Sonus SBC 1000 User manual

© 2015 Sonus Networks, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Revision
Date
Revised By
Comments
0.1
12/03/2015
Roman Kokes
Initial Publication
0.2
3/16/2015
Grant Gist
Internal review
0.4
3/26/2015
Andy N. Tran
Customer review
1.0
4/13/2015
Tech Pubs
Final Edit and Release
SBC 1000/2000 Configuration Guide with
Lync 2013 for Windstream/ LPAETEC SIP
Trunk Deployments
Application Notes
Rev. 1.0
Last Updated: April 10, 2015

Sonus –Network Design Group 2 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.

Sonus –Network Design Group 3 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
1Document Overview..............................................................................5
1.1 Glossary.................................................................................................................................. 5
1.2 Overview................................................................................................................................. 6
2Introduction ...........................................................................................6
2.1 Audience................................................................................................................................. 6
2.2 Requirements.......................................................................................................................... 7
2.3 Reference Configuration......................................................................................................... 8
Network Topology ............................................................................................................... 8
3Configuring Sonus SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 Series.............................9
3.1 External Peer Side SBC Configuration................................................................................. 10
Node Interfaces................................................................................................................. 10
SIP profile.......................................................................................................................... 12
Media Profile ..................................................................................................................... 13
Voice Codec Profiles .................................................................................................................14
SIP Server Tables......................................................................................................................15
Static IP Route Table ........................................................................................................ 15
Signaling Groups............................................................................................................... 16
Call Routing Table............................................................................................................. 17
Transformation Tables ...................................................................................................... 18
Trunk Registration............................................................................................................. 19
3.2 Internal Side SBC configuration............................................................................................ 20
Node Interfaces................................................................................................................. 20
SIP Profile ......................................................................................................................... 22
Media Profiles.................................................................................................................... 23
Voice Codec Profiles .................................................................................................................24
Signaling Group................................................................................................................. 25
Sip Server Table................................................................................................................ 26
Call Routing Table............................................................................................................. 27
Transformation Tables ...................................................................................................... 28
4Lync Server 2013 configuration........................................................... 31
4.1 Lync 2013 Configuration Settings......................................................................................... 31
Addition of the SBC to the Lync Server............................................................................. 31
Adding the SBC to Lync Server 2013 Routing.................................................................. 35

Sonus –Network Design Group 4 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
5SBC and Lync 2013 Specific Configurations...................................... 37
5.1 Initial Setup for All Calls........................................................................................................ 37
Calling number manipulation............................................................................................. 37
Called number................................................................................................................... 37
5.2 Initiating Transfers with REFER............................................................................................ 37
Call transfer via REFER method....................................................................................... 37
5.3 Initiating Transfers with Re-INVITE ...................................................................................... 38
Call transfer via Re-Invite method..................................................................................... 38

Sonus –Network Design Group 5 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
1 Document Overview
These Application Notes describe the configuration steps required for the Sonus Session Border Controller
(SBC) 1000 and SBC 2000 to interoperate with the Lync 2013 system and a SIP trunk group to PSTN.
The objective of the document is to describe the configuration procedures to be followed during interoperability
testing of SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 with Lync 2013 server over SIP trunk to PSTN.
For additional information on Sonus SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 series, visit http://www.sonus.net
For additional information on Lync 2013, visit http://www.microsoft.com
1.1 Glossary
Term
Definition
AOC
Advice Of Charge
B2B UA
Back to Back User Agent
CP
Calling Party
CPD
Call Progress Detection
CPE
Customer Premise Equipment –Cisco SIP Server is the CPE device
in this case.
CTI
Computer Telephony Integration
DNIS
Dialed Number Identification Service
IP
Internet Protocol
MS
Media Server
PBX
Private Branch Exchange
PSX
Policy Server Exchange
SDOP
Signaled Digits Out-Pulsed
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol
UUI
User to User Information

