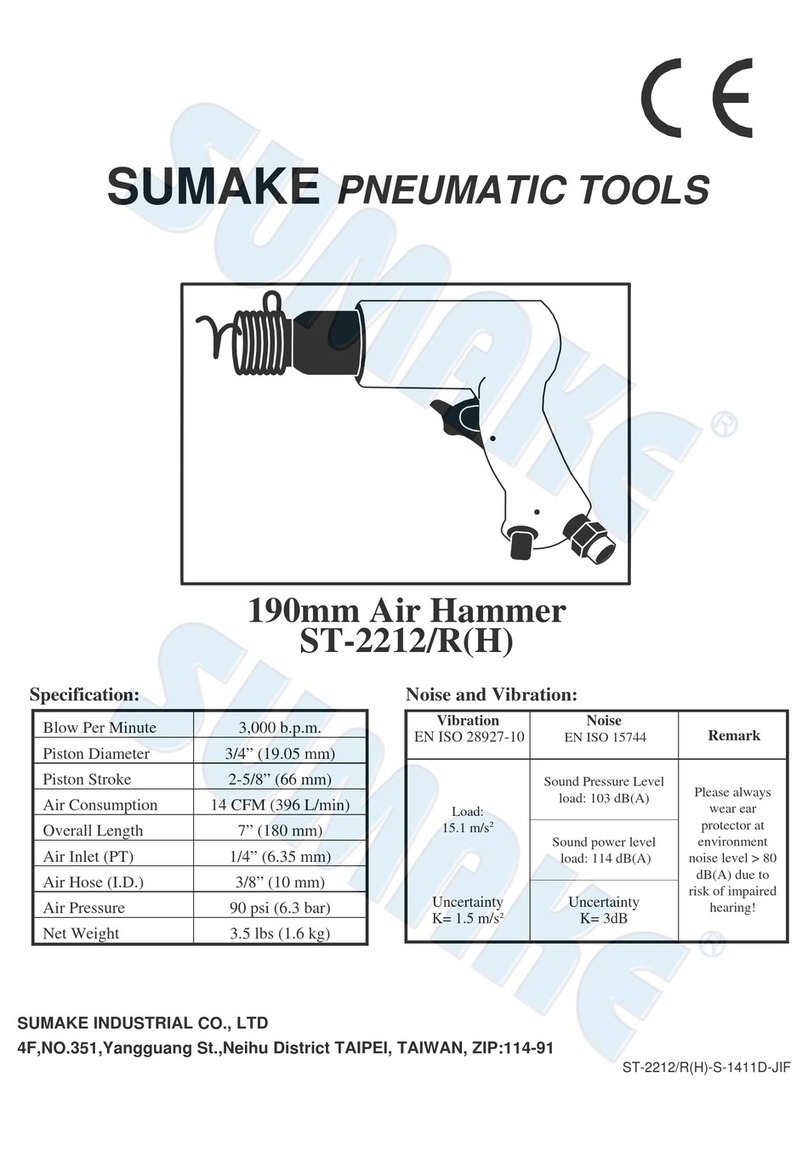
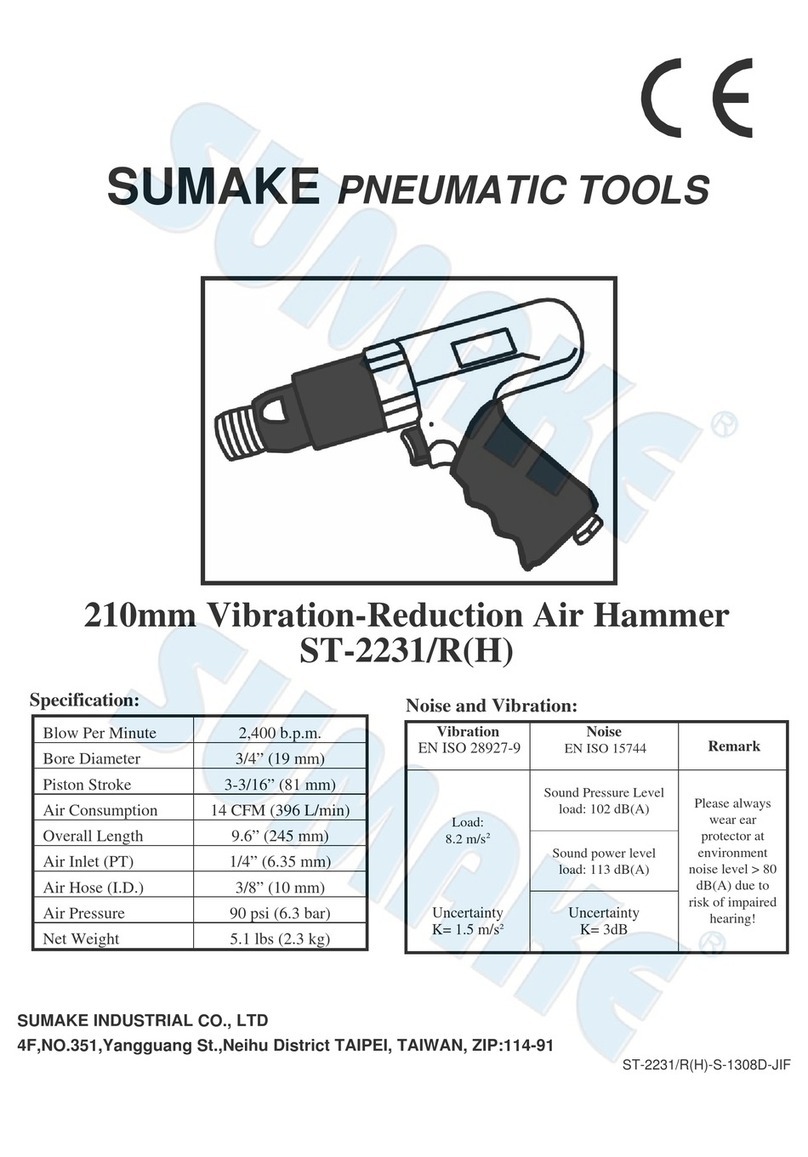
1 General warnings
1.1 Operator safety rules
While working the hammer vibrates: thus it is dangerous to touch it or leave any object on it.
