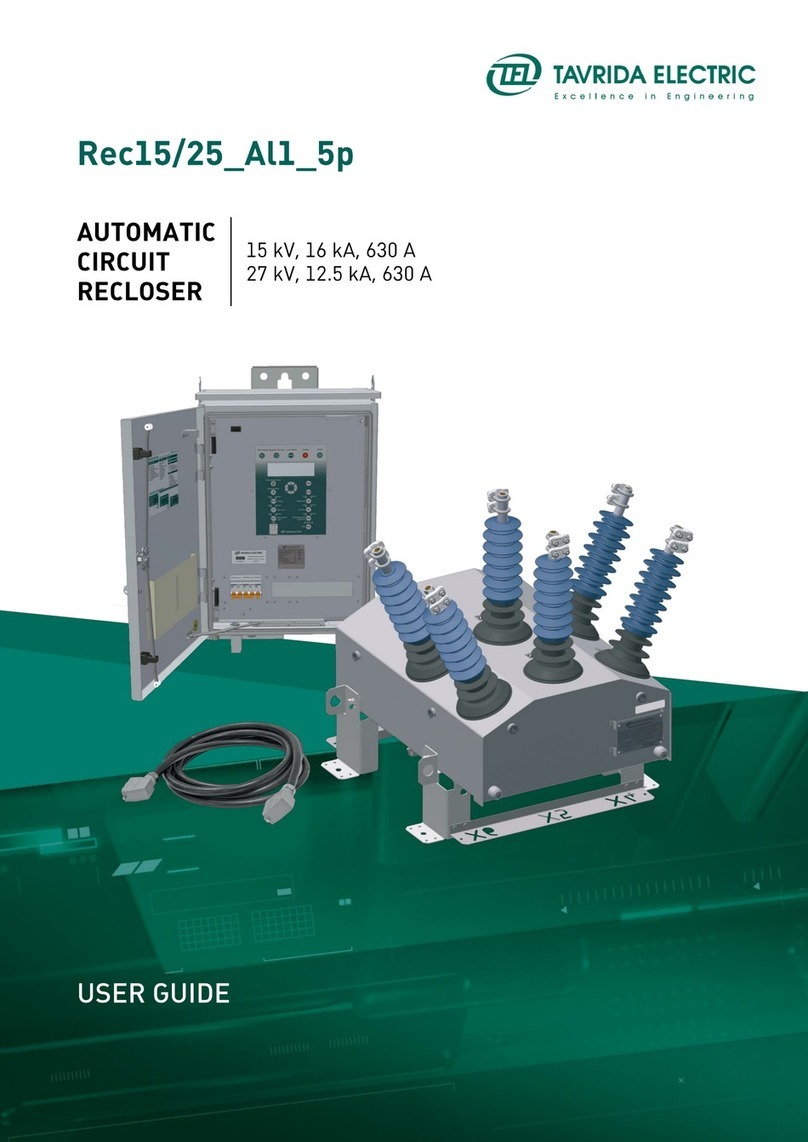
TAVRIDA ELECTRIC SG15 MILE User manual

SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
MEDIUM VOLTAGE SWITCHGEAR
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
ISO 9001:2015 certification
ISO 14001:2015 certification

