Thermowave TL Series User manual
thermowave
Gesellschaft für Wärmetechnik mbH
Eichenweg 4
06536 Berga
Telefon: +49 34651 418 0
Fax: +49 34651 418 13
E-mail: info@thermowave.de
Web: www.thermowave.de
BA EN 12.2019 Modification 02 from 01.12.19. Copies are not subject to the change service.
Manual
Plate heat exchanger
Type:
ID number:
Order number:
Position:
Project:

BA EN 12.2019 Modification 02 from 01.12.19. Copies are not subject to the change service. 2 of 41
Dear customer,
You have decided to purchase a quality product from thermowave GmbH.
Your plate heat exchanger represents an investment in a product that has been developed with respect to
the latest research results. The individual components are in line with the latest status of the respective
technology, and facilitate a high degree of functionality and reliability.
The following pages contain operating instructions for your plate heat exchanger. These operating
instructions list all the important measures that will facilitate smooth operations of your plate heat
exchanger. Please ensure that all persons who have anything to do with the installation, operations and
maintenance of the apparatus have understood and familiarised themselves with these operating
instructions.
thermowave GmbH cannot be held responsible for faults that emerge as a result of these operating
instructions having been ignored. In case your plate heat exchanger encounters problems that have not
been addressed in these operating instructions, we request you to promptly contact thermowave GmbH or
its respective representative.
We wish you plenty of happiness with regard to the operations of your
ThermoLine plate heat exchanger.
Your partner for your heat exchanger needs!
thermowave
Gesellschaft für Wärmetechnik mbH

Table of contents
3 of 41
BA EN 12.2019 Modification 02 from 01.12.19. Copies are not subject to the change service.
1Important basic information...............................................................................................5
1.1 Following the operating instructions............................................................................5
1.2 Limits of the apparatus ..............................................................................................5
1.3 Technical data..........................................................................................................5
1.4 Prescribed environmental conditions...........................................................................5
1.5 Other limits..............................................................................................................5
1.6 Interfaces.................................................................................................................6
1.7 Responsibilities ........................................................................................................6
1.7.1 The manufacturer’s responsibilities.......................................................................................6
1.7.2 Responsibilities of the operator or owner ..............................................................................6
1.8 Legal information .....................................................................................................7
1.9 Service address.........................................................................................................7
2Safety.................................................................................................................................8
2.1 Depiction of information............................................................................................8
2.1.1 Warning notices .....................................................................................................................8
2.1.2 Further information................................................................................................................8
2.1.3 Writing styles.........................................................................................................................8
2.2 Diagrams and figures ................................................................................................9
2.3 Intended use of the PHE ............................................................................................9
2.3.1 Personnel requirements..........................................................................................................9
2.3.2 Safety-relevant environmental conditions..............................................................................9
2.3.3 Safety-relevant instructions for specific life phases...............................................................9
2.4 Possible misuse ......................................................................................................10
3Technical data..................................................................................................................11
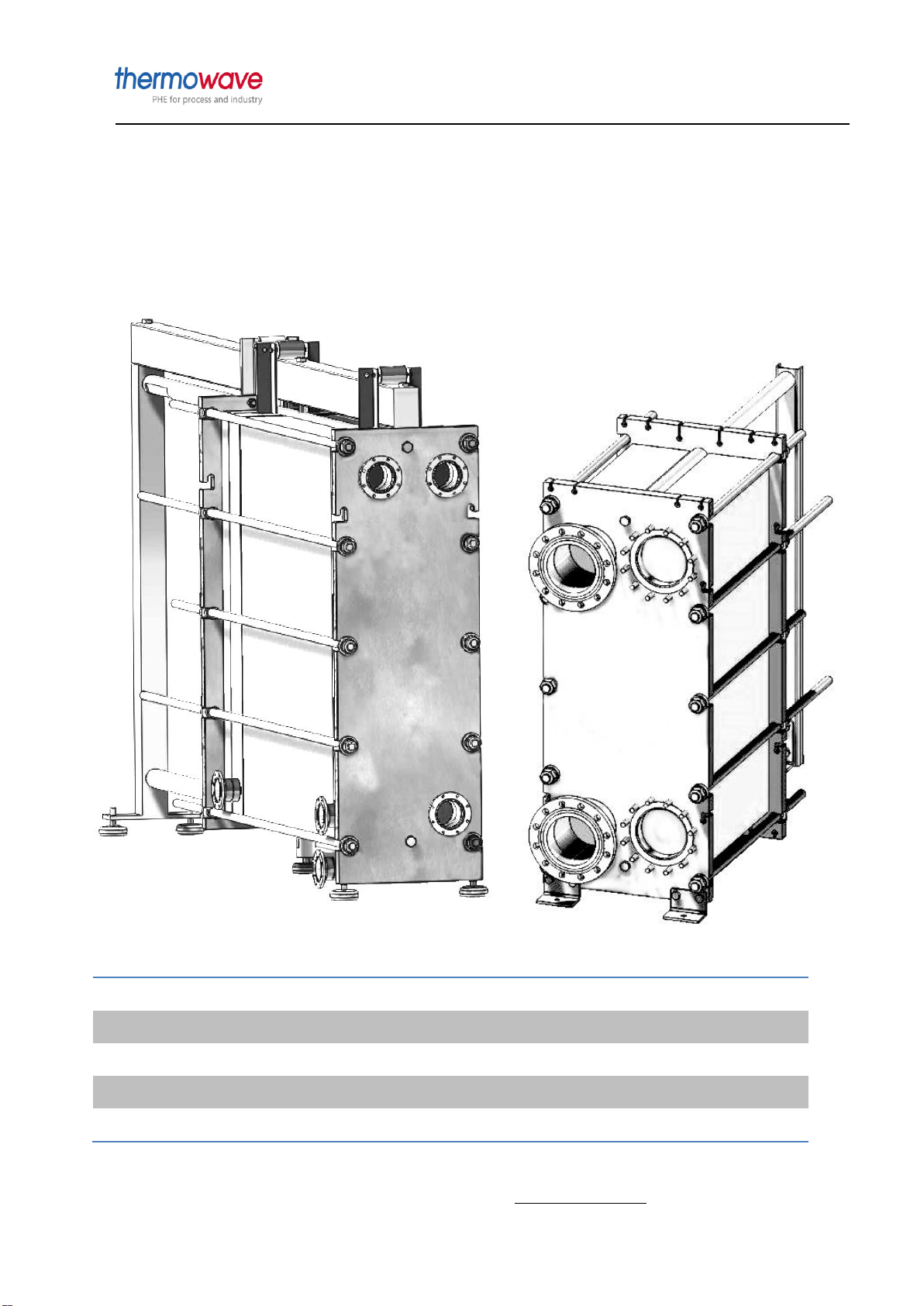
4Structure and function......................................................................................................12
4.1 Structure................................................................................................................12
