Spartus WRC310 User manual

User’s manual
Welding water cooler SPARTUS®
WRC400WRC310

WELDING EQUIPMENT SUITABLE FOR TODAY’S NEEDS
Thank you for purchasing our product!
You have made a right choice. Plasma welding and welding processes are
carried out in difficult conditions that expose welding equipment to extreme
tests of its strength. Only high quality equipment can ensure required reliability
and performance during realization of the above-mentioned processes. SPAR-
TUS® products are characterized by precisely such features: they are primarily
reliable and durable, but they are also versatile.We listen carefully to clients’
needs.Therefore, our offer covers such a wide assortment of products.Thank
you very much for your trust in our company. We would like to invite you to
familiarize yourself with the remaining products and offer at www.spartus.
info or directly at alocal distributor of SPARTUS® products.

Before using this product, read the instruction manual in its entirety, with understanding.
Keep the instructions for quick reference to it if necessary. Pay special attention to safety
instructions provided for your protection. In the event of any points of misunderstanding
instructions, contact your supplier or supervisor.
IMPORTANT!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.
SAFE USE – HAZARDS ASSOCIATED WITH ARC WELDING AND PLASMA CUTTING
.............. 2
1.1 General safety rules ............................................................................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Electric shock can kill ............................................................................................................................................................ 2
1.3 Welding arc radiation can be dangerous ..................................................................................................................... 3
1.4 Vapours and gases can be dangerous .......................................................................................................................... 3
1.5 Noise can be harmful ........................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.6 Fire or explosion hazard ...................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.7 Other hazards .......................................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.8 Other informations ............................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.9 Symbols used in instructions ............................................................................................................................................ 7
2.
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD (EMF) ............................................................................................................ 7
3.
ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY (EMC) ........................................................................................ 7
3.1 General informations ........................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 Assesment of area ................................................................................................................................................................. 8
3.3 Methods of reducing emmisions .................................................................................................................................... 8
4.
CONFORMITY WITH STANDARDS ........................................................................................................... 8
4.1 CE marking ............................................................................................................................................................................... 8
4.2 Rating plate .............................................................................................................................................................................. 8
5.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................. 8
5.1 Purpose of use ......................................................................................................................................................................... 9
6.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................................... 9
6.1 Operation, storage and transport ................................................................................................................................... 9
6.2 Technical parameters of device ..................................................................................................................................... 10
7.
INSTALLATION AND USE ......................................................................................................................... 10
7.1 Proper cooling ....................................................................................................................................................................... 10
7.2 Movement and handling .................................................................................................................................................. 10
7.3 Description of construction ............................................................................................................................................. 11
7.4 Connecting to power supply .......................................................................................................................................... 12
7.5 Connecting the device ....................................................................................................................................................... 12
8.
MAINTENANCE ........................................................................................................................................... 13
9.
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ........................................................................................................... 13
9.1 Liquid coolant ....................................................................................................................................................................... 13
10.
TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................................................................. 14