2
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
Copyright©TavridaElectric,
All Rights Reserved
This document is copyrighted and is intended for users and distributors of Tavrida Electric products. It contains information that is the
intellectual property of Tavrida Electric and this document, or any part there of, should not be copied or reproduced in any form without
prior written permission of Tavrida Electric.
isatrademarkofTavrida Electricandshouldnotbereproducedorusedinanywaywithoutwrittenauthorization.
Tavrida Electric applies a policy of ongoing development and reserves the right to change products without prior notice. Tavrida Electric
does not accept any responsibility for loss or damage incurred as a result of acting or refraining from acting based on information in this
Technical Manual.
Itisabsolutely necessary to read thisdocument carefully before starting the installation or operationof SG_Mile switchgear and to
adhere to the instructions and the relevant regulations contained in it.
SAFETY FIRST
Make sure that during installation, commissioning, maintenance and operation, the respective legal regulations (such
as IEC) and appropriate national safety regulations are adhered to.
Make sure that the installation, commissioning and the operation are carried out by electrical specialists.
Onlyinstalltheswitchgear inclosedroomsdesignatedforelectricalequipment.
Make sure that the specified data are not exceeded under the switchgear operation.
Make sure that this manual is available to all persons concerned with installation, commissioning and operation.
Payspecialattention tothehazard statements throughout this manual:
Useful Features:
Useful and helpful information
TIPS: Examples of calculations, hints
WARNING:
Indicates a potentially hazardous
situationthat,ifnotavoided,couldresultin
personal injuryor equipment damage
DANGER!
Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation that, if not avoided, could result in death
or serious injury
Technical stuff:
Indicates important information
about installation and maintenance
Always follow the instruction manual and respect the rules of good engineering practice!
Hazardous voltage can cause electrical shocks and burns. Disconnect power, then earth and short-circuit before proceeding with
any work on this equipment.
Lowvoltagedevices(reclosercontrolleralltypes)meettherequirementsoftheEMCDirective2014/30/ÅÑ,theLow
VoltageDirective2014/35/EU

3
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABBREVIATION
.............................................................................................................................................5
MAINTENANCE MANUAL...................................................................................................................................6
1.
GENERAL
........................................................................................................................................6
1.1
Presentation .................................................................................................................................6
1.2
Applicable standards......................................................................................................................6
1.3
Degrees of protection.....................................................................................................................7
1.5 Type testing ..................................................................................................................................7
1.4 Normal service conditions ...............................................................................................................7
1.6
Routine tests ................................................................................................................................8
1.7
Internal arc proof ..........................................................................................................................9
2.
DESIGNE
....................................................................................................................................... 12
2.1
Compartments............................................................................................................................ 12
2.2
Draw-out units............................................................................................................................ 14
2.3
Main busbars .............................................................................................................................. 15
2.4
Branch connections ..................................................................................................................... 15
2.5
Earthing busbar .......................................................................................................................... 16
2.6
Bushing insulators and shutters .................................................................................................... 16
2.7
Cables ...................................................................................................................................... 16
2.8
Auxiliary wiring ........................................................................................................................... 17
2.9
Pressure relief flaps and gas exhaust duct
..................................................................................... 17
2.10
Doors
...................................................................................................................................... 18
2.11
Natural ventilation circuit
................................................................................................................. 18
2.12
Current transformers ................................................................................................................... 18
2.13
Top installation (earthing switch) .................................................................................................. 18
2.14
Top installation (voltage transformer)............................................................................................ 19
2.15
Panel attachment ........................................................................................................................ 19
2.16
Busbar bridge............................................................................................................................. 19
3.
BASIC STRUCTURE
........................................................................................................................... 20
4.
MAINTENANCE
................................................................................................................................ 22
4.1
Visual inspection of all switchgear compartments ( low-voltage, circuit-breaker, cable, busbar)
......................... 23
4.2
Functional tests
............................................................................................................................. 24
4.3
Greasing of moving and current conducting parts
................................................................................... 24
4.4
Insulation resistance tests
............................................................................................................. 27
4.5
Measurement of the resistance of the main conducting circuits
.............................................................. 27
5.
TROUBLESHOOTING
........................................................................................................................ 29
5.1
Switchgear troubleshooting
........................................................................................................ 29
5.2
Draw-out unit troubleshooting
.................................................................................................... 30
5.3
Control Module troubleshooting
.................................................................................................. 31

4
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
6.
INTERLOCKS AND LOCKINGDEVICES
................................................................................................... 31
7.
OPERATION.................................................................................................................................... 33
7.1
Withdrawable parts position definitions ........................................................................................... 33
7.2
Interlocking Conditions ................................................................................................................ 34
7.3
Interlocks .................................................................................................................................. 35
7.4
Locking facilities ......................................................................................................................... 40
7.5
Busbar earthing switch close operation conditions ........................................................................... 40
7.6
Appearance and interface of panel with draw-out unit with circuit breaker (IF, OF, BC, BT)................... 41
7.7
Appearance and interface of panel with DOU and without circuit breaker (MES, M, BRES, BR, BRM) ........... 43
7.8
Load-break switch panel LBSF ...................................................................................................... 45
7.9
Service trolley operation .............................................................................................................. 48
8.
DISPOSAL
..................................................................................................................................... 57

