SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
6
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
RANGE OF APPLICATIONS
Generally, the power rating of an electrical appliance
indicates the amount of work that can be done by it.
The electric power required for operating an electrical
appliance is not always equal to the output wattage of
the appliance. The electrical appliances generally have a
label showing their rated voltage, frequency, and power
consumption (input wattage). The power consumption of
an electrical appliance is the power necessary for using
it. When using a generator for operating an electrical
appliance, the power factor and starting wattage must
be taken into consideration.
In order to determine the right size generator, it is
necessary to add the total wattage of all appliances to
be connected to the unit.
Refer to the followings to calculate the power consumption
of each appliance or equipment by its type.
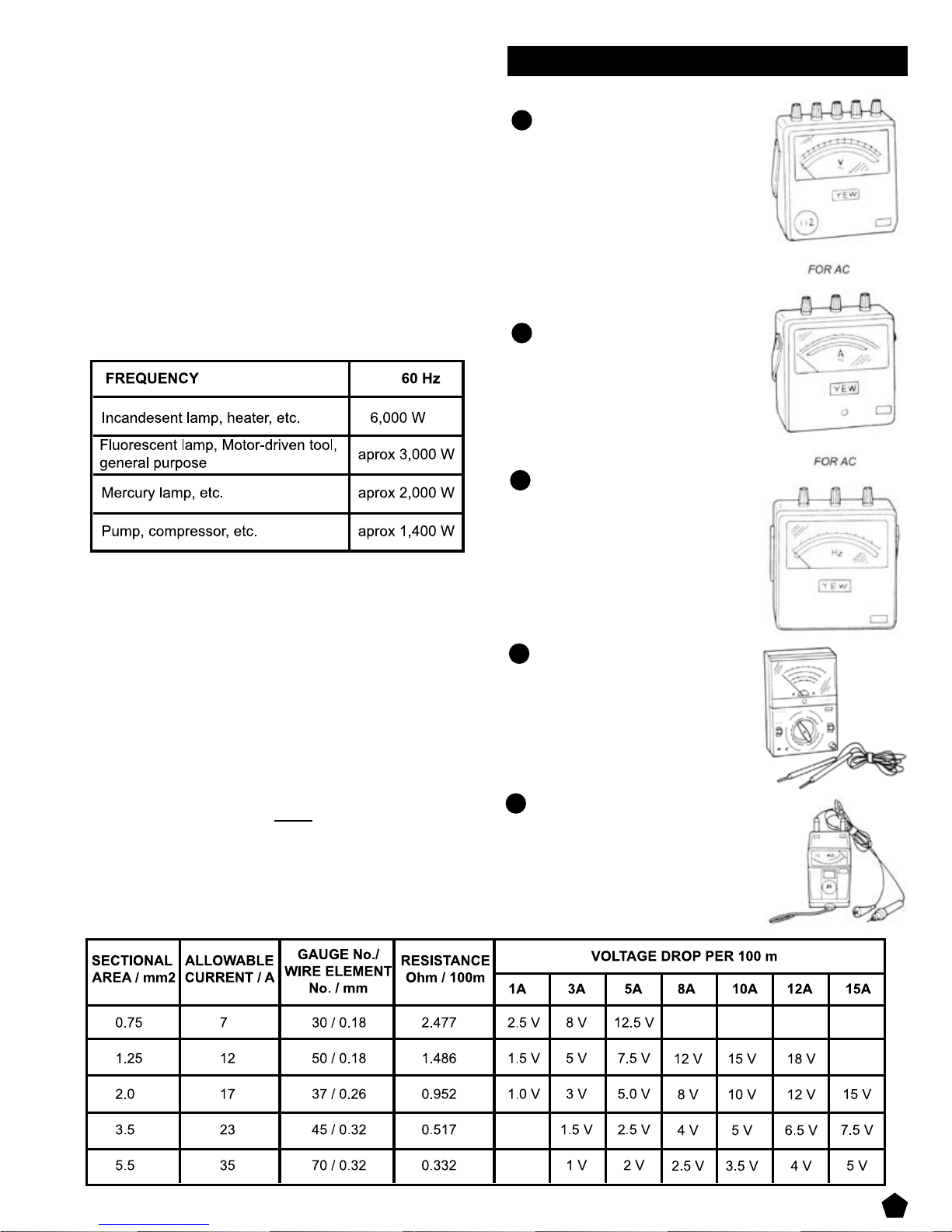
Incandescent lamp, heater, etc. with a power factor
of 1.0
Total power consumption must be equal to or less than
the rated output of the generator.