USER’S MANUAL EN
2
Arc welding and plasma cutting are processes
that can pose hazards for the operator and per-
sons in his vicinity. The operator and his close
surroundings are exposed, among others, to
the risk of fire, explosion, electric shock, bur-
ning, as well as the risk of getting injured by
moving parts of the device.
Once proper safety measures are provided,
electric welding and plasma cutting are rela-
tively safe processes. For this reason, it is cru-
cial to strictly follow the valid OSH principles
during welding operations.
The informations provided below do not re-
lease the operator from the obligation to follow
the OSH rules that are binding in his plant/
workplace.
1.1 GENERAL SAFETY RULES
Welding operators and persons working in
the vicinity of the welding process should be
made aware of the following hazards associa-
ted with arc welding. They should be made
aware of protective measures as specified in
relevant international and national standards
and regulations.
1.1.1 Equipment condition
and maintenance
• Check the technical condition of the device
and accessories before starting to weld/
plasma cutting. It is forbidden to use equi-
pment that is unserviceable.
• Equipment damaged or defective should
be immediately repaired or removed from
service.
1.1.2 Operation and carrying
• Apply appropriate protective measures in
the space around the zone, where welding
operations are expected to be carried out.
• All equipment should be placed so that it
does not present a hazard in passageways,
on ladders or stairways, etc.
• Falling objects can cause injuries or kill.
Protect device before accidentally falling.
• Welding equipment may be heavy (e.g. wire
feeder fitted with spool and harness). Care
shall be taken during manual handling.
• To handle heavy elements, use hoists/
trucks/transport equipment designed
especially for this purpose. Make sure
the weight ofequipment to be handled
does not exceed the admissible maximum
lifting capacity of used hoist/truck/transport
equipment.
• It is forbidden for unauthorized persons,
especially children, to be in the vicinity of
the device during its use.
•
The device is not suitable for pipe defrosting.
• Device use non-compliant with its intended
purpose is forbidden.
1.1.3 Training
• Only professionally trained and qualified
personnel may install, operate, maintain
and repair the device.
• For operators and their supervisors training
is essential in: the safe use of the equipment;
the processes; the emergency procedures.
1.2 ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
• Before starting to weld and during the wel-
ding process, the operator should insulate
himself from the ground and the environ-
ment by means of dry and undamaged
protective clothes. It is forbidden to work
on wet ground.
• It is forbidden to touch SK sockets ( „+” and/
or „-”) when the device is in operation (con-
nected to a power supply source).
• It is forbidden to touch live electric compo-
nents of the device.
1. SAFE USE – HAZARDS ASSOCIATED WITH ARC WELDING AND
PLASMA CUTTING
USER’S MANUAL
EN
3
• Power supply must never be connected
before the accessories of SK sockets/con-
nectors are properly installed in the device.
• Use dry and undamaged welding gloves
and protective clothing, in order to ensure
proper insulation of the body. It is forbidden
to touch with a bare hand any elements that
are parts of an electric circuit.
• The operator must always make sure that
there is a good electric connection of the
return conductor to the element to be wel-
ded. The connection should be located as
close to the welding zone as possible.
• Maintain the electrode grip, the welding
torch, the chassis ground clamp, welding
cables and the welding machine in proper
technical condition that ensures safe ope-
ration. Damaged cable insulation should be
replaced with new insulation.
• Never dip an electrode into water, to cool
it down.
• When working above the floor level (at
aheight), use a safety harness to protect
yourself against falling, in the case of po-
tential electric shock.
• Exercise special caution, when using the
device in small rooms or in rooms with
elevated humidity levels.
1.3 WELDING ARC RADIATION CAN BE
DANGEROUS
The arc generates:
• ultraviolet radiation (can damage skin and
eyes);
• visible light (can dazzle and impair vision);
• infrared (heat) radiation (can damage skin
and eyes).
Such radiation can be direct or reflected from
surfaces such as bright metals and light colo-
ured objects.
1.3.1 Eye and face protection
• Use welder’s helmet/shield with an appro-
priate filter to protect you face and eyes
against sparks and welding arc radiation.
• The shield / helmet should provide eye and
face protection against injuries that may
result in welding spatters.
• Welding helmet/shield should be made in
accordance with applicable standards.
1.3.2 Body protection
• The body should be protected by suitab-
le clothing in accordance with applicable
standards.
• Use appropriate protective clothing made
of durable and fire-resistant material, to
ensure proper skin protection.
• The use of neck protection can be necessary
against reflected radiation.
1.3.3 Protection of persons in the vicinity
of an arc
• Protect the remaining personnel present
in the vicinity of welding works against
negative impact of arc radiation and wel-
ding splatters. Warn them about the hazard
resulting from exposure to the welding arc.
In the vicinity of an arc, non-reflective cur-
tains or screens should be used to isolate
persons from the arc radiation. A warning,
e.g. a symbol for eye protection, should
refer to the hazard of arc optical radiation.
Welder’s assistants should also wear
appropriate protective clothing.
1.4 VAPOURS AND GASES
CAN BE DANGEROUS