5
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
ABBREVIATION
AC Alternating current
BC Bus Coupler
BR Bus Riser
BRES Bus Riser with Earth Switch
BRM Bus Riser with Metering Transformer
BT Bus-Tie
CB Circuit breaker
CC Cable compartment
CM Control module
CT Current transformer
CO Close-open (operation)
DC Direct current
DIN German institute for standardization
DOU Draw-out unit
EMC Electromagnetic compatibility
ES Earthing switch
GOST
State standard of the Russian Federation
HCD Handheld closing generator
HD Heavy duty switching module
IAC Internal arc classification
IEC International Electrotechnical Commission
IF Incoming Panel
IP International protection
IP Ingress protection
ISM Indoor switching module
KD Knocked down (panel)
LBS Load break switch
LBSF Load-Break Switch with Fuses
LD Low duty switching module
LED Light-emitting diode
LSC Loss of service continuity (class)
LV Low voltage
M Metering panel
ManGen
Manual generator
MES Metering panel with Earth Switch
MV Medium voltage
OF Outgoing Panel
PB Power block
PCD Pole-to-center distance
PD Partial discharge
PM Metallic partitions (class)
R&D Research and development
SA Surge arrester
SCADA
Supervisory control and data acquisition
SG_Mile
Medium-Voltage switchgear Mile series
Shell Shell type switching module
SP Switchgear panel
STP Service Transformer Panel
TEE AS Tavrida Electric Export
TEL Tavrida Electric (registered TM)
VCB Vacuum circuit breaker
VT Voltage transformer

6
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
This manual provides information on maintenance and operation of SG_Mile series switchgear.
1.
GENERAL
1.1
Presentation
The SG_Mile series switchgear is designed for primary
distribution networks with rated voltages of 12kV, 17.5kV and
24kV 50/60Hz intended for indoor installation. The SG_Mile
series switchgear is air insulated LSC2B-PM class, with single
busbar design. The switchgear concept meets today's owner
requirements such as reliability, personnel and operational
safety,economyandefficiencyinanoptimalway.
The SG_Mile switchgear panels are successfully installed and
commissioned for wide range of applications: distribution
networks, industry, mining, Oil&Gas etc.
The switchgear is modular and is built by placing standardized
units side by side in a coordinated way. The switchgear is easy to
configure and selection of the apparatus and instruments does
not imply dedicated solutions.
The functional units of the switchgear are guaranteed arc proof
AFLR 31.5kA 1sin accordance with the IEC 62271-200 standard,
appendix AA, class A accessibility, criteria 1 to 5. All start-up,
maintenance and service operations can be carried out from the
front. The switchgear and earthing switches are operated from
the front with the door closed. The SG_Mile series switchgear
can be configured with front access or with both front and rear
access.
1.2
Applicable standards
The switchgear and its main apparatus comply with the
following standards:
Table 1.1.
Applicable standards
Description
Standard
High-voltage switchgear and control gear –Part 1: Common specifications
IEC 62271-1
High-voltage switchgear and controlgear –Part 200: AC metal-enclosed switchgear and controlgear for
rated voltages above 1 kV and up to and including 52 kV
IEC 62271-200
High-voltage switchgear and control gear –Part 200: High-voltage alternating current disconnectors
and earthing switches
IEC 62271-102
Insulation co-ordination –Part 2: Application guide
IEC 60071-2
High-voltage switchgear and control gear –Part 100: High-voltage alternating current circuit-breakers
IEC 62271-100
Instrument transformers - Part 2: Additional requirements for current transformers
IEC 61869-2
Instrumenttransformers-Part3:Additionalrequirementsforinductivevoltagetransformers
IEC 61869-3
High-voltage switchgear and control gear - Part 103: Switches for rated voltages above 1 kV up to and
including 52 kV
IEC 62271-103
Unsealed metal-enclosed switchgear and controlgear for voltages up to 10 kV.General specifications
GOST 14693-90
Factory-assembled metal-enclosed switchgear for rated voltages up to and including 35 kV. General
specifications
GOST R 55190-2012
Alternating-current circuit-breakers for voltages from 3 to 750kV. General specifications
GOST R 52565-2006

