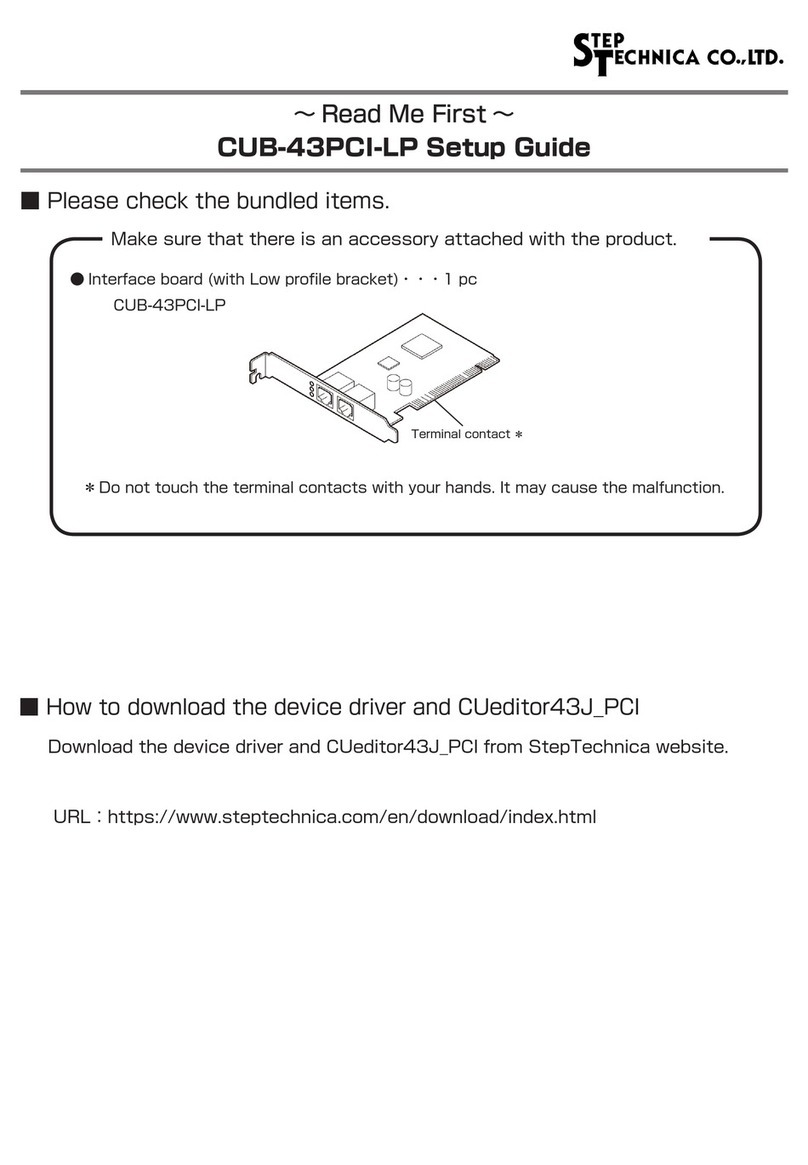
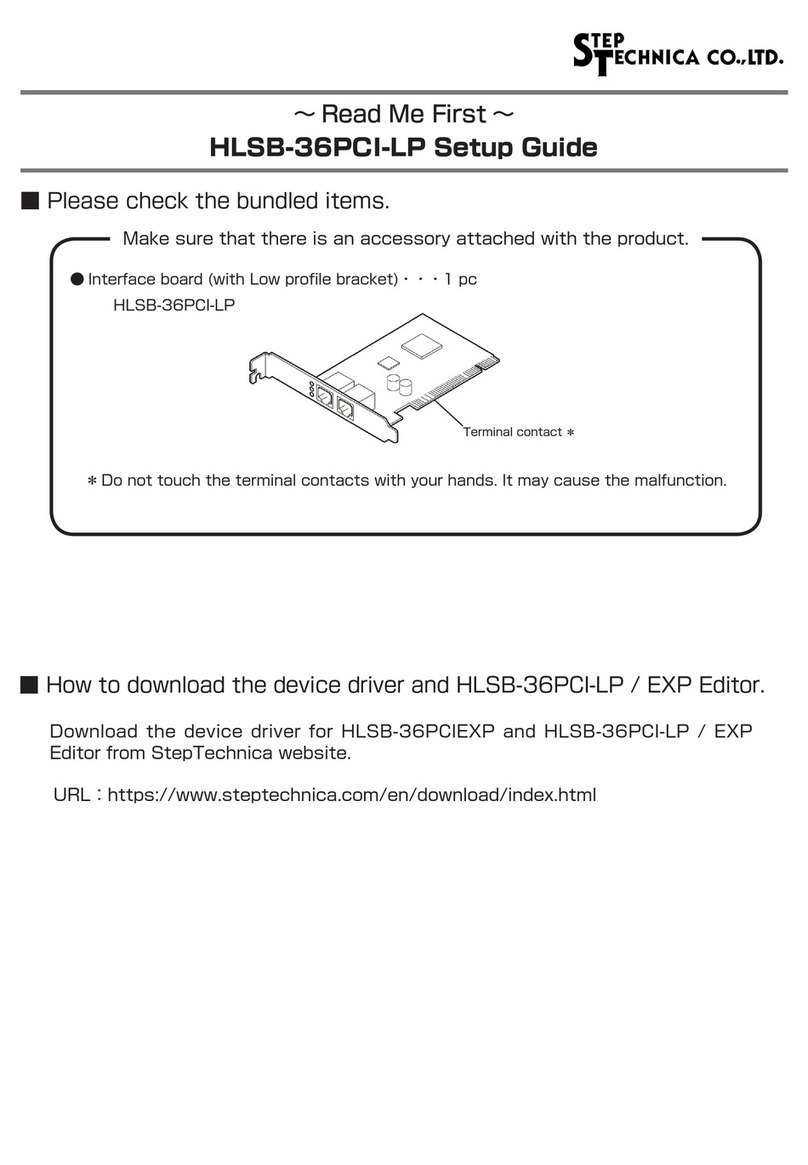
Step Technica MKY02 User manual

