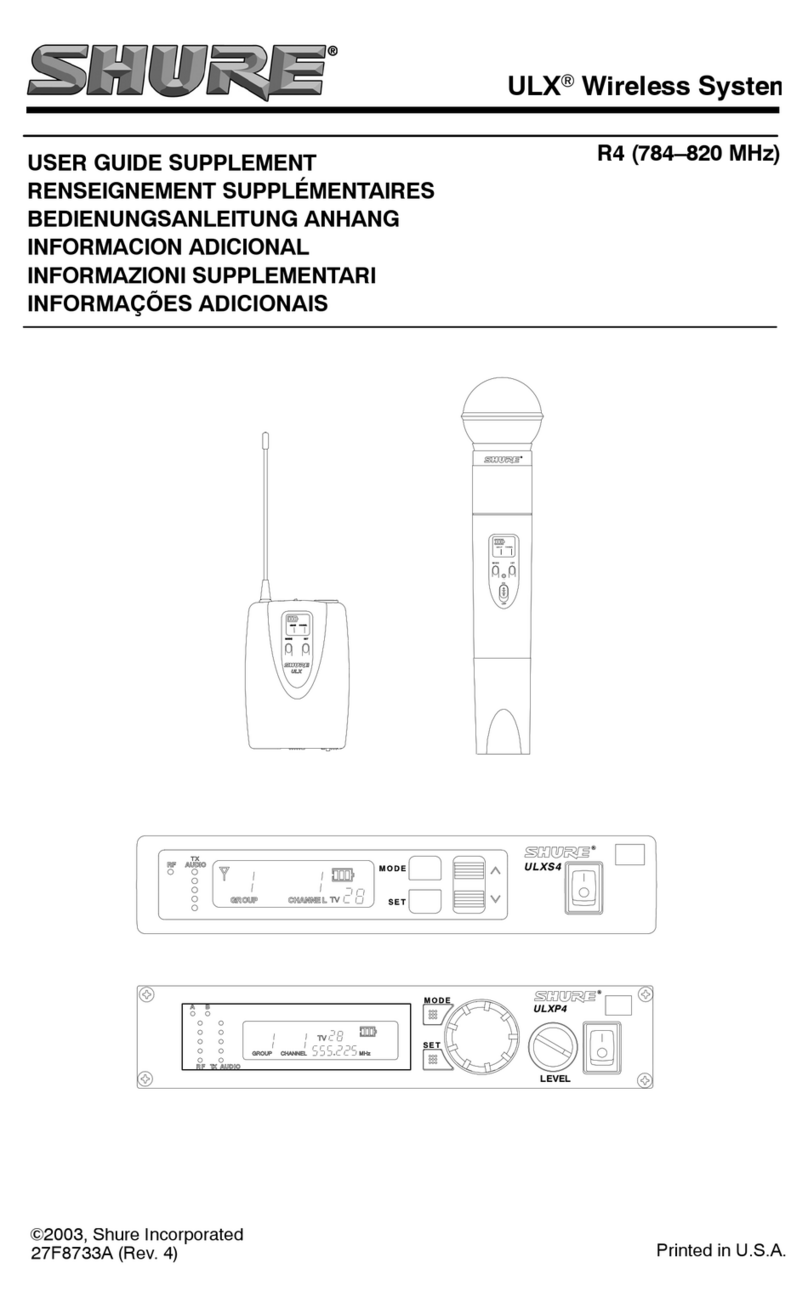
GLX-D operates within the 2.4GHz ISM band which is utilized by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other wireless devices. The benefit of 2.4GHz is that it's a global band that can
be
used
anywhere in the world, license free.
