Toto Link wireless N router User manual

User Manual
Wireless-N ADSL2+ Modem Router

1
Table of Contents
1. ABOUT THIS GUIDE...................................................................................................................3
1.1 Navigation of the User’s Guide............................................................................................................. 3
2. PRODUCT OVERVIEW ..............................................................................................................3
2.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................ 3
2.2 Features .................................................................................................................................................. 3
2.3 Panel Layout .......................................................................................................................................... 4
2.3.1 Front Panel ........................................................................................................................................................4
2.3.2 Rear Panel .........................................................................................................................................................4
3. HARDWARE INSTALLATION...................................................................................................5
3.1 Hardware Installation ........................................................................................................................... 5
3.2 Check the Installation............................................................................................................................ 5
3.3 Set up the Computer.............................................................................................................................. 6
4. CONNECTING TO INTERNET..................................................................................................7
4.1 Accessing Web page............................................................................................................................... 7
4.2 Changing Password............................................................................................................................... 9
4.3 Status....................................................................................................................................................... 9
4.4 Operation Mode................................................................................................................................... 10
4.5 Network .................................................................................................................................................11
4.5.1 WAN Interface.................................................................................................................................................12
4.5.1.1 Static IP....................................................................................................................................................13
4.5.1.2 DHCP Client ............................................................................................................................................13
4.5.1.3 PPPoE.......................................................................................................................................................14
4.5.2 LAN Interface..................................................................................................................................................15
4.5.3 Static DHCP Settings.......................................................................................................................................17
4.5.4 VLAN Settings................................................................................................................................................17
4.6 Wireless Setting.................................................................................................................................... 18
4.6.1 Wireless Status ................................................................................................................................................18
4.6.2 Wireless AP.....................................................................................................................................................18
4.6.3 Multiple SSID .................................................................................................................................................20
4.6.4 Wireless Repeater............................................................................................................................................21
4.6.5 Advanced Settings...........................................................................................................................................22
4.6.6 Wireless WDS Settings....................................................................................................................................24
4.6.7 Wireless WPS Settings....................................................................................................................................25
4.6.8 Access Control.................................................................................................................................................26
4.6.9 Schedule..........................................................................................................................................................26
4.8 Firewall................................................................................................................................................. 27
4.8.1 IP Filtering.......................................................................................................................................................28

2
4.8.2 Port Filtering ...................................................................................................................................................29
4.8.3 MAC Filtering.................................................................................................................................................29
4.8.4 URL Filtering ..................................................................................................................................................30
4.8.5 Port Forwarding...............................................................................................................................................31
4.8.6 DMZ................................................................................................................................................................31
4.9 Management......................................................................................................................................... 32
4.9.1 DDNS..............................................................................................................................................................32
4.9.2 Time Zone Setting ...........................................................................................................................................32
4.9.3 Denial-of-Service ............................................................................................................................................33
4.9.4 Upgrade Firmware...........................................................................................................................................34
4.9.5 Reload Factory Settings...................................................................................................................................34
4.9.6 Password..........................................................................................................................................................35
4.9.7 Schedule Reboot..............................................................................................................................................35
4.9.8 Reboot Router..................................................................................................................................................35

3
1.ABOUTTHISGUIDE
Thank you very much for purchasing the wireless N router. This guide will introduce the
features of this router and tell you how to connect, use and configure the router to access
Internet. Please follow the instructions in this guide to avoid affecting the router’s
performance by improper operation.
1.1 Navigation of the User’s Guide
Product Overview: Describes the router’s function and its features.
Hardware Installation: Describes the hardware installation and settings on user’s
computer.
Connecting to Internet: Tells you how to connect your computer to Internet successfully
by the router.
Advanced Settings: Lists all technical functions including Wireless, TCP/IP Settings,
Firewall and System of the router.
2. PRODUCT OVERVIEW
2.1 Introduction
This is a wireless router which integrates with internet-sharing router, 4-port switch and
firewall all-in-one. Multiple encryptions including wireless LAN 64/128-bit WEP, WPA/WPA2
and WPA-mixed security are supported by the router. The VLAN function also makes
amazing interactive entertainment experience of IPTV be achieved easily. The IP, Port,
URL and MAC address filtering function also makes it easy for user management. In view
of the above, it will allow you to connect your network wirelessly in an easy and secure way
better than ever. It is really a high performance and cost-effective solution for home and
small offices.
2.2 Features
¾Complies with IEEE 802.11n/g/b standards for 2.4GHz Wireless LAN.
¾Supports DHCP, Static IP, PPPoE broadband functions.
¾Provides three operation modes: Gateway, Repeater Bridge and Repeater WISP.
¾Connects to secure network easily and fast using WPS (one-button).
¾Provides 64/128-bit WEP, WPA/WPA2 and WPA-Mixed security.
¾Supports VLAN function.
¾Supports IP, Port, MAC, URL filtering and Port Forwarding.
¾QoS function allocates network bandwidth reasonably.