HUB-IC MKY02
User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
STD-HLS02-V1.7E

Note
1. The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice. Before using this
product, please confirm that this is the latest version of this document.
2. Technical information in this document, such as explanations and circuit examples, are refer-
ences for this product. When actually using this product, always fully evaluate the entire sys-
tem according to the design purpose based on considerations of peripheral circuits and the
PC board environment. We assume no responsibility for any incompatibility between this
product and your system.
3. We assume no responsibility whatsoever for any losses or damages arising from the use of
the information, products, and circuits in this document, or for infringement of patents and any
other rights of a third party.
4. When using this product and the information and circuits in this document, we do not guaran-
tee the right to use any property rights, intellectual property rights, and any other rights of a
third party.
5. This product is not designed for use in critical applications, such as life support systems. Con-
tact us when considering such applications.
6. No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without
prior written permission from StepTechnica Co., Ltd..
Trademark “HLS” is licensed by Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.

MKY02 User’s Manual
- iii -
Preface
This manual describes the MKY02, or a kind of HUB-IC in a Hi-speed Link System.
Be sure to read “Hi-speed Link System Introduction Guide” before understanding this manual
and the MKY02.
In this manual, the Hi-speed Link System is abbreviated as “HLS”.
zTarget Readers
This manual is for:
yThose who first build an HLS
yThose who first use StepTechnica's various ICs to build an HLS
zPrerequisites
This manual assumes that you are familiar with:
yNetwork technology
ySemiconductor products (especially microcontrollers and memory)
zRelated Manuals
yHi-speed Link System Introduction Guide
yHi-speed Link System Technical Guide
yHi-speed Link System Center IC Manuals
[Caution]
ySome terms in this manual are different from those used on our website and in our product bro-
chures. The brochure uses ordinary terms to help many people in various industries understand
our products.
Please understand technical information on HLS Family and CUnet Family based on technical
documents (manuals).