4.1.1 Main components................................................................................................................ 12
4.1.2 Marking on the apparatus.................................................................................................... 13
4.1.2.1 Sign as per PED (pressure equipment directive)…………………………………………………………...13
4.1.2.2 Screw locking varnish ……………………………………………………………………………………………..14
4.2 Nomenclature.........................................................................................................14
4.3 Frames ..................................................................................................................15
4.4 Function ................................................................................................................16
4.5 Heat exchanger plates and modules...........................................................................17
4.5.1 Gasketed heat exchanger plates .......................................................................................... 17
4.5.2 Welded modules.................................................................................................................. 17
5Delivery, transport, installation.........................................................................................18
5.1 Delivery ................................................................................................................18
5.2 Transport variants...................................................................................................18
5.3 Transport...............................................................................................................18
5.4 Installing the apparatus at the installation site.............................................................19
5.4.1 Horizontal delivery - On the side........................................................................................ 20
5.4.2 Horizontal delivery - On the head plate.............................................................................. 21
5.4.3 Vertical delivery.................................................................................................................. 22
5.4.4 Vertical delivery with base of the apparatus....................................................................... 23

BA EN 12.2019 Modification 02 from 01.12.19. Copies are not subject to the change service. 4 of 41
6Connection, activation and shutdown................................................................................24
6.1 Connection.............................................................................................................24
6.2 Activation..............................................................................................................25
6.3 Shutdown ..............................................................................................................26
6.4 Reactivation after shutdown.....................................................................................26
7Operations .......................................................................................................................27
7.1 Safety....................................................................................................................27
7.2 General..................................................................................................................27
8Troubleshooting ...............................................................................................................28
8.1 Safety....................................................................................................................28
8.2 Service address.......................................................................................................28
8.3 Performance loss ....................................................................................................29
8.4 Lack of leak-tightness .............................................................................................30
9Maintenance, servicing and cleaning .................................................................................31
9.1 Safety....................................................................................................................31
9.2 Service address.......................................................................................................31
9.3 Maintenance schedule .............................................................................................32
9.4 Servicing work.......................................................................................................32
9.4.1 Replacing the gaskets.......................................................................................................... 32
9.4.2 Repairing leakages.............................................................................................................. 33
9.5 Opening and closing the plate packet.........................................................................33
9.5.1 Opening the plate packet..................................................................................................... 33