Overcoming
the
Challenges
of 2.4 GHz
The challenge of 2.4 GHz is that Wi-Fi traffic can be
unpredictable. GLX-D meets these challenges
in
the
following ways:
Coexisting with Wi-Fi Challenging Wireless
Environments
Some environments are more difficult than others for 2.4 GHz
wireless system performance. Additionall
y,
body absorption
has a greater impact in the 2.4 GHz spectrum compared to
the UHF spectrum. The simplest solution
in
many cases is to
reduce transmitter-to-receiver distance by placing receivers
• Prioritizes and transmits on the best three frequen-
cies perchannel (choosing from a pool of six fre-
quencies across the 2.4 GHz band)
Seamlessly moves away from interference to back-
up
frequencies without audio interruption
If you plan to use Wi-Fi during a perfor-
mance, turn on Wi-Fi devices prior to turning
on GLX-D and scanning for the best chan-
nel. GLX-D detects and avoids other Wi-Fi
traffic
by
scanning the entire 2.4 GHz en-
vironment and selecting the three best fre-
quencies to transmit on. This method avoids
Wi-Fi signals and results in reliable perfor-
mance for your GLX-D wireless system. on the stage with a clear line
of
sight. You can also mount
antennas remotely using Shure directional antennas to reduce
transmitter-to-antenna distance.
Optional GLX-D Frequency Manager improves RF
reliability for systems with more than two receivers
• Continuously scans during usage to rank all fre-
quencies (both current and backup frequencies)
"Bursting" Wi-Fi is harder to detect as it is
periodic; however, because GLX-D only re-
peats the most important information, even
bursts at very high levels don't have an ef-
fect on your audio performance.
Challenging environments include:
Areas with few reflective surfaces such as:
-Outdoors
-Buildings with very high ceilings
• Antenna mounting accessories and directional
antennas (available separately) help reduce trans-
mitter-to-antenna distance and connect to antenna
splitter
Three or more GLXD4R receivers in use and not connected
to a GLX-D Frequency Manager
Areas with a strong Wi-Fi presence
2.4 GHz systems from other manufacturers in use
Note: Unlike analog TV band wireless system which typically use the same type of transmissions across manufacturers, all 2.4 GHz wireless currently on the market use dif-