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
- iv -
CONTENTS
Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
1.1 Role of MKY02 ....................................................................................................... 1-3
1.2 Basic HLS Configuration ...................................................................................... 1-3
1.3 HLS Configuration using HUBs ........................................................................... 1-4
1.3.1 Extending Total Length of Network Cable ................................................................ 1-4
1.3.2 Branching Multi-dropped Network Cables................................................................ 1-6
1.3.3 Eliminating Connection or Disconnection of Termination Resistor
to or from Each Device ............................................................................................... 1-7
1.3.4 Star Topology ..............................................................................................................1-8
1.4 Basic HUB Connection ......................................................................................... 1-9
1.5 Multi-drop Network of HUBs .............................................................................. 1-10
1.6 Port Addition to HUB .......................................................................................... 1-11
1.7 MKY02 Operation ................................................................................................ 1-12
1.7.1 Receiving and Sending Packets .............................................................................. 1-12
1.7.2 Signal Correction....................................................................................................... 1-13
1.7.3 Detection of Error Packet ......................................................................................... 1-13
1.8 Features of MKY02 .............................................................................................. 1-14
Chapter 2 MKY02 Hardware ................................................................................2-3
Chapter 3 Single Connection of MKY02
3.1 Voltage Levels of Pins Connecting to Signal Pins............................................. 3-4
3.2 Supplying Driving Clock and Hardware Reset Signal ....................................... 3-5
3.2.1 Supplying Driving Clock ............................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.2 Setting Cascade Clock and Baud Rate...................................................................... 3-6
3.2.3 Hardware Reset ........................................................................................................... 3-7
3.3 Connecting Network Interface ............................................................................. 3-8
3.3.1 Selecting Communication Mode ................................................................................ 3-8
3.3.2 Connection of Port 0 ................................................................................................... 3-8
3.3.3 Connection of Ports 1 to 7.......................................................................................... 3-9
3.3.4 Recommended Network Connection....................................................................... 3-10
3.4 Connecting Monitor LEDs .................................................................................. 3-11
3.4.1 Packet Receive Monitor ............................................................................................ 3-11
3.4.2 Packet Error Monitor ................................................................................................. 3-12
3.4.3 Port Receive Monitor................................................................................................. 3-13
3.5 Handling Cascade Connection Pins.................................................................. 3-15
3.6 Cautions for Designing HUB .............................................................................. 3-15
3.7 Example Circuit for Single Connection of MKY02 ........................................... 3-16

MKY02 User’s Manual
- v -
Chapter 4 Cascade Connection of MKY02
4.1 Concepts of Port Addition.................................................................................... 4-3
4.1.1 Port Addition by Stacking Method............................................................................. 4-3
4.1.2 Port Addition by Cascade Connection ...................................................................... 4-4
4.1.3 Maximum Available Cascade Connections............................................................... 4-4
4.2 Practical Side of Cascade Connection................................................................ 4-5
4.2.1 Cascade Pins ...............................................................................................................4-5
4.2.2 Operation of Cascade Connection Pins .................................................................... 4-6
4.2.3 Connection of Cascade Clocks and Determination of Baud Rate .......................... 4-7
4.2.4 Connection of Hardware Reset Signal ...................................................................... 4-7
4.2.5 Selecting Communication Mode ................................................................................ 4-8
4.2.6 Connection of Each Port............................................................................................. 4-8
4.2.7 Placement of Monitor LEDs........................................................................................ 4-9
4.3 Example Circuit for Port-added HUB by Cascade Connection....................... 4-10
Chapter 5 Ratings
5.1 Electrical Ratings .................................................................................................. 5-3
5.2 AC Characteristics ................................................................................................ 5-3
5.2.1 Clock and Reset Timing.............................................................................................. 5-4
5.2.2 Port Pin Timing (TXE0 to 7, TXD0, TXD17, RXD0 to 7)............................................. 5-5
5.2.3 Cascade Connection Pin Timing................................................................................ 5-6
5.2.4 Output Timing of #LEDRCV and #LEDRZE Pins ...................................................... 5-6
5.2.5 Timing of Receive Monitor Pin of Individual Port (RLLD, RLDT, RLCK) ................ 5-7
5.3 Package Dimensions ............................................................................................ 5-8
5.4 Recommended Soldering Conditions ................................................................. 5-9
5.5 Recommended Reflow Conditions ...................................................................... 5-9