USER’S MANUAL EN
4
Arc welding and allied processes produce wel-
ding fume which may pollute the atmosphere
surrounding the work. Welding fume is a vary-
ing mixture of airborne gases and fine particles
which, if inhaled or swallowed, constitute a
health hazard.
The degree of risk is depend on:
• the composition of the fume;
• the concentration of the fume;
• the duration of exposure.
A systematic approach to the assessment of
exposure is necessary, taking into account the
particular circumstances of the operator and the
ancillary worker who can be exposed.
Welding fume may be controlled by a wide
range of measures, e.g. process modifications,
engineering controls, methods of work, personal
protection and administrative action.
First it is necessary to consider whether ex-
posure can be prevented by eliminating the
generation of welding fume altogether. Where
this cannot be done, measures for reducing the
quantity of welding fume generated should be
investigated, after which the control of welding
fume at source should be considered. The use
of respiratory equipment should not be con-
templated until all other possibilities have been
eliminated. Normally, respiratory protective
equipment should be used only as an interim
measure. However, there cannot be a situation
in which, in addition to ventilation, the use of
personal protection is necessary.
1.4.1 VAPOURS AND GASES.
ADDITIONAL PRECAUTIONS
• Welding operations can involve generation
of vapours and gases that are hazardous
to health. Inhaling the vapours should be
avoided. Keep your head away from vapours
during welding operations. Ensure proper
ventilation and/or mechanical welding ex-
haust draught to keep vapours and gases
away from the breathing zone.
• When welding is carried out in a confined
space, operators should only be permitted
to weld when other persons, who have
been instructed and who are able to react
in case of an emergency, are in the imme-
diate vicinity.
• In closed rooms or in certain circumstances
during outdoor operations, it may be re-
quired to use individual equipment for the
protection of the welder’s airways, e.g. a re-
spirator. Additional safety measures are also
required when galvanized steel is welded.
• Welding operations must not be performed
in the vicinity of chlorinated hydrocarbons
generated during degreasing, cleaning or
spraying. Heat and radiation generated
by the arc may enter into a reaction with
vapours of solvents, which may lead to the
formation of phosgene – ahighly toxic gas.
• The shielding gas used during arc welding
may force the air out of a room. This may
lead to a health hazard or even death. Pro-
per ventilation, especially in closed rooms,
should always be provided, to ensure appro-
priate amount of air that is indispensable for
safe breathing.
1.5 NOISE CAN BE HARMFUL
In the welding environment, damaging levels of
noise can exist. Continued exposure to a high
noise level on the unprotected ear is injurious.
The noise levels should be reduced to the lo-
west practicable level.
High levels may be tolerated for very short
periods by wearing adequate ear protection in
accordance with the national or local regulation.
In case of doubt, checks by an expert should be
made to establish noise levels in any particular
environment, and, if these are in excess of the
prescribed limit, one of the following alterna-
tives may apply:
a) insulation of the noise source as far as po-
ssible, e.g. by fitting silencers or sound proof
enclosures,
b) insulation of the operator from the noise
USER’S MANUAL
EN
5
source,
c) effective maintenance of sound protection
devices,
d) indication as „ear protection areas” where
applicable,
e) restriction of entry to these„ear protection
areas”to authorized persons,
f) protect your hearing with appropriate per-
sonal protection measures, e.g. earplugs or
hearing protectors.
1.6 FIRE OR EXPLOSION HAZARD
Arc welding and allied processes can cause fire
and explosions. Precautions should be taken
to prevent these hazards.
1.6.1 Fire hazard
• Before setting to perform welding opera-
tions, ensure that elements involving fire
hazard are removed from the zone where
welding operations will take place. If it is
impossible, protect all flammable elements
against the impact of sparks. Remember
that sparks and hot metal may penetrate
through small cracks and openings into the
adjacent area.
• Avoid welding in the vicinity of hydraulic
conduits.
• The welding arc throws sparks and splatters
out. Welders should wear clean and dry
protective clothing (staining with oil should
be avoided in particular) such as welding
gloves, welder’s apron, welder’s trousers,
welder’s boots, protective hood/cap, etc.
• When welding operations are not carried
out, make sure that no part of the electrode
comes into contact with the workpiece or
protective earthing. Accidental contact may
lead to overheating and create a fire hazard.
• The fire extinguisher should be ready for use
and located in an easily accessible place.
• The surroundings of the work should be
observed for an adequate period after its
termination.
• „Hot spots” and immediate surroundings
should be observed until their temperature
has dropped to normal.
1.6.2 Explosion hazard
It is forbidden to heat up, cut or weld tanks,
barrels or containers that contained toxic or
flammable materials. For there is an explosion
hazard, even if the containers have been emp-
tied and cleaned.
1.6.3 Use of cylinders with shielding gas
In case compressed gases are used in the work
place, apply special safety measures to prevent
dangerous situations.
• Use gas cylinders with appropriate shielding
gas, foreseen for a particular process. Addi-
tional equipment (pressure regulator, hoses,
connectors) should be in good technical
condition. A gas cylinder and accessories
should have the required valid attestations
and approvals for use.
• Gas cylinders should always be stored in
vertical position, fixed to an undercarriage
or permanent support.
• Gas cylinders should be placed far away
from areas, where they could be exposed
to the risk of being overthrown or suffering
physical damage.
• Ensure gas cylinders are at a safe distance
from places where electric welding or cut-
ting operations are to be performed, away
from other sources of heat, sparks or flames.
• Care shall be taken to prevent gas cylinders
in the vicinity of the workpiece becoming
part of the welding circuit.
• Never allow the electrode, electrode holder
or any other live electric part to get in con-
tact with the gas cylinder.
• Keep your face and head away from the