7
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.3
Degrees of protection
The degrees of protection of the switchgear conforms with IEC
60529 standard. The SG_Mile series switchgear is normally
suppliedwiththefollowingstandarddegreesofprotection:
IP4X on the external housing.
IP3X with the doors open.
Note: IP41 on request
1.5 Type testing
The SG_Mile switchgear has successfully passed all the tests
specified by relevant IEC (International Standard) and GOST
(state standard of the Russian Federation) standards. As noted
within the regulations of these standards, the tests were carried
out on the switchgear units considered to be the most sensitive
to stresses applied within the tests and, therefore, assigned to
be valid through the whole range.
Table 1.4.
Type tests
1.4 Normal service conditions
The rated characteristics of the switchgear are guaranteed
underthe followingambient conditions:
1)
Dielectric test on main and auxiliary circuits
Table 1.2.
Parameter
Parameter value
Minimum ambient temperature
-25°C*
Maximum ambient temperature
+55°C**
Maximum altitude above sea level
1000 m***
Relative humidity
95%
Ambient atmosphere in accordance with IEC 60721-2-1-
"Wda": non-explosive, uncontaminated and non-corrosive.
Atmosphere type II according to GOST 15150-69.
* - The value is limited by instrument transformers
**- IEC 62271-200 limits the upper level of ambient temperature at
+40°C
***- Forinstallations inaltitudes above 1000m,the external insulation
is calculated as multiplication of rated insulation with Ka in accordance
with IEC 62271-1
2)
Temperature rise and main circuit impedance
measurement
3)
Peak and rated short-time withstand currents test on
primary and earthing circuits, including draw-out unit and
earthing switch
4)
Making and breaking capacity of the switching devices and
apparatus
5)
Mechanical operations of the switching devices and draw-
out units
6)
Verification of the IP protection code
7)
Verification of auxiliary and control circuits
8)
Internalarctest(IACclassification:AFLR,31.5(25)kA,1s)
Table 1.3.
Altitude above sea level,
m
Air dielectric strength factor
Ka
1000
1,00
1200
0,98
1500
0,95
1800
0,92
2000
0,90
2500
0,85
3000
0,80
Test

8
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
1.6
Routine tests
Routine tests are performed by the assembly factory as
specified in the standard IEC 62271-200 to ensure the superior
qualityofeachproductdeliveredtoacustomersite:
Table 1.5. Routine tests
Dielectrictestonthemaincircuits
Tests on auxiliary and control circuits, and verification of
conformity to the circuit diagrams
Functional tests
Verification of protection against electrical shock
Dielectric tests on the auxiliary circuits
Measurementoftheresistanceofthemaincircuit
Design and visual checks
Mechanical operation tests
Tests of auxiliary electrical devices (interlock)
Voltage and current transformers ratios, polarity check
Primary current injection test (CT-Protection-VCB check)
Voltageinjectiontest for protectionand metering
Test