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
- vi -
Figures
Fig. 1.1 Basic HLS Configuration.............................................................................. 1-3
Fig. 1.2 Extension of Network Cable Length ........................................................... 1-4
Fig. 1.3 Multipoint Connection of Network Cables.................................................. 1-6
Fig. 1.4 Eliminating Problems with Termination Resistors .................................... 1-7
Fig. 1.5 Star Topology................................................................................................ 1-8
Fig. 1.6 Basic Connection and Number of Inserted HUBs ..................................... 1-9
Fig. 1.7 HUB in Intermediate Position of Multi-drop Network .............................. 1-10
Fig. 1.8 Adding Ports by Cascading MKY02s ........................................................ 1-11
Fig. 1.9 Inserted Count of HUBs with Added Ports............................................... 1-11
Fig. 1.10 MKY02 Operating Principles...................................................................... 1-12
Fig. 1.11 Example of Signal Transformation and Correction ................................. 1-13
Fig. 2.1 MKY02 Pin Assignment................................................................................ 2-3
Fig. 2.2 Pin Electrical Characteristics in I/O Circuit Types of MKY02 ................... 2-6
Fig. 3.1 Connection Causing Leakage Current........................................................ 3-4
Fig. 3.2 Cascade Clock Generation .......................................................................... 3-6
Fig. 3.3 Clock Connection ......................................................................................... 3-6
Fig. 3.4 Hardware Reset............................................................................................. 3-7
Fig. 3.5 Selecting Communication Mode ................................................................. 3-8
Fig. 3.6 TRX Connection of Port 0 ............................................................................ 3-8
Fig. 3.7 TRX Connection of Ports 1 to 7 ................................................................... 3-9
Fig. 3.8 TRX Connection of HUB with 4 Ports ......................................................... 3-9
Fig. 3.9 Recommended Network Connection ........................................................ 3-10
Fig. 3.10 Connection of Receive Monitor LED......................................................... 3-11
Fig. 3.11 Connection of Packet Error Monitor LED ................................................. 3-12
Fig. 3.12 RLLD, RLDT, and RLCK Outputs............................................................... 3-13
Fig. 3.13 8-port Receive Monitor ............................................................................... 3-14
Fig. 3.14 4-port Receive Monitor ............................................................................... 3-14
Fig. 3.15 Handling of Cascade Connection Pins ..................................................... 3-15
Fig. 3.16 Example of Single Connection Circuit in Half-duplex Mode................... 3-16
Fig. 3.17 Example of Single Connection Circuit in Full-duplex Mode ................... 3-17

MKY02 User’s Manual
- vii -
Fig. 4.1 Addition of Three-stacked Ports ................................................................. 4-3
Fig. 4.2 Port Addition by Three Cascade Connections........................................... 4-4
Fig. 4.3 Cascade Pin Connection for Three MKY02s .............................................. 4-5
Fig. 4.4 Cascade Pin Connection for Two MKY02s................................................. 4-5
Fig. 4.5 Center Ports and Operation during Receiving........................................... 4-6
Fig. 4.6 Satellite Ports and Operation during Receiving ........................................ 4-6
Fig. 4.7 Connection of Cascade Clocks ................................................................... 4-7
Fig. 4.8 Selection of Communication Mode ............................................................. 4-8
Fig. 4.9 Monitor Placement Example for Port-added HUB ..................................... 4-9
Fig. 4.10 Example Circuit for HUB with 22 Ports..................................................... 4-10
Fig. 4.11 Example of Connection in Full-duplex Mode ........................................... 4-13
Tables
Table 1-1 Baud Rates and Recommended Total Extension Number
of Inserted HUBs.......................................................................................... 1-4
Table 2-1 Pin Functions of MKY02.............................................................................. 2-4
Table 2-2 Electrical Ratings of MKY02........................................................................ 2-6
Table 3-1 Output Frequencies of Cascade Clocks .................................................... 3-6
Table 5-1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ........................................................................ 5-3
Table 5-2 Electrical Ratings......................................................................................... 5-3
Table 5-3 AC Characteristics Measurement Conditions ........................................... 5-3