4
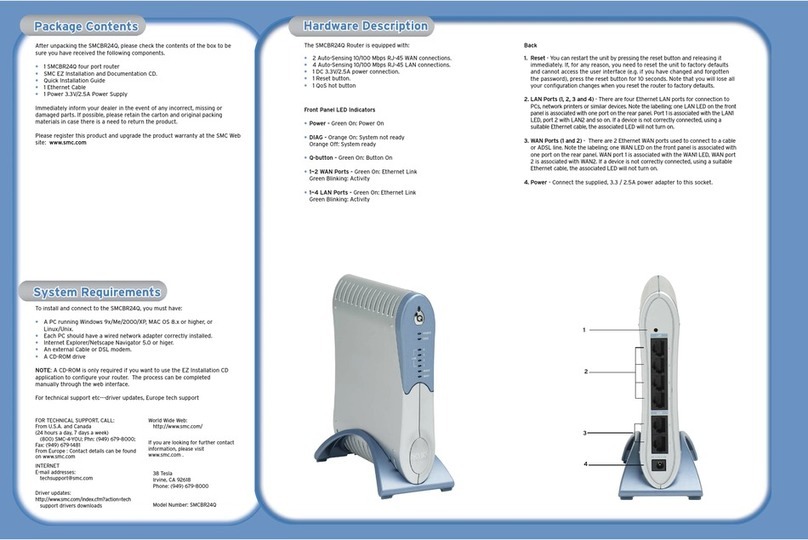
2.3 Panel Layout
2.3.1 Front Panel
The front panel of this router consists of 8 LEDs, which is designed to indicate connection
status.
POWER This indicator lights blue when the router powered on, otherwise it is off.
CPU This indicator blinks blue when router powered on.
WLAN This indicator blinks blue when there are wireless devices connected and
transmitting data to the router.
On When the WAN port is connected successfully the indicator lights blue.
Blink During transmitting or receiving data through the WAN port the indicator
blinks blue.
WAN
Off There is no device linked to the WAN port.
On When the LAN port has a successful connection, the corresponding
indicator lights blue.
Blink During transmitting or receiving data through the LAN port the
corresponding indicator blinks blue.
1/2/3/4
LAN
Off There is no device linked to the LAN port.
2.3.2 Rear Panel
The figure below shows the rear panel of this router.

5
DC IN The Power socket is where you will connect the power adapter.
WAN This port is where you will connect with the cable to access Internet.
1/2/3/4 LAN This port connects the router to local PC.
RST-WPS
Button
Press for about 2~3 seconds, the system LED indicator keep solid light, it
means WPS working, while press for about 10 seconds, all LEDs blinks
quickly, the device will restore to factory default settings.
3.HARDWAREINSTALLATION
3.1 Hardware Installation
For those computers you wish to connect with Internet by this router, each of the computers
must be properly connected with the router through provided Ethernet cables.
1. Connect the Modem to ADSL Filter using RJ11 network cable, LINE port to LINE port.
2. Connect the ADSL’s LAN port to Router’s WAN port using RJ45 network cable.
3. Connect your PC to any one of router’s LAN port.
4. Plug the Power Adapter into the router and then into an outlet.
5. Turn on your computer.
6. Check and confirm that the Power & LAN LED on the router are ON.
3.2 Check the Installation
The control LEDs of the router are clearly visible and the status of the network link can be
seen instantly:
1. With the power source on, once the device is connected to the broadband modem, the