USER’S MANUAL EN
6
cylinder valve socket when the valve is
being opened.
• Special valve shield should always be in-
stalled during cylinder transportation or
when the cylinder is not used.
1.7 OTHER HAZARDS
Arc welding and allied processes carrying other
hazards not listed before.
1.7.1 Burns
• Never touch hot parts with bare hands.
• Before handling an element, wait until it
cools down.
• Use appropriate tools to grip and handle hot
elements and wear special welding gloves
and clothing that protects against burns.
1.7.2 Plasma arc is dangerous
Highly concentrated plasma arc poses a ha-
zard for health and life. It is forbidden to aim
plasma arc at people.
1.7.3 Welding wire can cause injuries
Accidental pressing of the button on the wel-
ding torch can cause welding wire to advance
in an uncontrolled manner. The welding wire
tip may be sharp.
Never aim the burner tip of the welding torch
at your face, eyes or other people.
1.7.4 Moving elements can be dangerous
All protective elements and device housing
should be in place and in good technical con-
dition. Keep your hands, hair, clothes and tools
away from gear wheels, fans and other moving
parts during their operation.
Do not bring your hands close to fan motors.
It is forbidden to stop a fan by pressing its axis.
1.7.5 HF – high frequency ignition may
cause interference
As welding by the TIG method or plasma cut-
ting involves high frequency ignition, it can
interfere with mobile phones, radio equipment,
TV equipment or improperly protected compu-
ters and industrial robots, which leads to total
disabling of such devices.
1.8 OTHER INFORMATIONS
When performing welding work, you must
apply equally to the health and safety requi-
rements contained in the current normative
acts, applicable in your country.

USER’S MANUAL
EN
7
WARNING!
The maximum voltage of 15kV. Accidental pressing of the microswitch
results in unintentional arc ignition. Never bring a bare hand close to the
electrode, when the device is connected to a power source.
1.9 SYMBOLS USED IN INSTRUCTIONS
We use this symbol to pay your attention about important information.
2. ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS (EMF)
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized electric and magnetic fields
(EMF). All welders should use the following procedures in order to minimize the risk associated
with exposure to EMF from the welding circuit:
• Route the welding cables together – secure them with tape when possible.
• Place your torso and head as far away as possible from the welding circuit
• Never coil welding cables around your body.
• Do not place your body between welding cables. Keep both welding cables on the same
side of your body.
• Connect the return cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area being welded.
• It is forbidden to sit or lean on power source while working.
• Do not weld whilst carrying the welding power source or wire feeder.
WARNING!
The electromagnetic field (EMF) generated during welding (and allied processes) may interfere
with the operation of implanted medical devices for example: cardiac pacemakers. Persons with
implanted medical devices such as cardiac pacemakers are obliged to consult a doctor before
starting to weld/plasma cutting and to exercise special caution during work. It is forbidden for
such persons to be present in the vicinity of the place where welding/plasma cutting processes
are realized without previous consultation of a doctor.
3. ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY (EMC)
WARNING!
This Class A equipment is not intended for use in residential locations where the electrical
power is provided by the public low-voltage supply system. There can be potential difficulties
in ensuring electromagnetic compatibility in those locations due to conducted as well radiated
radio-frequency disturbances.
3.1 GENERAL INFORMATIONS
The user is responsible for installing and using the arc welding equipment according to the
manufacturer’s instructions. If electromagnetic disturbances are detected, then it shall be the
responsibility of the user of the arc welding equipment to resolve the situation with the tech-
nical assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases this remedial action may be as simple as
earthing the welding circuit. In other cases, it could involve constructing an electromagnetic
screen enclosing the welding power source and the work complete with associated input fil-
ters. In all cases electromagnetic disturbances shall be reduced to the point where they are no
longer troublesome.
Welding and plasma cutting processes may emit additional interferences. User is
responsibility for the interferences caused by welding and plasma cutting.
USER’S MANUAL EN
8
3.2 ASSESMENT OF AREA
Before installing arc welding equipment, the user shall make an assessment of potential elec-
tromagnetic interferences in the surrounding area. The following shall be taken into account:
a) other supply cables, control cables, signaling and telephone cables, above, below and adja-
cent to the arc welding equipment,
b) radio and television transmitters and receivers,
c) computer and other control equipment,
d) safety critical equipment, for example guarding of industrial equipment,
e) the health of the people around, for example the use of pacemakers and hearing aids,
f) equipment used for calibration or measurement,
g) the immunity of other equipment in the environment. The user shall ensure that other equi-
pment being used in the environment is compatible. This may require additional protection
measures.
h) the time of day that welding or other activities are to be carried out.
The size of the surrounding area to be considered will depend on the structure of the building
and other activities that are taking place. The surrounding area may extend beyond the boun-
daries of the premises.
3.3 METHODS OF REDUCING EMMISIONS
Methods of reducing electromagnetic interference are listed in detail in the standard
EN 60974-9 –„Arc welding equipment – Part 9: Installation and use”.
4. CONFORMITY WITH STANDARDS
The SPARTUS® WRC310 / WRC400 water coolers are in conformity with the relevant Union har-
monization legislation:
LVD 2014/35/UE Low Voltage Directive
harmonized standards:
EN 60974-2 Arc Welding Equipment – Part 1: Liquid Cooling Systems
4.1 CE MARKING
CE marking is placed on the nameplate of device and/or on the front panel of device.
4.2 RATING PLATE
Rating plate and serial number are located on the device case.