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
- viii -

Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
This chapter describes the concepts for using the MKY02 (HUB) in the Hi-speed Link
System (HLS).
1.1 Role of MKY02................................................................................1-3
1.2 Basic HLS Configuration ..............................................................1-3
1.3 HLS Configuration using HUBs....................................................1-4
1.4 Basic HUB Connection..................................................................1-9
1.5 Multi-drop Network of HUBs.......................................................1-10
1.6 Port Addition to HUB...................................................................1-11
1.7 MKY02 Operation.........................................................................1-12
1.8 Features of MKY02 ......................................................................1-14


Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
1 - 3
Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
This chapter describes the concepts for use of the MKY02 (HUB) in the HLS.
1.1 Role of MKY02
MKY02 is a kind of HUB-IC that constitutes a HUB to be used in the HLS network.
Be sure to read “Hi-speed Link System Introduction Guide” and “Center IC User’s Manuals” before
using the MKY02 and understanding this manual.
1.2 Basic HLS Configuration
Figure 1.1 shows the basic HLS configuration with one center IC and multiple satellite ICs connected on a
multi-drop network. Rt in the figure indicates a termination resistor.
Some user systems may need the following for the basic HLS configuration:
(1) To extend the total length of a network cable.
(2) To branch pieces of multi-dropped network.
(3) To eliminate connection or disconnection of termination resistor to or from each device.
There will be difficulty solving these needs using such basic HLS configuration shown in Figure 1.1.

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
1 - 4
1.3 HLS Configuration using HUBs
Adding HUBs to the HLS network, the user system can satisfy it’s own needs (1) to (3) described above.
When adding a HUB to the network, the center IC constituting the HLS must be compatible
with the HUB. If incompatible, the center IC does not link correctly with satellite ICs.
1.3.1 Extending Total Length of Network Cable
Adding HUB(s) to the HLS network, the user can extend the total length of the network cable. Figure 1.2
shows an example of extending the total length of the network cable. Rt in the figure indicates a termination
resistor.
The user system can extend the recommended network cable length by adding the inserted count of HUBs
+1 to the basic HLS configuration. For example, adding a single HUB doubles cable length, adding two
HUBs triples cable length, and adding seven HUBs increases the cable length eightfold. Table 1-1 shows
the baud rates and the recommended total extension based on the number of the inserted HUBs when using
the recommended network connection.
Table 1-1 Baud Rates and Recommended Total Extension Number of Inserted HUBs
Number of inserted HUBs
Baud rate 0 (Basic configuration) 1234567
12 Mbps 100 m 200 m 300 m 400 m 500 m 600 m 700 m 800 m
6 Mbps 200 m 400 m 600 m 800 m 1 km 1.2 km 1.4 km 1.6 km
3 Mbps 300 m 600 m 900 m 1.2 km 1.5 km 1.8 km 2.1 km 2.4 km

Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
1 - 5
The practical limit of network cable length varies with the performance of drivers/receiv-
ers, cable types, cabling environments, and how many cables are multi-drop connected.
StepTechnica's recommended network cable length is about 1/2 of the cable length limit
obtained from our practical experiments. These values are provided as a guide for stable
HLS operation in various user systems (,but performance is not guaranteed).
Therefore, in many user systems, the user can use the network cable longer than the total
length shown in Table 1-1.
The maximum number of HUBs that can be added is determined by the function of the cen-
ter IC. For example, if the user system uses the MKY36 as a center IC, the user can add up
to seven HUBs. For details, refer to “Center IC User’s Manual”.

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
1 - 6
1.3.2 Branching Multi-dropped Network Cables
The network cables can be branched by adding HUBs to the HLS network. Figure 1.3 shows an example of
an HLS configuration in which network cables are branched.
Figure 1.3 shows the network cables that are branched in T shape. Adding a HUB using the MKY02 also
enables multiple branchings with many ports.

Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
1 - 7
1.3.3 Eliminating Connection or Disconnection of Termination Resistor to or
from Each Device
In a network using the HLS, termination resistors (Rt) cannot be connected to the terminal connected in the
intermediate position (the halfway position in the network cable) of the multi-drop network. However, a
“one-to-one” connection between all terminals can eliminate connection or disconnection of termination
resistor to or from each device and simplifies the complexity of system installation as shown in Figure 1.4.