The hammer must be started by the operator whose working position is in front of the control board of the
carrier.
The person in charge of the safety rules must give the operator all the instructions for the correct
use of the hammer. The operator must also know how the carrier works, enquire about its safety
measures and strictly obserre them.
The operator must be familiar with the technical characteristics of the hammer and especially with
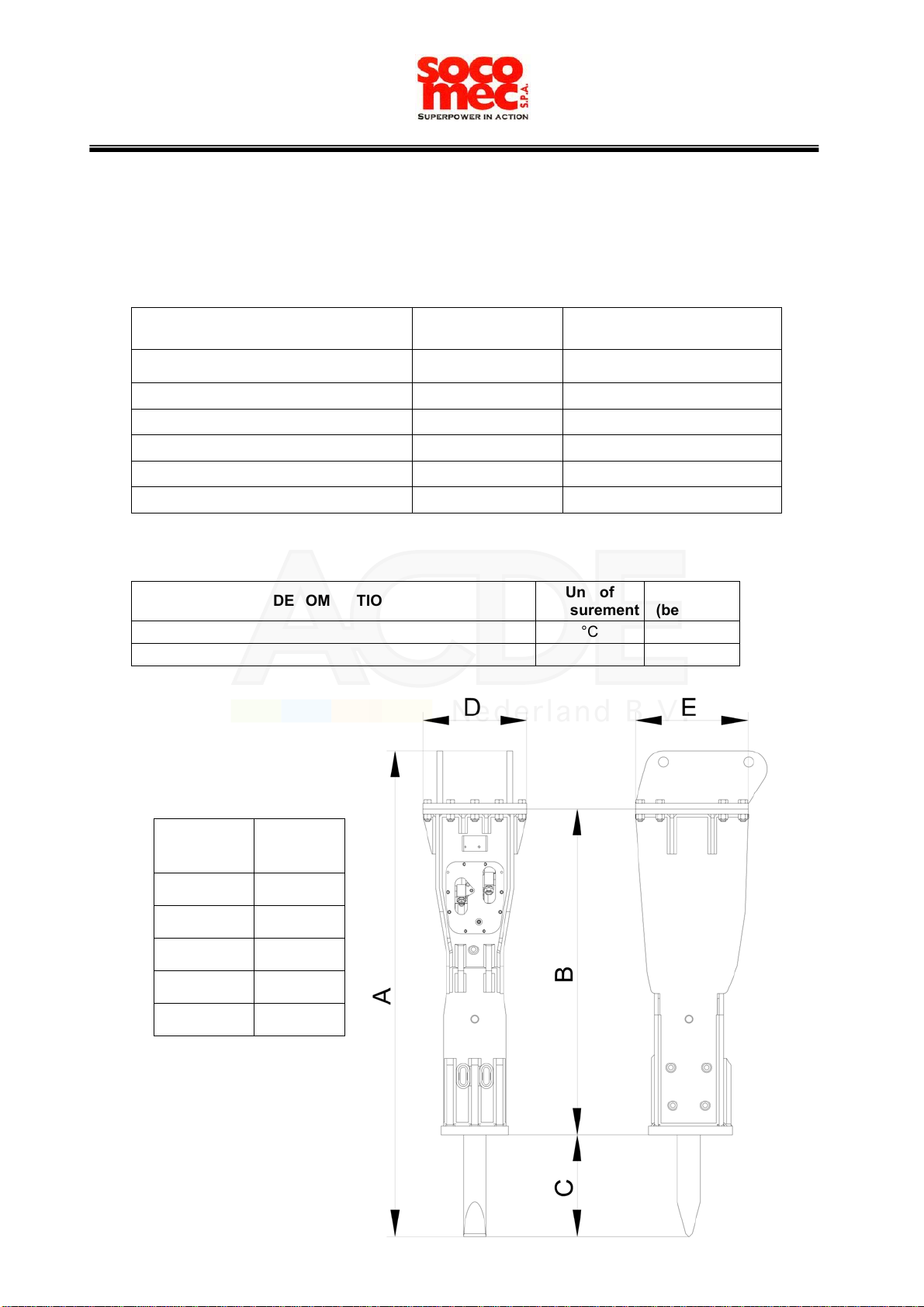
pressures, oil flow rates, dimensions of the flexible hoses and connections.