11
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1.7
Internal arc proof
The personnel safety factor was a primary goal when SG_Mile
switchgear was designed. Thus, the SG_Mile switchgear has
beendesigned andtestedtowithstand aninternalarcdue to a
short-circuit current of the same levels as the panel rated
breaking currents. These tests ensure that the metal
construction of the SG_Mile switchgear is able to protect
personnel operating near the switchgear subjected to an
internal arc fault. The internal arc is treated to be the most
unlikely event from all type of faults, however, a small
percentage of occurrence still exists due to many factors
including improper connection of incoming cables and
tightening contact connections, intrusion of animals,
deterioration of insulation over time, severe atmospheric
conditions and human factors. The proven characteristics of the
SG_Mile switchgear drastically reduce the incidence of these
causes in generation of faults, but not all can be fully eliminated.
An internal arc event produces a large amount of energy which
instantly transforms into phenomena such as rapid increase of
internal pressure and temperature, visual and sound effects,
which consequently result in high mechanical stresses on the
switchgear structure, and/or in melting and evaporation of the
materials.
Such significant stresses, unless properly controlled, may
causea serious threat tothe servicepersonneldue toharmful
effects(shock-wave,flyingparts,doors opening,emissionof hot
gases, open flame).
The IEC 62271-200 standard describes the test-methods
required. The SG_Mile switchgear conforms to all criteria
stated inAnnex A of the standard:
Thedoorsof theswitchgear must remainclosedandno
opening of the cover panels must occur.
No part of the switchgear, which may be hazardous for
personnel, may be ejected.
Arcing does not cause holes in the accessible sides up to a
height of 2 m.
Vertically and horizontally arranged fabric indicators
placed outside the switchgear may not get burnt.
All the switchgear earthing connections must remain
effective.
The SG_Mile switchgear is IAC classified: AFLR 31.5kA, 1s. For
the installation of the SG_Mile switchgear the following factors
are obligatory to be considered:
Level of the fault current (16. 31.5 kA).
Duration of the fault current (0.1. 1s).
Hot gases evacuation routes.
Dimensions of the switchboard room, with special
attention to the height.
TEE has developed various solutions providing effective control
and protection over the arc initiation at earlier stages as well as
passivetypeprotectionbasedonconstruction.
0 100 200 400 ms
19 ms

10
Medium-Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE, SG25_MILE
10
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
Arcing time minimization
The energy released in an arc flash is directly proportional to the
arcing time (V x I x t), where V is voltage, I - current, t - time. As V
x I are given by the service conditions, only the arcing time (t) is
changeable. The less arcing time, the less destruction can result
from the arc flash. The circuit breaker operation time consist of:
1.
Arc Flash relay operation time. Normally - 7ms.
2.
Circuit breaker breaking time (opening time of circuit breaker
and arcing time). Normally 100ms for motor spring charged
drive circuit breakers.
The application of modern Arc Flash Relays with optical sensors
makesitpossibletominimizerelayresponsetimesupto2ms.
Tavrida circuit breakers are designed with this concept in mind –
optimizing the vacuum interrupter, insulation, magnetic
actuator and control modules. This has resulted in the fastest
circuit breaker, the one cycle interrupter - a breakthrough for
fast switching and arc flash protection technology. The reaction
time of the CM16 control module series is minimized to 4ms
(special version) . The opening time of the fastest circuit breaker
-
7ms (special version), theaverage arcing time - 8ms, which
results in ultra-fast arc flash interruption of 20ms, that is equal
to a period with frequency 50Hz, while other manufacturers
advertise 5 cycles.
Table 1.6. Arc flash mitigation with Tavrida circuit breaker
Arc flash relay reaction time
2ms
CM 16 reaction time
4ms
Shell FT type VCB opening time
7ms
Arcing time
7ms
Totally:
20ms


12
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
2.
DESIGNE
2.1
Compartments
The SG_Mile switchgear panel is assembled with standard, pre-
fabricated, hot-dip zinc galvanized sheet steel units forming a
rigid, free standing structure. The switchgear consists of four
compartments which are separated from each other by means
of earthed metal partitions. The switchgear is supplied with
cassettetypedraw-outunit.WithintheaspectsofIEC62271-200
related to the definition of Loss of Service Continuity, the design
category of SG_Mile series switchgear is defined as LSC2B-PM.
Compartments of the SG_Mile series switchgear are presented
below.
A - Busbar compartment
B - Circuit Breaker compartment
C-Low-voltagecompartment
D - Cable compartment
Fig.2.1. SG_Mile cassette type
2.1.1
Busbar compartment
The busbar compartment houses the main busbar system
connected to the fixed upper isolating contacts of the circuit
breaker by means of branch connections. The main busbars are
made of electrolytic copper. The busbar compartment of each
panel is segregated from the busbar compartments of the
neighboring panels with bushing insulators. The bushing
insulators were tested with electrodynamic forces load
withstand during the flow offault current.
Optionally the busbars can be covered with heat shrinkable
insulation sleeves. It is possible for maintenance personnel to
access the busbar compartment from the front (through the
circuit breaker compartment), as well as from the rear
(removablepartitionofbusbarcompartment)oftheswitchgear.