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
1 - 8
1.3.4 Star Topology
Mounting a HUB-IC to the terminal containing the center IC of the HLS can offer a star topology (Fig. 1.5).
Furthermore, network cables in a star topology can also be multi-drop-connected.

Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
1 - 9
1.4 Basic HUB Connection
When adding HUBs to the HLS, connect them so that the HLS can be a tree structure as shown in Figure 1.6.
In such a tree structure, the route node close to the center equipment is called the “center side”. Be sure to
connect port 0 to the center side.
The number of HUBs to be added in the routes derived from the center equipment is called the “number of
inserted (HUBs)”. The “number of inserted” HUBs is determined by the type of center IC and settings made
at the center IC by the user system.
In the system using the MKY36 as a center IC, the user can add up to seven HUBs. No
HUBs can be into a system using the MKY33 as a center IC. For details on each of center
ICs, refer to “User’s Manual” for the center IC.

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
1 - 10
1.5 Multi-drop Network of HUBs
When adding HUBs to the HLS, the user can connect HUBs as multi-drop (Fig. 1.7).
The multi-drop network of HUBs is suitable for a user system in which the network cables should be
divided.
The number of inserted HUBs shown in Figure 1.7 is “1”.
As shown in Figure 1.7, in cases where port 0 of the HUB is placed in the intermediate position (the halfway
position in the network cable) of a multi-drop network, do not connect a termination resistor to the port 0.
For details of the connection of a termination resistor, refer to “Hi-speed Link System Technical Guide”.

Chapter 1 Concepts for Using MKY02 (HUB)
1 - 11
1.6 Port Addition to HUB
By cascading MKY02s, the user can add more ports to a HUB composed of the MKY02.
For example, a cascade connection of three MKY02s enables the HUB to have port 0 connecting the center
side and 21 ports (7 ports ×3) connecting the satellite side (Fig. 1.8).
If a HUB with ports added by cascading MKY02s is added to a network, the number of inserted HUBs
between terminals and the center IC connected to each port of the HUB is “1” (Fig. 1.9).
Adding ports by cascading MKY02s is helpful to setup cables on multi-drop network or star topology. For
details of cascading MKY02s, refer to “Chapter 4 Cascade Connection of MKY02”.

MKY02 User’s Manual
(for Hi-speed Link System)
1 - 12
1.7 MKY02 Operation
This section describes the operation of the MKY02. Be sure to read this section before adding HUBs to the
HLS.
1.7.1 Receiving and Sending Packets
The MKY02 operates as follows:
(1) When the MKY02 receives a packet from port 0 (center side port), it corrects the signals constituting
the packet into a complete format, and sends the corrected packet to ports 1 to 7.
(2) When the MKY02 receives a packet from any one of the ports 1 to 7 (satellite side ports), it corrects
the signals constituting the packet into a complete format, and sends the corrected packet to port 0.
During a series of operations, ports other than the active port do not receive a packet. (For example,
while port 3 is active, ports 1, 2, and 4 to 7 do not receive a packet.)
(3) When the FH pin of the MKY02 is High level (full-duplex mode), the above operations (1) and (2)
function independently.
(4) When the FH pin is Low level (half-duplex mode), either of the above operations (1) and (2) starting
first functions. During this period, no ports receive a packet.
As described in (1) and (2) above, the MKY02 corrects the received packet into a complete format and sends
it, resulting in a time lag of 52 ×T
BPS
(max.) from receiving to sending packets (Fig. 1.10). Each port of the
MKY02 has priorities to handle system exceptions generated when multiple ports receive a packet simulta-
neously. The MKY02 starts operation in ascending order of port numbers (Fig. 1.10). In full-duplex mode,
ports 0 and 1 have no priorities.
Most of communication HUBs other than StepTechnica's are designed to start sending after
receiving the full packet length. This mechanism decreases the signal response speed of the
entire system significantly, in particular in a system with inserted a lot of HUBs. As shown
in Figure 1.10, the MKY02 sends the corrected packet while receiving the packet, which
causes only a slight decrease in the signal response time of the entire system.
Other manuals for MKY02
1
Table of contents
Other Step Technica Computer Hardware manuals