9.5.2 Closing the plate packet...................................................................................................... 34
9.6 Removal and installation of the plate packet...............................................................36
9.6.1 Removal of the heat exchanger plates and the modules
in case of K, L, T and F (without intermediate frame) frames............................................ 36
9.6.2 Removal of the heat exchanger plates and the modules in case of H frame....................... 36
9.6.3 Removal of the heat exchanger plates and the modules
in case of N and F (with intermediate frame) frames.......................................................... 36
9.6.4 Installation of the heat exchanger plates............................................................................. 37
9.7 Cleaning................................................................................................................37
9.7.1 Cleaning the laser-welded modules .................................................................................... 38
9.7.2 CIP cleaning (cleaning in place)......................................................................................... 38
9.7.3 Manual cleaning.................................................................................................................. 39
10 Disassembly and disposal..................................................................................................40
10.1 Disassembly...........................................................................................................40
10.2 Disposal ................................................................................................................40
11 Annexe.............................................................................................................................41
11.1 Parts list.................................................................................................................41
11.2 Technical data sheet................................................................................................41
11.3 Diagram ................................................................................................................41
11.4 Declaration of conformity........................................................................................41

5 of 41
BA EN 12.2019 Modification 02 from 01.12.19. Copies are not subject to the change service.
1Important basic information
1.1 Following the operating instructions
➢Please read the operating instructions thoroughly and in full.
➢Ensure that the operating instructions are read and understood by all users who perform activities
associated with the plate heat exchanger.
➢Always store the operating instructions in a manner that ensures that they can be accessed by all users at
any time.
1.2 Limits of the apparatus
The plate heat exchanger (PHE) is not a universal apparatus. It has been designed to be used in conjunction
with specific mediums, pressures, temperatures and operating characteristics. The plate heat exchanger is a
component that is meant to be firmly embedded in a system or machine. Once it has been installed, it serves
to transfer heat from a heat-emitting flow medium to a heat-collecting flow medium.
Spatial limits
The PHE must be freely accessible. Minimum distance to building parts, other machines or internal traffic
routes [► chapter 11.3]. The installation of the PHE requires a stable and level surface (foundation/steel
construction).
Temporal limits
Expected service life of the PHE: In case of envisioned cycling
of <= 1000 start-ups/shutdowns.
Demarcation of work responsibilities for mounting, installation, activation:
•Activation, installation, servicing and maintenance only by skilled workers who have received
instructions pertaining to the specific hazards.
•The operator should prevent the system from being accessed by unauthorised persons.
1.3 Technical data
Reference to the order-related technical data sheet in the annexe or, as the case may be, the name plate.
1.4 Prescribed environmental conditions
Risk of corrosion and contamination!
➢Moisture and dirt may not be allowed to penetrate the PHE.
➢Protect the PHE from dust, contamination, moisture, wetness, damage and other harmful influences.
➢Do not store the PHE any longer than necessary. Store the PHE in the original packaging until it is
installed.
➢Until the PHE is installed, ensure that it is protected from damage and stored at a protected location that
is not exposed to the effects of dust, contamination and moisture.
➢Install the PHE in a manner that ensures that it is not damaged as a result of environmentally-induced
hazard sources. The installation procedure should also ensure that the functioning of the apparatus is not
disrupted by the actions of unauthorised entities.
➢Position the PHE in a manner that ensures that it cannot be damaged by internal traffic or transportation
operations.
➢Facilitate optimal monitoring of the PHE and optimal accessibility of the PHE:
-Position the PHE in a manner that ensures that it can always be monitored and checked from all sides.
-Ensure that there is enough room for servicing activities.
This manual suits for next models
25
Table of contents