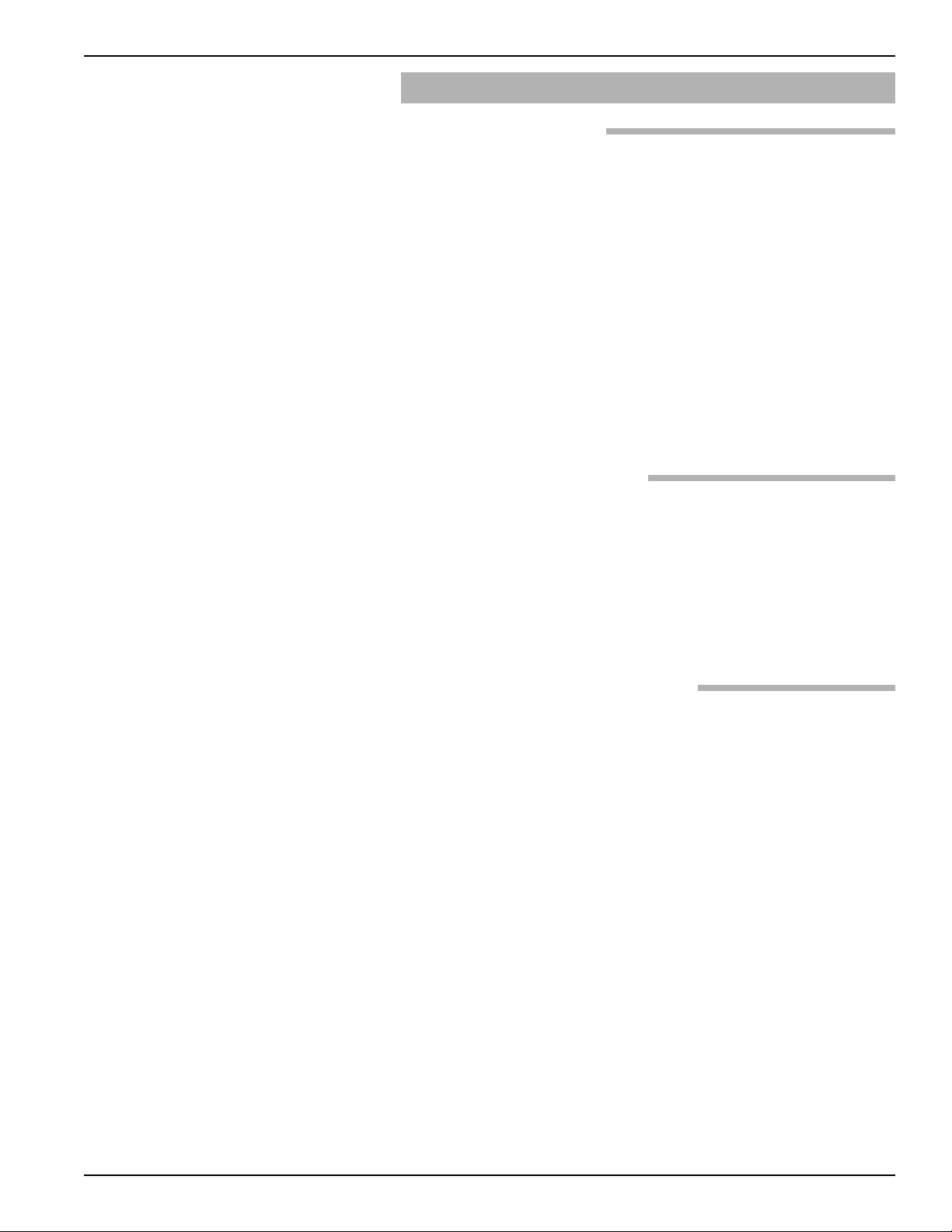50-608 Kotron Model 811 RF Point Level Sensor
Read this Manual Before Installing
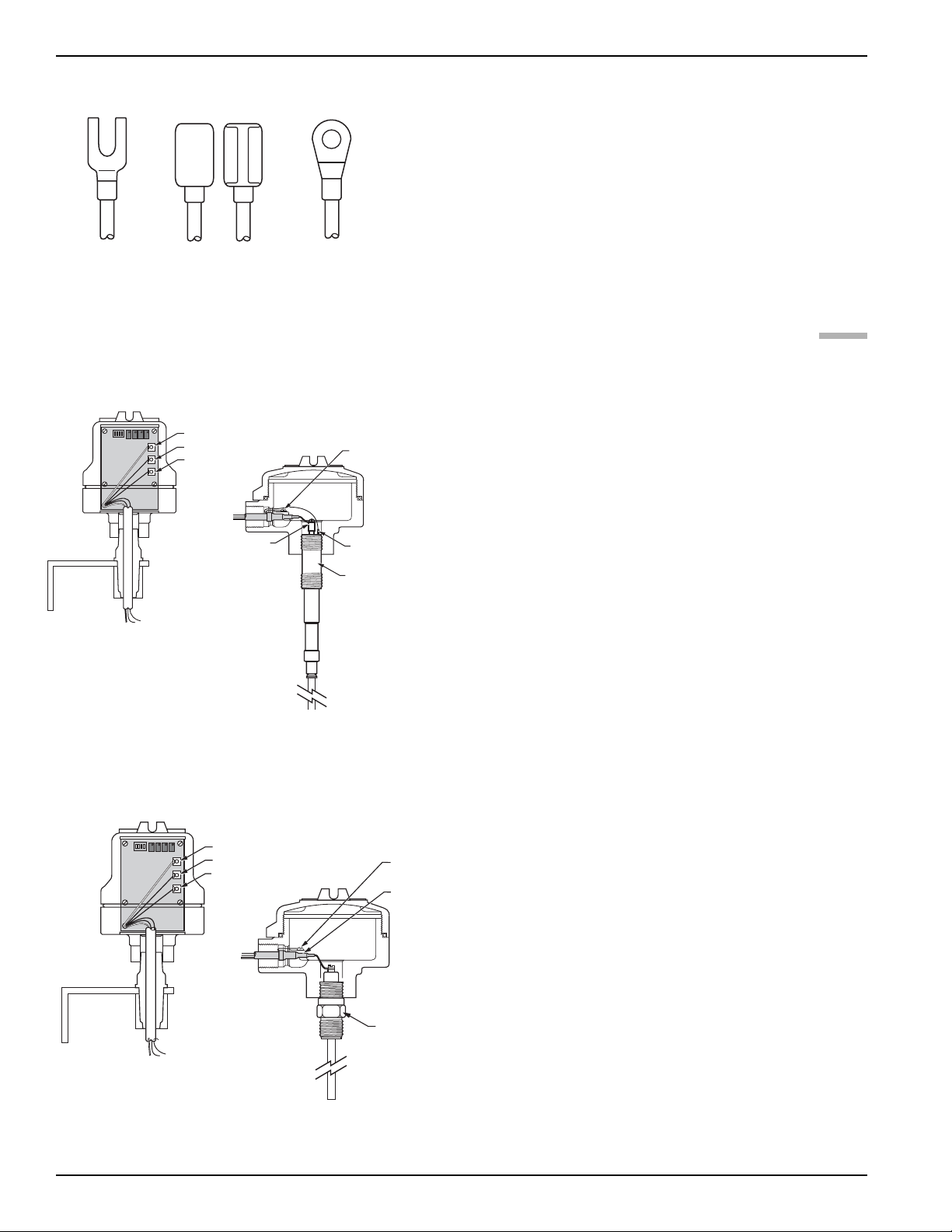
This manual provides information on the Kotron
Model 811 RF Point Level Sensor. It is important that all
instructions are read carefully and followed in sequence.
Detailed instructions are included in the Installation
section of this manual.
Conventions Used in this Manual
Certain conventions are used in this manual to convey
specific types of information. General technical material,
support data, and safety information are presented in
narrative form. The following styles are used for notes,
cautions, and warnings.
Notes
Notes contain information that augments or clarifies
an operating step. Notes do not normally contain
actions. They follow the procedural steps to which
they refer.
Cautions
Cautions alert the technician to special conditions that
could injure personnel, damage equipment, or reduce
a component’s mechanical integrity. Cautions are also
used to alert the technician to unsafe practices or the
need for special protective equipment or specific mate-
rials. In this manual, a caution box indicates a poten-
tially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in minor or moderate injury.
Warnings
Warnings identify potentially dangerous situations or
serious hazards. In this manual, a warning indicates an
imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in serious injury or death.
WARNING! Explosion hazard. Do not connect or dis-
connect equipment unless power has been switched off or
the area is known to be non-hazardous.
Safety Messages
The Kotron Model 811 system may be properly installed
in Category II, Pollution Degree 2 installations. Follow all
standard industry procedures for servicing electrical and
computer equipment when working with or around high
voltage. Always shut off the power supply before touching
any components. Although high voltage is not present in
this system, it may be present in other systems.
