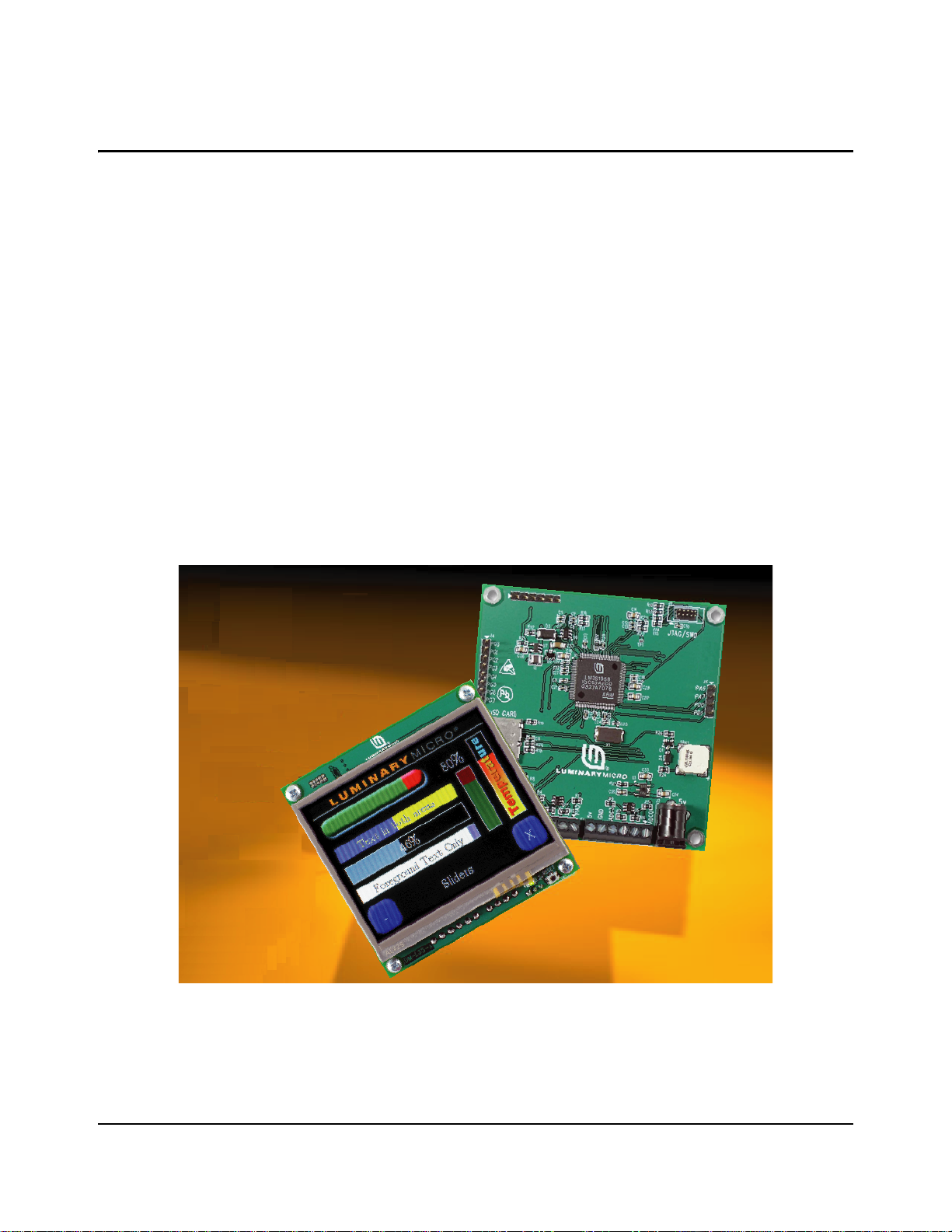
Stellaris® Intelligent Display Module with 3.5" Display
August 7, 2009 3
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Stellaris® Intelligent Display Module with3.5" Landscape Display Reference Design Kit Over-
view....................................................................................................................................................................9
Kit Contents......................................................................................................................................................10
Using the RDK..................................................................................................................................................10
Features............................................................................................................................................................10
Board Overview ................................................................................................................................................11
Chapter 2: Hardware Description..................................................................................................................13
Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................................13
Functional Description ......................................................................................................................................14
Microcontroller, Reset, and JTAG (Schematic page 1).................................................................................14
Microcontroller ..........................................................................................................................................14
Debugging.................................................................................................................................................14
LCD Panel and Voltage Regulators (Schematic page 2)..............................................................................14
LCD Panel.................................................................................................................................................14
Touch Panel..............................................................................................................................................15
High Power LED Driver.............................................................................................................................15
3.3 V DC Regulator...................................................................................................................................15
UART, microSD Card Slot, Speaker, Analog Inputs, Digital I/O (Schematic page 3)...................................15
RS232 Serial Port .....................................................................................................................................15
microSD Card Slot ....................................................................................................................................15
Speaker.....................................................................................................................................................15
Analog Inputs............................................................................................................................................16
Digital I/O ..................................................................................................................................................16
Serial Header............................................................................................................................................16
Chapter 3: Software Development ................................................................................................................17
Software Description.........................................................................................................................................17
Source Code.....................................................................................................................................................17
Tool Options .....................................................................................................................................................17
Programming the IDM.......................................................................................................................................18
Appendix A: Schematics................................................................................................................................21
Appendix B: Bill of Materials (BOM) .............................................................................................................25
Appendix C: Component Details...................................................................................................................29