Sonus –Network Design Group 6 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
1.2 Overview
The Sonus SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 session border controllers are designed to use the same application
software, boot image and Survivable Branch Appliance software. They differ in the number of physical Ethernet
connections and processing power but are otherwise viewed from a software standpoint as being the same.
With this in mind, this particular effort was tested with an SBC 1000 but is fully applicable to an SBC 2000.
2 Introduction
This document provides a configuration guide for Sonus SBC 1000 Series (Session Border Controller) when
connecting to a SIP trunk group and a Lync 2013.
The Sonus SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 are Session Border Controllers that connect disparate SIP trunks, SIP
PBXs, and communication applications within an enterprise. The SBC can also be used as a SIP routing and
integration engine.
The Sonus SBC is the point of connection between the SIP trunk group to PSTN and the Lync 2013.
2.1 Audience
This technical document is intended for telecommunication engineers with the purpose of configuring the Sonus
SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 and aspects of the SIP trunk group together with Lync 2013 product. There will be
steps that require navigating the third-party and Sonus SBC Command Line Interface (CLI). Understanding the
basic concepts of IP/Routing and SIP/RTP is also necessary to complete the configuration and for
troubleshooting, if necessary.
This configuration guide is offered as a convenience to Sonus customers. The specifications and information
regarding the product in this guide are subject to change without notice. All statements, information, and
recommendations in this guide are believed to be accurate but are presented without warranty of any kind,