13
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.1.2
Cable compartment
The cable compartment houses the branch connections,
earthing busbar, earthing switch, power cables, surge
arresters, instrument transformers (current transformers,
voltage transformers, zero-current transformers). The cable
compartment design allows up to 4 cables per phase
connections (in case of the withdrawable voltage transformer
truck present) or 7 cables per phase (in case of the voltage
transformer truck absent). Cable fixing plate is suitable for any
kind of cable. Optionally, insulation partitions can be situated in
the cable compartment between phases. Insulation partitions
are made from non-flammable material. Panel openings for
control cables can be made in the bottom of the switchgear if
they enter fromthe cable tunnel.
2.1.3
Circuit breaker compartment
The circuit breaker compartment houses the circuit breaker,
bushing insulators and contains fixed contacts for connection
of the circuit breaker to the busbars, to the cable compartment
and the shutter mechanism. The metallic shutters operate
automatically during movement of the circuit breaker from the
test position to the service position or vice versa. The position
of the circuit breaker can be seen from the front of the panel
through an inspection window. All necessary interlocks for
safetyoperationaccordingto IEC62271-200andothers canbe
added on request. The bushings are single-pole type and are
made of cast resin. Access to live parts is prevented with
movable metal shutters.
2.1.4
Low voltage compartment
The low-voltage compartment is designed to mount all
secondarycircuit connections within thesingle panel aswell
as interconnections between adjacent panels and transit
connections. Special holes are provided for transit cables. The
spacious compartment allows the installation of multi-
functional microprocessor protection relay, energy meters,
lighting, heating and many other devices. The sensors,
indicators, microprocessor protection relay management
blocks, mimic diagram, and control buttons are placed on the
front panel.

14
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
2.2
Draw-out units
The following types of draw-out units are available:
Draw-outunitwithVacuumCircuitBreakercassettetype.
Draw-outunitwithIsolating truckcassettetype.
Draw-out unit with Voltage Transformers cassette type (for
CB/CC).
Draw-outunitforCableService cassettetype.
Draw-outunitfor CableTestingcassettetype.
Draw-out unit with VACUUM CIRCUIT BREAKER
(cassette type)
Themainpurposeofadraw-outunitwithcircuitbreaker:
-
switchingofloadand short-circuit currents;
-
to make a visible break between the busbar and the cable
compartment. It is needed for maintenance purposes in
the cable compartment to guarantee personal safety. The
Draw- out unit is equipped with all necessary interlocks for
safeoperationwiththepanelinanycondition.
Draw-out unit with ISOLATING TRUCK
(cassette type)
Draw-out unit with Isolation truck is used for:
-
conducting rated load currents;
-
making a visible break between sections of switchboard
during maintenance procedures.
Draw-out unit with VOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS
A draw-out unit with voltage transformers is used for:
-
voltage metering for protection or/and commercial energy
metering.
Fig.2.2. Draw-out unit with VCB, cassette type
Fig.2.3. Draw-out unit with Isolating truck, cassette type
It can be placed in the circuit breaker or in the cable
compartment. All voltage transformers are equipped with
fuses to protect transformers against fault current. Blown
fuseindicationisavailableasanoptionalfeature.
CABLE SERVICE draw-out unit cassette type
Cable Service draw-out unit is used for safe cable insulation
testing,withoutdisconnectingthepowercables.
CABLE TESTING draw-out unit cassette type
Fig.2.4.
Draw-out unit with VT,
cassette type
(cable compartment)
Fig.2.5.
Draw-out unit with VT,
cassette type
(circuit breaker compartment)
Cable Testing draw-out unit is used for safe and convenient
cable insulation testing as well as primary current injection
testonpowercableswithoutdisconnectingthem.
Fig.2.6.
CABLE SERVICE draw-out unit cassette type
Fig.2.7.
CABLE TESTING draw-out unit cassette type