ferent variations of wireless transmission. These differences make it more difficult to mix and match 2.4 GHz systems from multiple manufacturers, as can bedone with
TV
band wireless solutions.
Tips
to
Improve
Wireless
System
Performance
--
-~-
-
--
~
·
O
"H
-
·
0
0'
' " ' •O
••
P · · ·
o-
-O
o0
'·0
0'
' • - < • U
hOO'-
- · -
or>-
0
0--
0 0 0' '
0'0
0
''"
'
·'-•
''
0 .
,,
·~
··
-··-
--
-
0 - ·
-
~---
'-'·
'
'
·'
•
·
-~'
-·
'·
·
0
.,
"
·'
' 4
,,
. ,
,_,
..
, 0
·•·-
. , ' • '
•>
-------
'-'-'••
'>
0 . ,
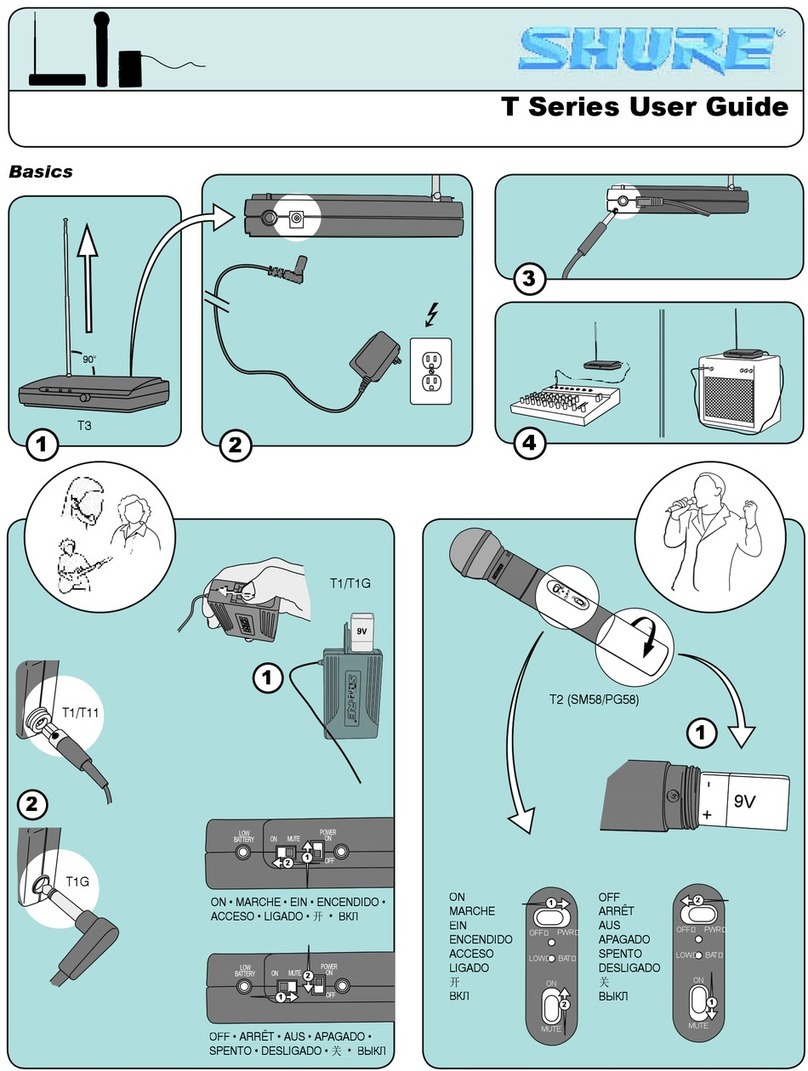
If you encounter interference
or
dropouts, try the following suggestions:
1.
Place receiver
atleast3
meters
(1
0 feet) away from Wi-Fi ac-
cess points, computers,
or
other active 2.4 GHz sources.
Avoid heavy Wi-Fi traffic activities such as downloading large files
or
viewing a
movie.
Turn on any Wi-Fi prior to turning on GLX-D and scanning for the best channel.
2. Reduce transmitter-to-receiver distance by placing receivers on stage
or
above the audience with a clear line of sight to the transmitter.
Move receiver to the top of the equipment rack for a clear line of sight.
Mount antennas remotely to place closer to transmitters and improve RF reli·
ability if receivers cannot
be
moved closer.
Make sure people
do
not block the line
of
sight between receiver and
transmitter.
Additional Tips
• Do not place competitive 2.4 GHz receivers near GLXD4R receivers.
• Connect more than two GLXD4R receivers to a GLX-D Frequency Manager
to improve
RF
reliability.
• Scan for the best available channel by pressing the
ch
annel button.
• Keep transmitters more than 2 meters (6 feet) apart. This is less critical with
shorter receiver-to-transmitter distances or if receivers are connected to a
GLX-D Frequency Manager.
Note: If transmitters are within 6 inches
of
non-GLX-D transmitters
or
micro-
phone cartridges, audible noise is possible.
• Move transmitter and receiver away from metal or other dense materials.
• During sound check, mark trouble spots and ask performers
to
avoid those
areas.
• If there is a strong source
of
Wi-Fi and you specifically want to use frequen-
cies within that Wi-
Fi
channel, use the following Group/Channel combina-
tions (best option listed first):
Wi-Fi
1:
Group 3/Channel 8, Group 3/Channel 4
Wi-Fi 6: Group 3/Channel
7,
Group 3/Channel 5
Wi-Fi 11: Group 3/Channel
2,
Group 3/Channel 1
J (!)
~
~
'.Jti"
...
..
-
-
---
-
- -
-
-
- -
- -
-
---
-
-
~J.
J
~
0
-:::=::c
f
~'"~
/
~
-
9