express or implied, and are provided “AS IS”. Users must take full responsibility for the application of the
specifications and information in this guide.
Technical support on SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 can be obtained through the following:
Phone: +1 888-391-3434 (Toll-free) or +1 978-614-8589 (Direct)
Web: http://www.sonus.net/company/maintenance/log-trouble-tickets
Sonus –Network Design Group 7 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
2.2 Requirements
The following equipment and software was used for the sample configuration provided:
Sonus Equipment
Type
Version
SBC 1000
SBC 1000
4.1.0 Build 369
3rd Party Equipment
Type
Version
Microsoft Lync 2013
Mediation Server
5.0.8308.420
Polycom CX500
Lync Edition
SIP Phone
4.0.7577.4455
Windstream Equipment
Type
Version
Broadsoft West
Broadsoft platform
R17 SP4
ACME SBC
ACME Net-Net 4250
SC6.2.0 Patch 3 (Build
497) Build
Date=02/12/10
Sonus –Network Design Group 8 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
2.3 Reference Configuration
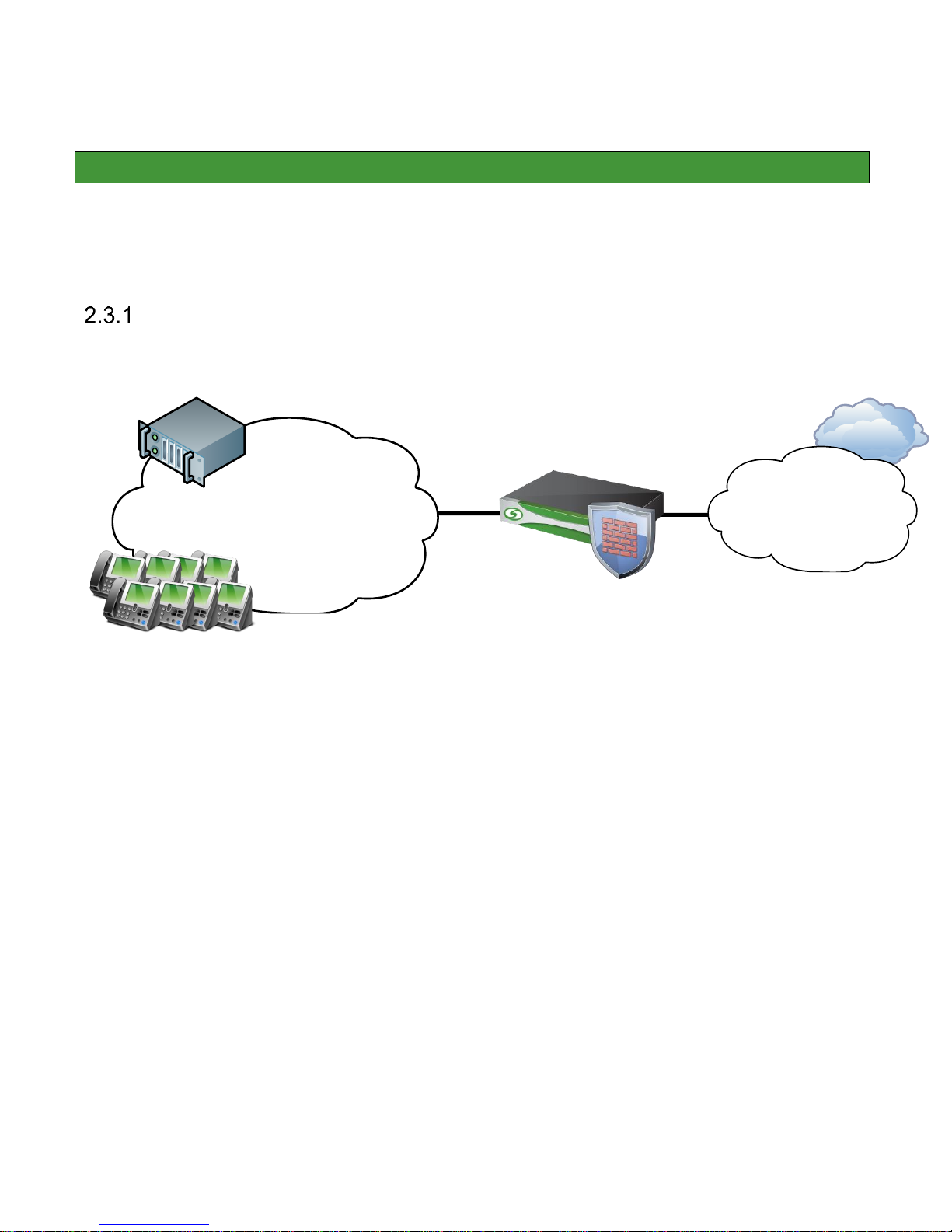
A simulated enterprise site consisting of a Lync 2013 and a SIP trunk group to PSTN connected over the SBC
1000. The SBC 1000 was running software version 4.1.0 Build 369 during testing.
Network Topology
PSTN
Lync 2013
Sonus
SBC 1000
Windstream
Internal IP Network
Figure 2.1 Network Topology
The figure above represents the equipment used for the integration and certification testing. The SBC 1000 is
used to route and facilitate calls between the PSTN and the Lync 2013 system.
The SBC 1000 under test has 2 Ethernet ports configured. The SBC 2000 can have up to 4 physical Ethernet
ports and two physical T1/E1 ports. For more information on Media port deployment options or other network
connectivity queries, refer to the SBC 1000 Network Deployment Guide or contact your local Sales team for
information regarding the Sonus Network Design professional services offerings.