USER’S MANUAL
EN
9
5. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
SPARTUS® WRC310 / WRC400watercoolers
The SPARTUS® WRC310 / WRC400 water coolers are designed to cool welding torches. It is cha-
racterized by high performance. The large-capacity coolant vessel is equipped with a coolant
level gauge. The machines are mains powered from single phase 230V source power.
SPARTUS® WRC310 / WRC400 water coolers are compatible with most of the branded welding
torches, thanks to the use of quick coupler (standard 21) on the inlet and outlet.
SPARTUS® water cooler that high quality, maintenance-free unit, guarantees tightness.This is de-
pendable and irreplaceable source of cooling systems.
5.1 PURPOSE OF USE
The SPARTUS® WRC310 / WRC400 water coolers are designed to cool welding torches in which
the handle and burner are cooled by liquid.
When the welding torch is connected with water cooler – the cooler and the welding torch
form a closed cooling circuit.
6. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
6.1 OPERATION, STORAGE AND TRANSPORT
Conditions during operation, storage and transport
Range of ambient air temperature
during operation
-20°C to +60°C
Relative humidity of the air up to 50% at +40°C
up to 90% at +20°C
Ambient air free from abnormal amounts of dust, acids,
corrosive substances etc. other than those
generated by the welding process
Base of the welding power source inclined no more than 10°
Range of ambient air temperature
during storage and transport
-20°C to +60°C
Height above sea level ≤1000 m
Duty cycle (def.)
Duty cycle is the time during which You can weld or cut at a certain load without causing overload.
Itis expressed in percent for period of complete cycle which equals 10 minutes. For example: 60% duty
cycle means that for 6 minutes device can operate at given load, after that required 4 minutes time
break (no-load operation).
The device has a degree of protection IP21. Which means that it is intended to be used in closed and
covered areas and suitable for use outdoors. However it is not designed to be used outdoor during
precipitation if it is not covered.