15
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.3
Main busbars
The busbar compartment contains the main busbar system
connected to the fixed upper contacts of the circuit breaker
compartment by means of branch connections. The main
busbars are made of electrolytic copper. The maximum rating of
busbar system with natural cooling is 3150A. With compulsory
cooling the busbar's nominal rating can exceed 4000A. The
busbars are normally covered with heat shrinkable sleeves for
voltage ratings exceeding 12kV. Each busbar compartment
within the panel is segregated from the others by means of
partitions and supported by pass through insulators. The
through insulators have been tested for their capability to
withstand stresses due to electro-dynamic forces at the rated
breaking currents.
2.4
Branch connections
The cable compartment contains the branch system for
connecting power cables to the fixed, lower contacts of the
circuit breaker compartment. The branch connections are made
ofelectrolytic copper.
2.4.1
Branch insulation
SG15_Mile switchboard with rated voltage up to 12kV - only
central upper and lower branch busbars L2 are covered with
heat-shrink insulation. Also, side isolating barriers are fixed to
segregate L1 and L3 busbars from earthed metal parts in cable
compartment. A complete heat-shrink insulation (including
jointscovers)canbeofferedunderacustomerrequest.
SG15_Mile and SG25_Mile switchboards with rated voltages
17.5kVand24kVaredeliveredwithfullyinsulatedbusbars.
TheL, T,I typejoint insulation coversare usedfor insulation of
corresponding busbar connections.
The normal load / cross-section dependency of main and branch
busbars are presented inthe table.
Table2.1.
Main busbars
Main busbars rated
c
urrent, А
Busbar, mm x mm
1250
1x10x80
1600
2x10x60
2000
2x10x80
2500
3x10x80
3150
3x10x100
Table2.2.
Branch busbars
Branch busbars rated current, А
Busbar,mm x mm
630
1x10x40
1250
1x10x80; 2x10x40
1600
2x10x60
2000
2x10x80
2500
3x10x80
3150
3x10x100

16
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
2.5
Earthing busbar
The earthing busbar is made of electrolytic copper. It runs along
all adjacent panels and connects to a main substation earthing
bar. All current carrying parts are interconnected with each
other to equipotential bonding to guarantee personal safety
against electric shock. The earthing busbars are capable of peak
withstandcurrent31.5kAandpeakvalue82kAfor3seconds.
2.6
Bushing insulators and shutters
Thebushinginsulatorsarelocatedinthecircuitbreaker
compartment to hold fixed contacts. They are also used for
connection of the withdrawable unit to the busbar compartment
and the cable compartment respectively. The bushing insulators
are single-pole type and are made of cast resin. The shutters are
made of metal and activated automatically during movement of
the withdrawable unit from the test position to the service
position or vice versa.
2.7
Cables
Single and three-core cables (up to a maximum of 6 per phase or
up to 4 cables with voltage transformers) can be used. The
construction of SG_Mile provides simple access to the cable
from the front side of the switchgear and gives the opportunity of
placing SG_Mile close to the wall.

17
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.8
Auxiliary wiring
Electrical wiring diagrams are the part of switchgear
documentation delivered with each order.
A complete set of wiring diagrams developed by TEE for a typical
substation is available with Protection Relays from other
manufacturers.
The following options are available:
Auxiliary supply voltage: 24 .. 240V DC/AC.
Any type of a microprocessor protection relay can be
adopted.
Solenoid and electromagnet interlocks for earthing switch,
draw-outunits,sectional earthing switch.
Heatingfor everycompartment,lighting.
SCADA different options.
Arcprotection variety selection.
Commercial metering.
Motor-drivendraw-outunitandearthingswitch.
2.9
Pressure relief flaps and gas exhaust duct
Pressure relief flaps allow hot gases to be released from the
compartment in the event of internal arc. A pressure relief flap is
mounted at the top of each power compartment of a panel. TEE
has designed different versions of the flaps depending on
required IP level, nominal currents and rated breaking currents.
The gas exhaust duct is presumed to evacuate hot gases into
dedicated areas. The evacuation of hot gases and other harmful
particles can be diverted to:
Neighboring rooms.
Outside to restricted areas.
Dedicated panel with extinguishing compartment equipped
with special filters.
Upstream(specialattentiontotheceilingheight).
The gas exhaust duct is fitted to SG_Mile at the top of each panel
and runs along the entire length of the switchboard. The
pressure generated by the internal arc opens pressure relief
flaps thus allowing hot gases to be evacuated to dedicated areas.
A complete solution for every installation is to be specified
separately.
Pressure relief flaps design samples
≤1250Arated current
Flat single sheet
>1250 A rated current
Louvre + mesh