Sonus –Network Design Group 9 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
3 Configuring Sonus SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 Series
The SBC 1000 and SBC 2000 share a common code base and user interface. In this example, we are using an
SBC 1000.
Lync 2013 Signaling Group
Internal
Lync 2013
External
Signaling Group: To/From Lync
Call Routing: From Lync
Signaling Group: To/From Windstream
Call Routing: From Windstream
10.35.180.136:5068
SIP over TCP Windstream
10.35.177.230:5060
64.199.64.220:5060
216.110.2.235:5060
SIP over UDP
Figure 3.1 SBC 1000 SIP Trunk Diagram

Sonus –Network Design Group 10 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
3.1 External Peer Side SBC Configuration
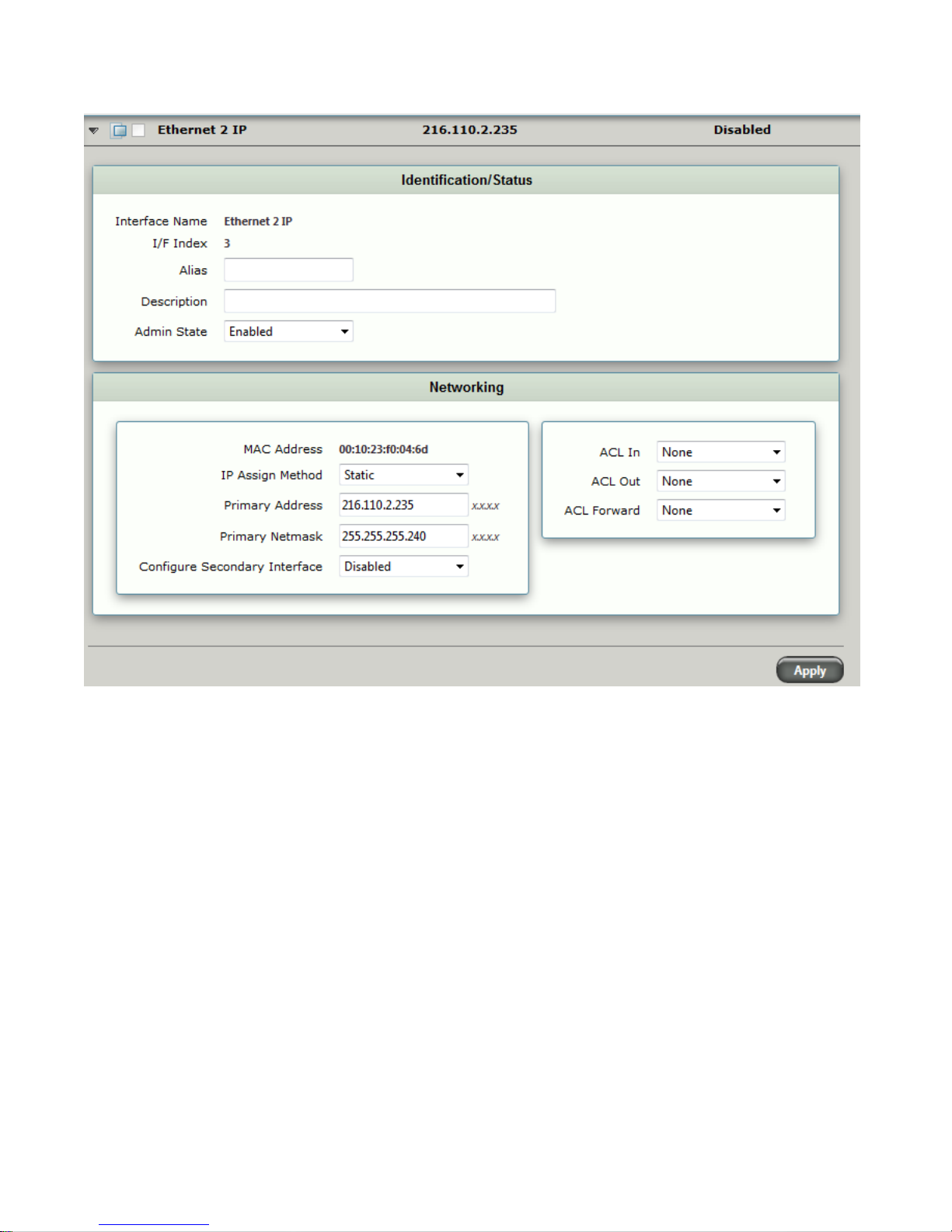
Node Interfaces
The Sonus SBC 1000 allows you to configure the identification information, Physical Data Layer, and Networking
Layer for the Ethernet ports. If you want to change the IP Address, you must configure the associated Logical
Interface or use the Modify Ethernet IP task found under the Tasks tab.
Settings for the Ethernet connection between the Sonus SBC 1000 and the public Internet are shown in the
figures below.
Figure 3.2 External Port
Sonus –Network Design Group 11 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Figure 3.3 Logical Interface

