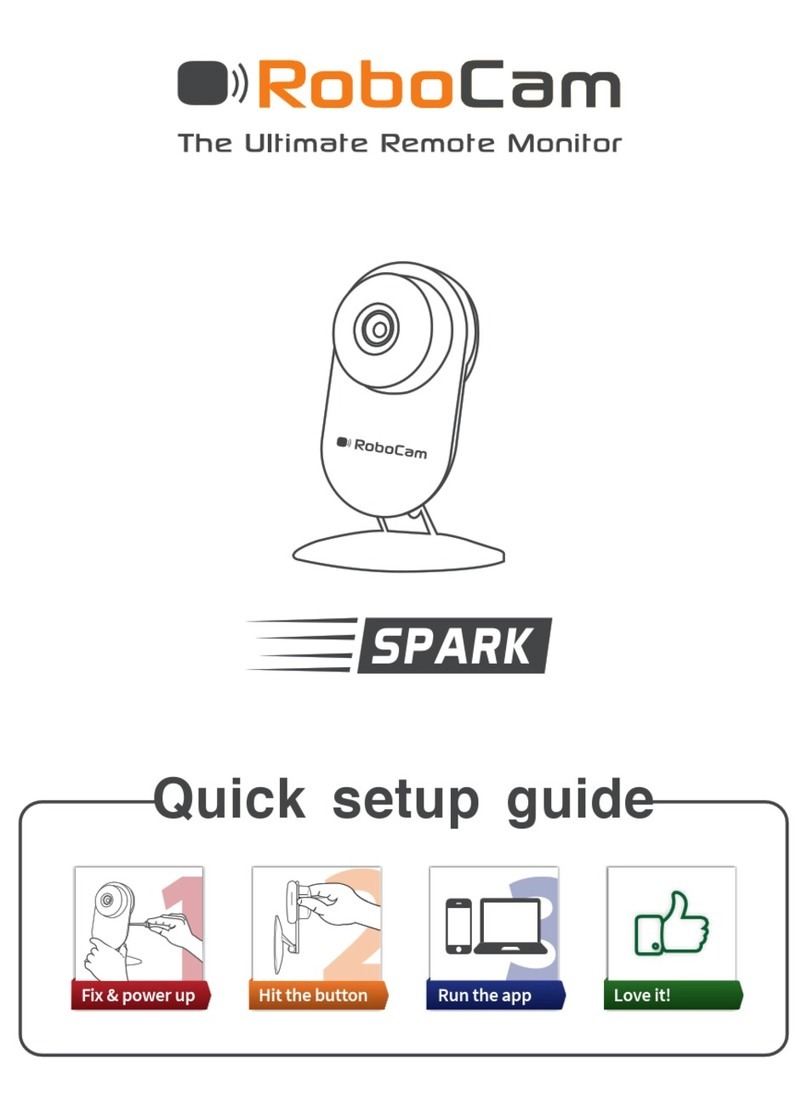
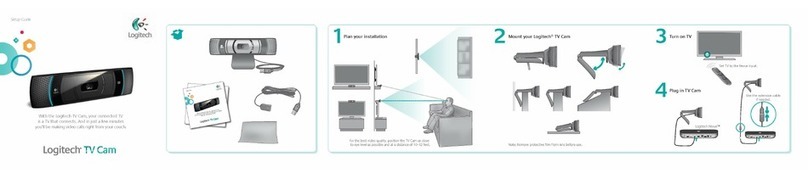
TRENDnet TV-PC301 User manual
Other TRENDnet Webcam manuals

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-IP762IC User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-PC350 User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-PC301 User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-PC100 User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-PC100 User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-PC350 User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-IP672WI User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-IP100 - DATA SHEETS User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-IP201W User manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TV-IP100 - DATA SHEETS User manual