Electrical components are sensitive to electrostatic dis-
charge. To prevent equipment damage, observe safety
procedures when working with electrostatic sensitive
components.
Low Voltage Directive
For use in Category II installations. If equipment is used
in a manner not specified by manufacturer, protection
provided by equipment may be impaired.
Notice of Trademark, Copyright, and Limitations
Kotron is a registered trademark of Magnetrol
International, Incorporated. Kotron Model 811 RF Point
Level Sensor is a tradename of Magnetrol International,
Incorporated.
Copyright © 2006 Magnetrol International, Incorporated.
Magnetrol reserves the right to make changes to the prod-
uct described in this manual at any time without notice.
Magnetrol makes no warranty with respect to the accuracy
of the information in this manual.
Warranty
All Magnetrol/STI electronic level and flow controls are
warranted free of defects in materials or workmanship for
one full year from the date of original factory
shipment.
If returned within the warranty period; and, upon
factory inspection of the control, the cause of the claim is
determined to be covered under the warranty; then,
Magnetrol/STI will repair or replace the control at
no cost to the purchaser (or owner) other than
transportation.
Magnetrol/STI shall not be liable for misapplication, labor
claims, direct or consequential damage or expense arising
from the installation or use of equipment. There are no
other warranties expressed or implied, except special writ-
ten warranties covering some Magnetrol/STI products.
Quality Assurance
The quality assurance system in place at Magnetrol/STI
guarantees the highest level of quality throughout the
company. Magnetrol/STI is committed to providing full
customer satisfaction both in quality products and
quality service.
Magnetrol’s quality assurance system
is registered to ISO 9001 affirming
its commitment to known inter-
national quality standards providing
the strongest assurance of product/
service quality available.