Sonus –Network Design Group 12 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
SIP profile
SIP Profiles control the how the Sonus SBC 1000/2000 communicates with SIP devices. They control important
characteristics such as: session timers, SIP header customization, SIP timers, MIME payloads, and option tags.
The default SIP profile used for the SBC 1000 for this testing effort is shown in the following figure.
Figure 3.4 SIP profile

Sonus –Network Design Group 13 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Media Profile
Media Profiles allow you to specify the individual voice codecs and their associated settings for inclusion in a
Media List. Different codecs provide varying levels of compression allowing one to reduce bandwidth
requirements at the expense of voice quality.
The Media Profile Used for the SBC 1000 is shown in the following figure and is for reference only.
Figure 3.5 Media List

Sonus –Network Design Group 14 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Voice Codec Profiles
The Voice Codec Profiles used for the SBC 1000 in this testing effort are shown in the figures below.
Figure 3.6 Voice codec configuration
Figure 3.7 Voice codec configuration

Sonus –Network Design Group 15 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
SIP Server Tables
SIP Server Tables contain information about the SIP devices connected to the Sonus SBC 1000/2000. The
entries in the tables provide information about the IP Addresses, ports, and protocols used to communicate with
each server. The Table Entries also contain links to counters that are useful for troubleshooting.
Figure 3.8 SIP Server Table
Static IP Route Table
The Static IP route table feature allows you to route subnets to different IP gateway..
Figure 3.9 SIP Host table
Sonus –Network Design Group 16 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
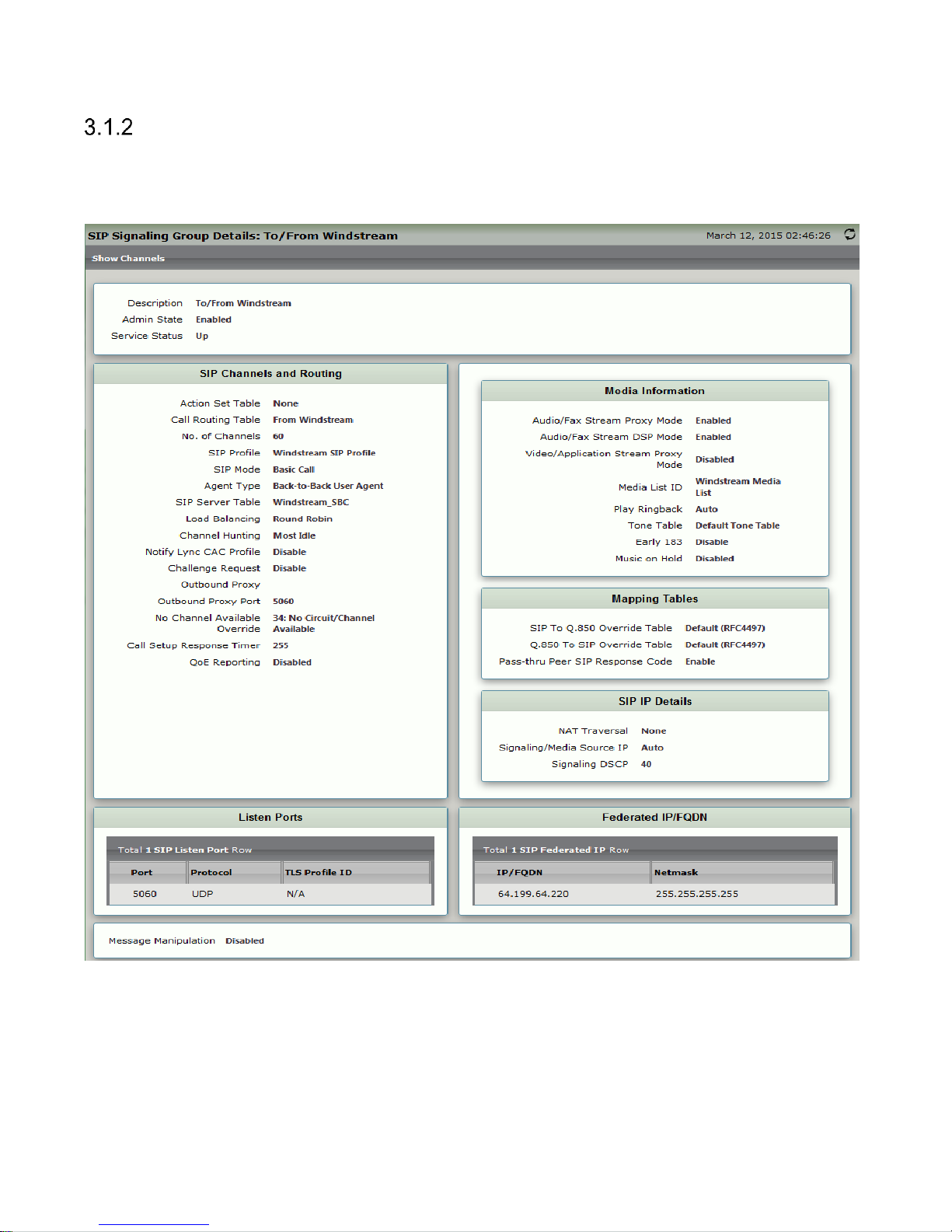
Signaling Groups
Signaling groups allow telephony channels to be grouped together for the purposes of routing and shared
configuration. They are the entity to which calls are routed, as well as the location from which Call Routes are
selected. They are also the location from which Tone Tables and Action Sets are selected. In the case of SIP,
they specify protocol settings and link to server, media and mapping tables.
Figure 3.10 SIP Signaling Group to Windstream