6
Power, WPS, LAN, WLAN and WAN port LEDs of the WLAN Router will light up indicating
a normal status.
2. When the WAN Port is connected to Internet successfully, the WAN LED will light up.
3. When the LAN Port is connected to the computer system, the LAN LED will light up.
3.3 Set up the Computer
The default IP address of the router is 192.168.1.1, the default Subnet Mask is
255.255.255.0. Both of these parameters can be changed as you want. In this guide, we
will use the default values for description.
Connect the local PC to the LAN port on the router. There are then two ways to configure
the IP address for your PC.
Configure the IP address manually
Configure the network parameters. The IP address is 192.168.1.xxx (“xxx” range from 2 to
254). The Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0 and Gateway is 192.168.1.1 (router’s default IP
address).
Obtain an IP address automatically
Set up the TCP/IP Protocol in Obtain an IP address automatically mode on your PC.
Now, you can run the Ping command in the command prompt to verify the network
connection between your PC and the router. Open a command prompt, and type in ping
192.168.1.1, then press Enter.
Figure 3-1 Successful Ping command
If the result displayed is similar to the figure 3-1, it means that the connection between your
PC and the router has been established.

7
Figure 3-2 Failure Ping command
If the result displayed is similar to the figure 3-2, it means that your PC has not connected to
the routersuccessfully. Please check it following below steps:
1. Is the connection between your PC and the router correct?
If correct, the LAN port on the router and LED on your PC’s adapter should be lit.
2. Is the TCP/IP configuration for your PC correct?
Since the router’s IP address is 192.168.1.1, your PC’s IP address must be within the range
of 192.168.1.2 ~ 192.168.1.254, the Gateway must be 192.168.1.1.
4.CONNECTINGTOINTERNET
This chapter introduces how to configure the basic functions of your router so that you can
surf the Internet.
4.1 Accessing Web page
Connect to the router by typing 192.168.1.1 in the address field of web browser. Then press
Enter key.
Then below window will pop up that requires you to enter valid User Name and Password.

8
Enter admin for User Name and Password, both in lower case letters. Then click OK
button or press Enter key.
Now you will get into the web interface of the device. The Main screen will appear.
Now you have logged into the web interface of the router. First, you will see the Easy Setup
page.
Note: If the above screen does not prompt, it means that your web-browser has been set to using a
proxy. Go to Tools menu>Internet Options>Connections>LAN Settings, in the screen that
appears, cancel the Using Proxy checkbox, and click OK to finish it.

9
4.2 Changing Password
Now, we recommend that you change the password to protect the security of your router.
Please go to Management—Password to change the password required to log in your
router.
User Name: type in the name that you use to login the web interface of the router.
New Password: new password is used for administrator authentication.
Confirm Password: new password should be re-entered to verify its accuracy.
4.3 Status
This page shows the current status and some basic parameters of the device.
Note: password length is 8 characters maximum, characters after the 8th position will be truncated.

10
4.4 Operation Mode
This parameter specifies the operating network modes for the Router. This router provides
three modes: Gateway, Repeater Bridge and Repeater WISP. You could refer to the
following description to choose the right one.

11
1. Gateway
In this mode, the device connects to the internet via an ADSL/Cable Modem. NAT is
enabled and PCs on LAN ports share the same IP Address to the ISP via the WAN port.
The connection type can be setup on the WAN page using PPPOE, DHCP client or static
IP.
2. Repeater Bridge
In this mode, all ethernet ports and wireless interfaces are bridged together and the NAT
function is disabled. All WAN related functions, including the firewall, are not supported.
3. Repeater WISP
In this mode, all ethernet ports are bridged together and the wireless client will connect to
the ISP access point. NAT is enabled and PCs on Ethernet ports share the same IP to the
ISP via the wireless LAN. You can connect to the ISP’s AP on the Site-Survey page. The
connection type can be setup on the WAN page using PPPOE, DHCP client or static IP.
4.5 Network

