How to avoid trouble | 9
Flow rates
Outgassing from soil sample
Temperature influences
Ion specification
Outgassing from water
Water discharge
Different ion composition and concen-
tration of water and soil affect the
value of the measured conductivity.
Make sure the ion composition and con-
centration of water and soil are similar.
If necessary adjust by adding CaCl2.
High flow rates erode the soil sample
and lead to wrong measuring results.
Air bubbles outgassing from the sample
reduce the conductivity.
Extremely high flow rates cause turbulent
flow and invalidate the methodology.
Keep the flow rates as low as possible.
The scientific literature recommends
an initial water column of 5 cm (2 in).
Soil samples can pass air bubbles that
form a film between the porous plate
and the soil sample. They reduce the
value of the measured conductivity.
Use degassed water. Saturate the soil
sample in vacuum.
A temperature raise reduces the viscosity
of the measuring fluid.
E. g. increasing temperature from 20 to
23° C (68 to 73.4 F) causes a 18% change
of the measuring result.
Measuring device, environment and
water should have the same temperature.
Keep the temperature of your lab constant.
Dissolved gases outgas and form a
bubble film between the porous plate
and the soil sample. They reduce the
value of the measured conductivity.
Use degassed water
(Boiling before measuring is ok).
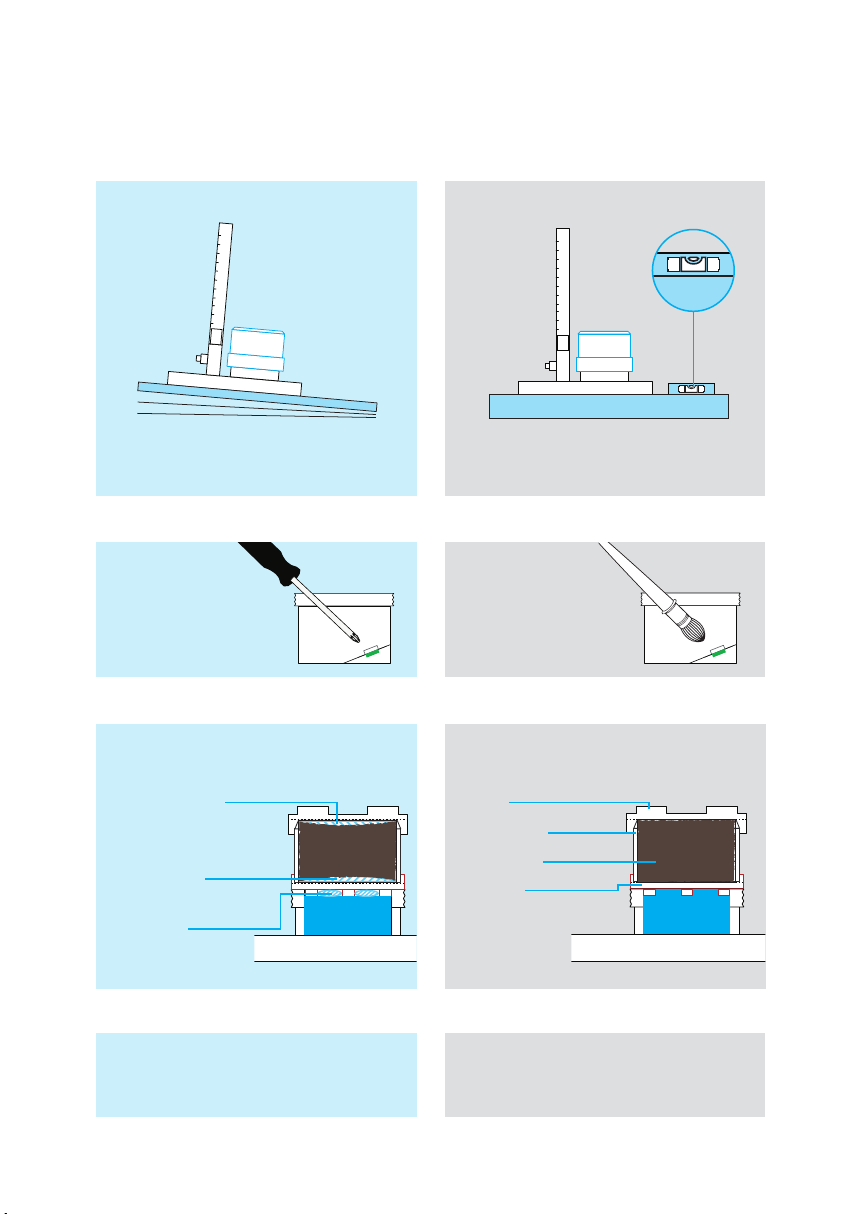
Eroded particles from instable materials
like sand may plug the discharge
channel of the device.
Clean the measuring dome, remove
particles and rinse thoroughly.