USER’S MANUAL EN
10
6.2 TECHNICAL PARAMETERS OF DEVICE
SPARTUS® water cooler
WRC310 WRC400
Input 1 ~ 230V ± 10% 50 / 60 Hz
Engine power 120W 111W
Max. pump efficiency 5.3l/min 5l/min
Tank capacity* 10l 9l
Max. coolant pressure 3 bar 4.2 bar
Protection class IP 21
Dimensions 570 x 330 x 333mm 470 x 250 x 310mm
Weight (empty tank) 20 kg 14 kg
* Recommended coolant for use with coolers: based on propylene glycol – 69.8% demineralised water, 30%
propylene glycol, 0.2% Benzotriazole.
7. INSTALLATION AND USE
WARNING!
SPARTUS® WRC water coolers are intended for professional and industrial applications.
Installation and use of the device may only be carried out appropriately trained professionals.
Qualified person (def.)
A person who has gained the relevant technical education, training took place and / or gained
experience to perceive the risk and avoid hazards during use of the product (IEC 60204-1).
7.1 PROPER COOLING
The unit should be placed stable on a dry and flat surface. Avoid too much slope and slippery
surfaces. Check regularly that the vents (inlet, outlet) are not covered. The minimum distance
between the cooler vents and walls should be 50cm.
7.2 MOVEMENT AND HANDLING
When moving the unit please take extra care. The device should be moved by using specially
designed transport lugs. If transport handle is damaged, then it needs to be repaired at an
authorized service center.
USER’S MANUAL
EN
11
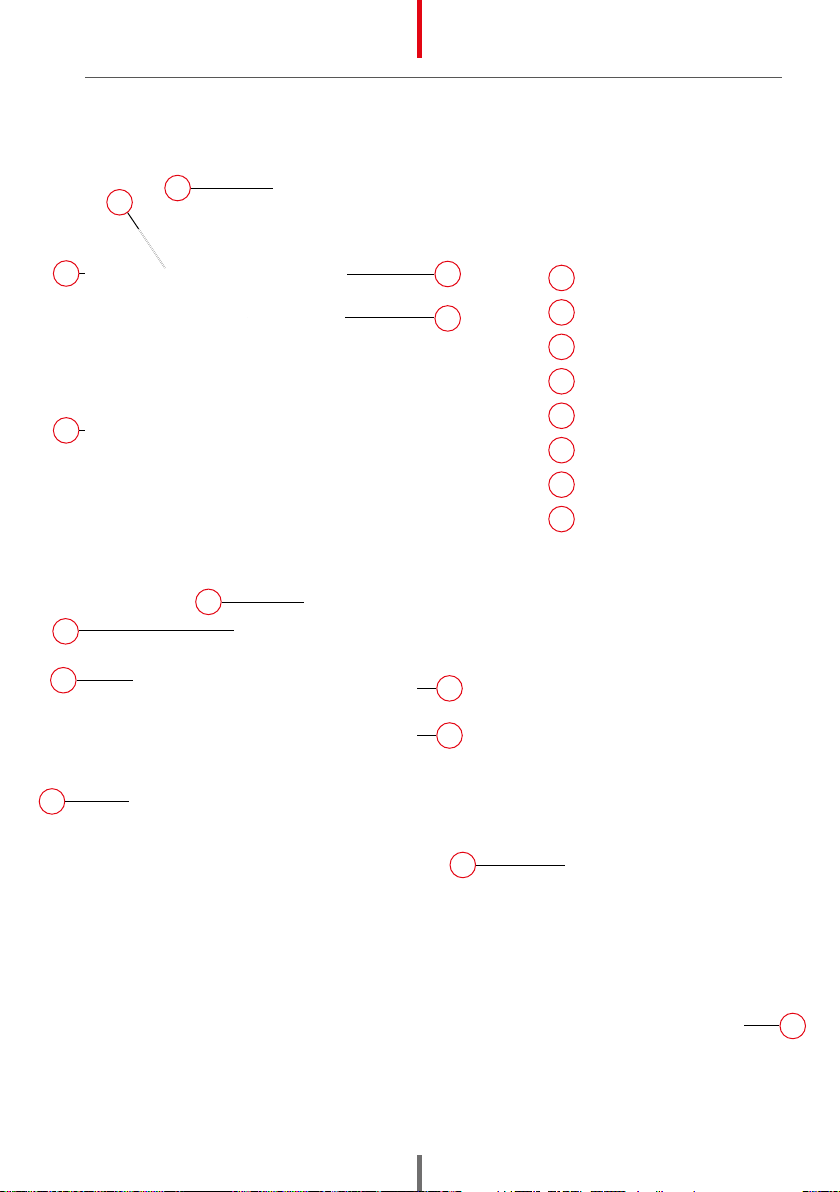
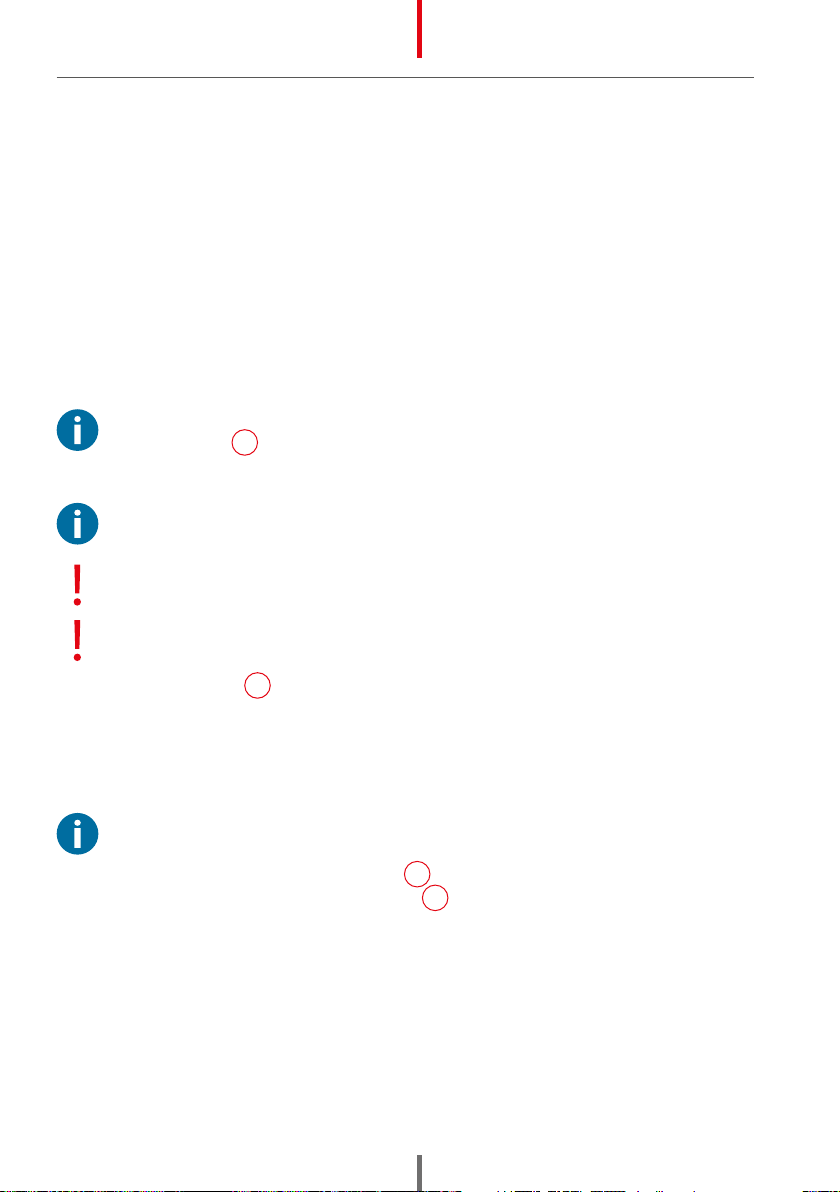
7.3 DESCRIPTION OF CONSTRUCTION
1Transport handle
2Coolant in
3Water level indicator
4Inlet (hot water)
5Outlet (cold water)
6Power switch
7Power cord
8Vents
1
3
8
6
6
2
2
5
7
4
1
3
5
4
USER’S MANUAL EN
12
7.4 CONNECTING TO POWER SUPPLY
Requirements for power network parameters (voltage, permissible range of mains voltage
fluctuations etc.) are given in the table with technical parameters of device and on the rating
plate of welding machine.
Before connecting the unit to the power source:
• Check whether the parameters comply with the requirements for unit.
•
Check: mechanical condition of the power cord and plug. The connection status of the power
cord with plug and unit (loose not allowed). If the power cord or plug is damaged or loose
connection is between them, it is forbidden to connect the device until fault has been rectified.
• The water cooler can be connected to the network only when the power socket is properly
grounded.
7.5 CONNECTING THE DEVICE
Before connecting equipment to the device, make sure that the device is disconnected from power
source and switch 6is in the OFF position.
7.5.1 Liquid – filling the tank
Cooling liquid must meet the requirements of the manufacturer of the welding torches.
It is forbidden to use a coolant (liquid) not intended for use in welding. Cooling liquid should be: non-