12
4.5.1 WAN Interface
This part allows you to configure the WAN port parameters so that your computer can
access Internet.
Enable UPnP: the UPnP (Universal Plug and play) protocol is supported to bring to
network connected devices the ease of installation and configuration which is already
available for directly connected PC peripherals with the existing Windows “Plug and Play”
system. You can enable this function so that the router doesn’t need to work out which port
need to be opened.
Enable IGMP Proxy: IGMP is the abbreviation of Internet Group Management Protocol. It
is a communication protocol which is mainly used for managing the membership of Internet
Protocol multicast groups. If you select this checkbox, the application of multicast will be
executed through WAN port. In addition, such function is available in NAT mode.
Enable Ping Access on WAN: enable users use Ping command to access WAN.
Enable Web Server Access on WAN: enable users to access Web Server on WAN.
Enable IPsec pass through on VPN connection: IPsec pass through is a technique for
allowing IPsec packets to pass through a NAT router.
Enable PPTP pass through on VPN connection: PPTP pass through is a technique for
allowing PPTP packets to pass through a NAT router.
Enable L2TP pass through on VPN connection: L2TP pass through is a technique for
allowing L2TP packets to pass through a NAT router.
Enable IPv6 pass through on VPN connection: IPv6 pass through is a technique for allowing

13
IPv6 packets to pass through a NAT router.
Clone MAC Address: MAC address is the physical address of your computer’s network
card. Generally, every network card has one unique Mac address. Since many ISPs only
allow one computer in LAN to access Internet, users can enable this function to make more
computers surf Internet.
4.5.1.1 Static IP
If your ISP has provided the fixed IP that allows you to access Internet, please choose this
option.
IP Address: the IP address provided by your ISP.
Subnet Mask: This is used to define the device IP classification for the chosen IP address
range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical net mask value for Class C networks. Generally it is
provided by your ISP.
Default Gateway: This is the IP address of the host router that resides on the external
network and provides the point of connection to the next hop towards the Internet. This can
be a DSL modem, Cable modem, or a WISP gateway router. The router will direct all the
packets to the gateway if the destination host is not within the local network.
MTU: it means Max Transmit Unit for packet. When using slow links, large packets can
cause some delays thereby increasing lag and latency.
DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet “phone book”, which translates
domain names to IP addresses. These fields identify the server IP addresses where the
DNS requested are forwarded by this router.
4.5.1.2 DHCP Client
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a local area network protocol. If you

14
choose this mode, you will get a dynamic IP address from your ISP automatically.
Host Name: the name of your computer, online neighbors will identify the computer
according to the name.
MTU: it means Max Transmit Unit for packet. When using slow links, large packets can
cause some delays thereby increasing lag and latency.
DNS: Domain Name System. Every Internet host must have a unique IP address, also they
may have a human-friendly, easy to remember name such as www.yahoo.com. The DNS
server converts the user-friendly name into its equivalent IP address.
4.5.1.3 PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a virtual private and secure connection
between two systems that enables encapsulated data transport. Select PPPoE option if ISP
provides a PPPoE connection. You should enter the following parameters.

15
User Name/Password: enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
Service Name (AC): this is optional. It describes the service name your ISP provided to
you. Generally, leaving these fields blank will work.
DNS: Domain Name System. If you select Set DNS Manually, you will have to type in the
DNS address by yourself. It is chosen to Attain DNS by default.
Connection Type: provides three modes to connect to the Internet.
zContinuous: the connection can be re-established automatically.
zConnection on demand: the Internet connection can be terminated automatically after
a specified inactivity period (idle time).
zManual: you can click Connect or Disconnect button to connect/disconnect
immediately.
Idle Time: it is a term which generally refers to a lack of motion or energy.
MTU: it means Max Transmit Unit for packet. When using slow links, large packets can
cause some delays thereby increasing lag and latency.
4.5.2 LAN Interface
Local Area Network (LAN) is a group of subnets regulated and ruled by router. The design
of network structure is related to what type of public IP addresses coming from your ISP.
This part allows you to configure the parameters for LAN which connects to the LAN port of
your Access Point.