Sonus –Network Design Group 17 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Call Routing Table
Call Routing allows calls to be carried between signaling groups, thus allowing calls to be carried between ports,
and between protocols (like ISDN to SIP). Routes are defined by Call Routing Tables, which allow for flexible
configuration of which calls are carried, and how they are translated. These tables are one of the central
connection points of the system, linking Transformation Tables, Message translations, Cause Code Reroute,
Tables, Media Lists and the three types of Signaling Groups (ISDN, SIP and CAS).
Figure 3.11 Call Routing Table PSTN to Lync 2013

Sonus –Network Design Group 18 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Transformation Tables
Transformation Tables facilitate the conversion of names, numbers and other fields when routing a call. They
can, for example, convert a public PSTN number into a private extension number, or into a SIP address (URI).
Every entry in a Call Routing Table requires a Transformation Table, and they are selected from there. In
addition, Transformation tables are configurable as a reusable pool that Action Sets can reference.
Figure 3.12 Transformation Table Match 713343376 range

Sonus –Network Design Group 19 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Trunk Registration
Windstream requires authentication when establishing a SIP Trunk group to the SBC 1000. The Contact
Registrant Table is used for registration with remote address and specific configuration.The Remote
Authorization table is used for authorization configuration for remote registration.
Figure 3.13 Contact registrant table
Figure 3.14 Remote Authorization table

Sonus –Network Design Group 20 of 39
Copyright © 2015, Sonus and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
3.2 Internal Side SBC configuration
Node Interfaces
The Sonus SBC 1000 allows you to configure the Identification information, Physical Data Layer, and Networking
Layer for the Ethernet ports. If you want to change the IP Address, you must configure the associated Logical
Interface or use the Modify Ethernet IP task found under the Tasks tab.
Settings for the Ethernet connection between the Sonus SBC 100 and Lync 2013 are shown in the figures below.
Figure 3.15 Node Port
Other manuals for SBC 1000
1
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Sonus Controllers manuals