18
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
2.10
D
oors
The SG_Mile powder coated doors are made of galvanized steel
sheets, it provides a rigid structure and is resistant to
mechanical stresses. Robust hinges and handles provide for
convenient and safe closing.
Inspection windows are made of explosion-proof glass,
providing maximum safety for personal.
2.11
Natural ventilation circuit
Тhere is a natural ventilation circuit arranged around the circuit
breaker to provide dissipation of heat due to circuit breaker
operating at high currents or at high ambient temperatures. The
cool air is sucked into the circuit, passing underneath the circuit
breaker and primary contacts and withdrawn from the panel
through thegas exhaust channel. In case of internal arc blast,
the reverse air current boosted by a high pressure instantly
closes the special valve inside the intermediate plate, thus
preventing personnel injuries due to the escape of hot gases. If
thepressurereliefflapstype-louvresapplied,itisusedaspart
ofventilation circuit.
2.12
Currenttransformers
For convenient access to the current transformers, inside cable
compartment, arotatingCTmounting platedesign isemployed.
The CT mounting plate may beopened:
-
using central mounting bolts in case of CT assembly;
-
using lower mounting bolts in case of CT replacement.
2.13
Top installation (earthing switch)
Depending on panel requirements and structure, the busbar
earthing switch or voltage transformers can be installed over
the top ofany panel.
A top installed earthing switch can be equipped with support
insulators, with capacitive sensors, electromagnet for
providing necessaryinterlocksand signalling.

19
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.14
Top installation (voltage transformer)
Depending on panel requirements and structure, the busbar
earthing switch or voltage transformers can be installed over
the top ofany panel.
A top installed earthing switch can be equipped with support
insulators, with capacitive sensors, electromagnet for
providing necessaryinterlocksandsignalling.
2.15
Panel attachment
The following solutions are available for non-standard
installationssuchasrearorsideinput,cableorbusbarinput:
-
rear attachment for cable or busbar input;
-
left side attachment for cable or busbar input;
-
right side attachment for cable or busbar input.
2.16
Busbar bridge
Section coupling can be also done with a busbar bridge (bus
duct). Normally the connection of the busbar bridge is done with
the help of rear attachments of the panels at the opposite sides.
Thebusbarbridgeisdesignedperprojectrequirements.

20
Medium Voltage Switchgear SG15_MILE / SG25_MILE
3.
BASIC STRUCTURE
An indoor substation switchboard consists of different numbers and types of SG panels with switching devices, control and protection
relays, signaling and metering devices and other auxiliary equipment, which are interconnected by control cabling. The base structure of
the typical SG panelis given below.
1.
Vacuum circuitbreaker
2.
Primary contactsinsulators
3.
Current transformers
4.
Draw-out unit with voltage transformers
5.
Surge arresters
6.
Sealed cable entries
7.
Earthing switch
8.
Gasexhaustchannelofthecircuitbreakercompartment
9.
Gas exhaust channel of the busbar compartment
10.
Gas exhaust channel of the cable compartment
11.
Pressure relief flaps
12.
Support insulators with voltage indicator
13.
Shutter mechanism
14.
Circuit breaker door with inspection window
15.
Through insulators
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other TAVRIDA ELECTRIC Industrial Equipment manuals