16
IP Address: This is the IP addresses to be represented by the LAN (including WLAN)
interface that is connected to the internal network. This IP will be used for the routing of the
internal network (it will be the Gateway IP for all the devices connected on the internal
network).
Subnet Mask: This is used to define the device IP classification for the chosen IP address
range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical netmask value for Class C networks which support IP
address range from 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. Class C network netmask uses 24 bits to
identify the network and 8 bits to identify the host.
Default Gateway: This is the IP address of the host router that resides on the external
network and provides the point of connection to the next hop towards the Internet. This can
be a DSL modem, Cable modem, or a WISP gateway router. The router will direct all the
packets to the gateway if the destination host is not within the local network.
DHCP: You can disable or enable DHCP Server here.
DHCP Client Range: the range of IP addresses that will be assigned to each computer
connected with the router.
DHCP Lease Time: the IP addresses given out by the DHCP server will only be valid for
the duration specified by the lease time. Increasing the time ensure client operation without
interrupt, but could introduce potential conflicts. Lowering the lease time will avoid potential
address conflicts, but might cause more slight interruptions to the client while it will acquire
new IP addresses from the DHCP server. The time is expressed in seconds.
Domain name: this represents the name of your IP address.
Active DHCP Client Table: the table will list the detailed information of your users.

17
4.5.3 Static DHCP Settings
It allows you to reserve IP addresses and assign the same IP address to the network device
with the specified MAC address any time it requests an IP address.
4.5.4 VLAN Settings
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) provides you a very convenient way to manage hosts
by grouping them based on the physical port. You can also manage the in/out rate of each
port. VLANs are created to provide the segmentation services traditionally provided by
routers.
Advanced Settings: this option enables VLAN function.

18
Ethernet/Wireless: specifies the WAN port and wireless AP.
WAN/LAN: defines the WAN port or LAN port.
Forwarding Rule: VLAN feature also support forwarding rule as bridge and NAT between
LAN port and WAN port.
Tag: The router will add specific VLAN number to all packets on the LAN while sending
them out. If enable the function of VLAN with tag, please type the tag value and specify the
priority for the packets sending by LAN.
VID: type the value as Port-base VLAN ID.
Priority: Type the packet priority number for such VLAN. The range is from 0 to 7.
CFI: enable the CFI function which indicates whether MAC is encapsulated by standard
format.
After the VLAN settings, please click Apply to finish Network Settings.
4.6 Wireless Setting
4.6.1 Wireless Status
This page displays the current wireless status of the router.
4.6.2 Wireless AP
This page allows you to setup wireless encryption to protect your wireless network from

19
unauthorized access.
Encryption: This router supports WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA-Mixed security options. Please
select one according to the Access Point security policy.
1) WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard and uses the RC4
encryption algorithm. Enabling WEP allows you to increase security by encryption data
being transferred over your wireless network. WEP is the oldest security algorithm, and
there are few applications that can decrypt the WEP key in less than 10 minutes.
Key Length: 64-bit/128-bit, by default it is 64-bit.
64-bit—For 64 bits WEP key, either 5 ASCII characters, such as 12345 (or 10
hexadecimal digitals leading by 0x, such as 0x414234445.)
128-bit—For 128 bits WEP key, either 13 ASCII characters, such as ABCDEFGHIJKLM
(or 26 hexadecimal digits leading by 0x, such as 0x4142434445464748494A4B4C4D).
Key Format: If you choose 64 bit, there will be two Key Formats selectable: ASCII (5
characters) and Hex (10 characters). If 128-bit, the Key Formats should comply with ASCII
(13 characters) or Hex (26 characters)
Table of contents
Other Toto Link Wireless Router manuals

Toto Link
Toto Link A2004NS User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link N300RH User manual
Toto Link
Toto Link G150R User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link N300RH User manual
Toto Link
Toto Link N302R Plus User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link N200RE User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link Wireless-N Broadband Router User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link N300RH User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link N300RU User manual

Toto Link
Toto Link N600R User manual