flammable, antifreeze, non-conductive.
It is forbidden to operate the water cooler when the tank is empty and/or there is no liquind in the
cooling circuit. The pump can’t operate without liquid.
1. Unscrew the filler cap 2.
2. With aprropriate precautions pour the tank with cooling liquid. Remember to take care of
right liquid level in tank. Control it according to water level indicator.
3. Screw the filler cap.
7.5.2 Connecting the welding torch
SPARTUS® WRC410 water cooler has built-in quick couplings. It is the most popular standard 21.
Welding torch should be equipped with water hoses armed in type 21 couplings (male plug).
1. Connect (hot water hose) into inlet coupler 6.
2. Connect (cold water hose) into outlet coupler 7.
3. Turn on the water cooler, check there is no leakage. Check the liquid circuit.
USER’S MANUAL
EN
13
8. MAINTENANCE
WARNING!
Before performing any maintenance or repairing of device, disconnect welding machine from
the power source and wait at least 5 minutes. The voltage accumulated in capacitors should
be discharged at this time to a safe level. But even after that operation you should be careful.
Maintenance and repair work may be performed only by qualified personnel with the appropriate per-
missions. Regular maintenance provides adequate service life and trouble-free operation of the device.
Routine maintenance (daily: before use/installation):
• Perform a visual inspection of the housing.
• Inspect (visual inspection) the power cord and power plug. Check the insulation of the cable.
• Check if cooling fan is working properly.
• Make sure that all vents are not obstructed.
• Check the level of coolant in the tank.
• Check the tightness of the connections.
At least once a month:
• Regularly remove dust from inside of the machine. Use for this compressed air. The pressure
should be sufficiently low so as not to damage small components inside the machine. If in
the workplace, dust levels are high. You should clean machine often.
• Perform inspection of connection of internal electrical components. If anywhere the joints
are loose, tighten them.
Once a year:
• You should send device to an authorized service center for an interim review.
Liquid coolant:
• The frequency of replacement of the coolant with the new one should be in accordance with
the requirements of the safety data sheet.
9. ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
The product must not be disposed of into an ordinary waste container. It is totally
forbidden to dispose of electric or electronic equipment marked with a crossed-
-out trash can symbol by throwing it into ordinary waste containers. According
to the WEEE directive (directive 2012/19/UE), binding within the European Union,
such products should be disposed of according to local regulations.