Example: A rated 3000W generator can turn on thirty
100W incandescent lamps.
Fluorescent lamps, motor driven tools, light electrical
appliances, etc. with a smaller power factor
Select a generator with a rated output equivalent to
1.2 to 2 times of the power consumption of the load.
Generally the starting wattage of motor driven tools and
light electrical appliances are 1.2 to 3 times lager than
their running wattage.
Example: A rated 250 W electric drill requires a 400 W
generator to start it.
NOTE 1: If a power factor correction capacitor is not
applied to the fluorescent lamp, the more
power shall be required to drive the lamps.
NOTE 2: Nominal wattage of the fluorescent lamp
generally indicates the output wattage of the lamp.
Therefore, if the fluorescent lamp has no special
indication as to the power consumption,
efficiency should be taken into account as explained in
ltem (5) on the following page.
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
5
2
3
4
Appliances without any indication as to power
consumption
Some appliances have no indication as to power
consumption; but instead the work load (output) is
indicated. In such a case, power consumption is to
be worked out according to the numerical formula
mentioned below.
= (Power consumption)
(Output of electrical appliance)
(Efficiency)
Use extreme caution near fuel. A constant danger of
explosion of fire exist.
Do not fill fuel tank while the engine is running. Do not
smoke or use open flame near the fuel tank. Be careful
not to spill fuel when refueling. If split, wipe it and let dry
before starting the engine.
Do not place inflammable materials near the
generator.
Be careful not to put fuel matches, gunpowder, oily cloth,
straw, and any other inflammables near the generator.
Do not operate the generator in a room, cave or
tunnel. Always operate in a well-ventilated area
Otherwise the engine may overheat and also, the
poisonous carbon monoxide contained in the exhaust
gases will endanger human lives. Keep the generator
at least 1 m (4 feet) away from structures or facilities
during use.
Operate the generator on a level surface.
If the generator is tilted or moved during use, there is a
danger of fuel spillage and a chance that the generator
may tip over.
Do not operate with wet hands or in the rain.
Severe electric shock may occur. If the generator is
wet by rain or snow, wipe it and thoroughly dry it before
starting. Don`t pour water over the generator directly
nor wash it with water. If the generator is wet with water,
the insulations will be adversely affected and may cause
current leakage and electric shock.
Do not connect the generator to the commercial
power lines.
This may cause a short-circuit or damage to the
generator. Use a transfer switch (optional parts) for
connecting with indoor wiring.
Be sure to check and remedy the cause of circuit
breaker tripping before resetting it on.
CAUTION: If the circuit breaker tripped off as a
result of using an electrical appliance, the cause can
be an overload or a short-circuit. In such a case,
stop operation immediately and carefully check the
electrical appliance and AC plugs for faulty wiring.
Mercury lamps with a smaller power factor
Loads for mercury lamps require 2 to 3 times the
indicated wattage during start-up.
Example : A 400 W mercury lamp requires 800 W to
1200 W power source to be turned on. A rated 3000
W generator can power two or three 400 W mercury
lamps.
Initially loaded motor driven appliances such as
water pumps, compressors, etc.
These appliances require large starting wattage which
is 3 to 5 times of running wattage.
Example : A rated 900 W compressor requires a 4500
W generator to drive it.
NOTE 1: Motor-driven appliances require the above
mentioned generator output only at the starting. Once
their motors are started, the appliances consume about
1.2 to 2 times their rated power consumption so that the
excess power generated by the generator can be used
for other electrical appliances.
NOTE 2 : Motor-driven appliances mentioned in items
(3) and (4) vary in their required motor
starting power depending on the kind of motor and
start-up load. If it is difficult to determine the optimum
generator capacity, select a generator with a larger
capacity.