Before using the hammer and according to the type of work, the operator must get the following
equipments: safety glasses, dust-mask, helmet, earmufes, etc.
Large and loose clothes, watches and other types of bracelets are dangerous,
The operator must not make use alcohol or drugs medicines which can produce sleepiness while
working.
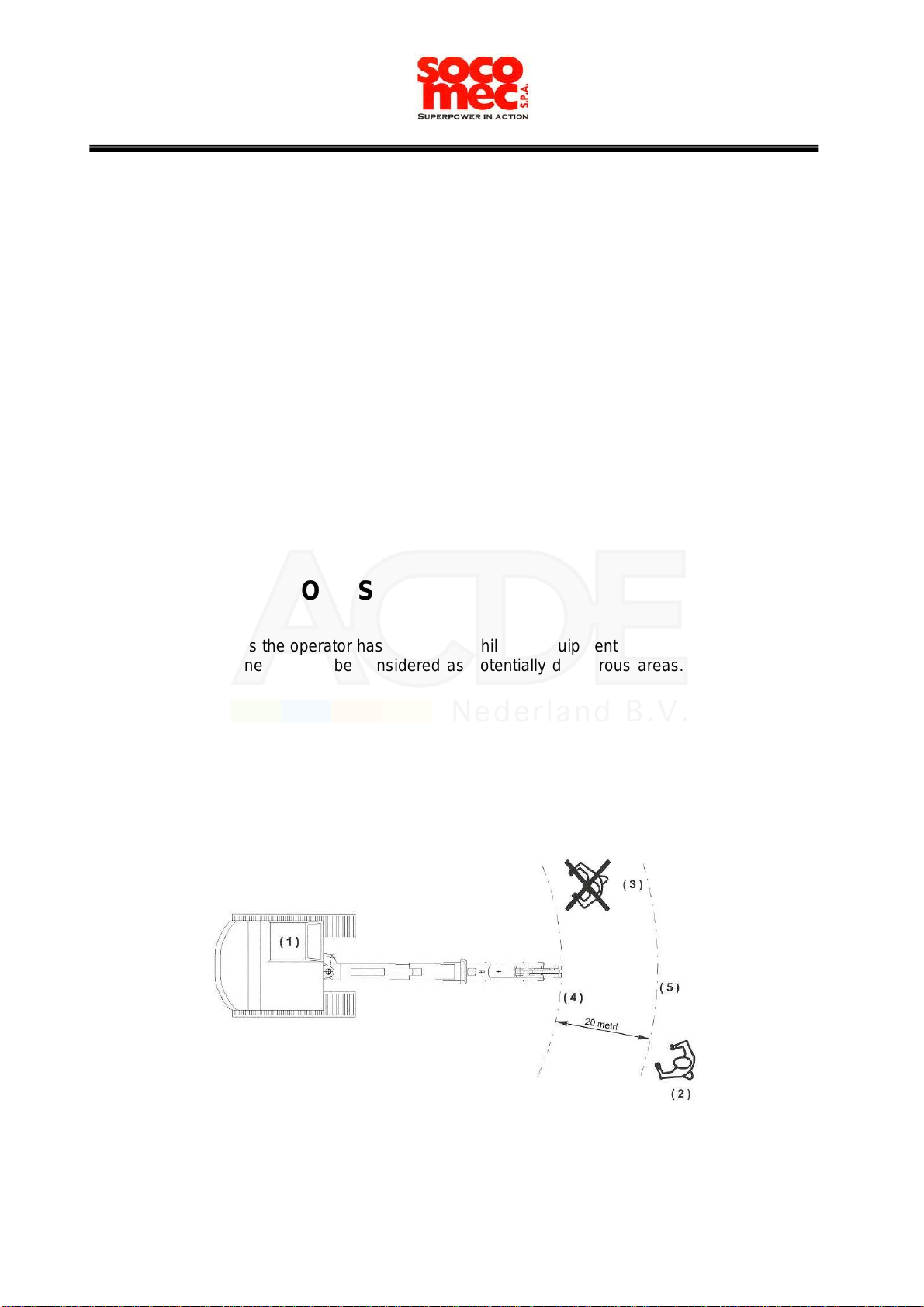
The working area must be indicated and illuminated.
The operator must follow the maintenance program proposed by the manufacturer and make sure
that the hammer is in good conditions.
After work, the temperature of the tool can be very high: so it is necessary to leave it to cool before
touching or in any case to protect hands with working gloves.
It is absolutely forbidden to temper with the safety devices and to eliminate or
modify the protections.
All actions representing a situation of potential danger for the operators are pointed out by
the sign reproduced aside.
“Operator” we mean the person or the people in charge of installing, operating, servicing,
cleaning, repairing and transporting the machine.