USER’S MANUAL EN
14
9.1 LIQUID COOLANT
Replacement of the coolant and its subsequent disposal should be carried out in accordance
with the requirements of the safety data sheet and the laws of the country of use.
10. TROUBLESHOOTING
Not all problems with functioning of the device, are the evidence of failure. You can independently carry
out an analysis in search of probable failure. In case of doubt, please contact to SPARTUS® dealer or
authorized service center.
During the warranty period all repairs should be carried by authorized service center. Repairs carried
out by unauthorized persons will void the warranty.
PROBLEMS WITH THE DEVICE
Whe the power switch is on,
the water cooler doesn’t work.
Power switch is damaged.
No input power.
No liquids in circuit.
The circuit is aerated.
No liquid in the tank.
Water pump is damaged.
Water ow is too slow. Water pump is damaged.
Clogged hose.
The fan does not work. Fan is damaged.
Wrong input.
04.2023

Notes

Notes

Simple solutions and an attractive price – these are
the features of SPARTUS® Easy series devices. Our
equipment has been designed with ease of use and
ergonomics at work in mind.
A masterly combination of high quality production,
excellent parameters and ergonomics – these are fea-
tures of the SPARTUS® Master series of devices, which
were created with demanding welding jobs in mind.
Precision, functionality, excellent parameters and
resistance to high workloads – these are the features
of the SPARTUS® Pro industrial series of devices. This
series consists of specialised solutions which will
satisfy even the most demanding users.

Videopresentation of products
Subscribe to the channel SPARTUS.INFO
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Popular Water Dispenser manuals by other brands

Kinetico
Kinetico 2020c installation instructions

BWT
BWT AQA drink 1 installation manual

Scotsman
Scotsman SCW 8 LBP Service manual

Whirlpool
Whirlpool HD1000XSW8 Installation Instructions and Use & Care Guide

InSinkErator
InSinkErator Indulge Modern F-HC3300 Specifications

WaterLogic
WaterLogic 4 Firewall user manual











