10
Note: A Test program can be downloaded from our web site.
The source code (VB) is also available. (English only)
1) Instructions for software design :
As the instructions consist of a string of ASCII characters, it is easy to design
software which transmits the instructions via the serial port of the PC.
Port settings are: 2400/8/N/1
For wired operation, the instruction sequence needs to be sent at least twice.
For wireless operation, we recommend to send the instruction string at least 5
times in a row to ensure proper reception under all conditions. For improved
reliability, add a pause of a least 300ms between two different instructions.
Please note that environmental conditions can interfere with the signal.
Therefore, the unit is not suited for use as or as part of any kind of equipment
which might cause harm to people or property if a malfunction should occur.
2) Instruction sequence :
To execute a command, the correct sequence needs to be sent to the K8056.
Basically, a command sequence looks like this :
1. CHR$(13)
2. card address (1..255)
3. instruction
4. address (1..255) or relay# ('1'..'9' ASCII)
5. checksum (2-complement of the sum of the 4 previous bytes + 1)
3) Instructions :
'E' : Emergency stop all cards, regardless of address. Carefull, relays turned
on by open collector inputs will not be turned off by this command).
'D' : Display address. All cards show their current address in a binary fashion.
(LD1 : MSB , LD8 : LSB)
'S' : Set a relay. 'S'-instruction should be followed by relay # '1' to '8'.
('9' sets all relays at once).
'C' : Clear a relay. 'C'-instruction should be followed by a relay # '1' to '8'.
('9' clears all relays at once.)
'T' : Toggle a relay. 'T'-instruction should be followed by a relay # '1' to '8'.
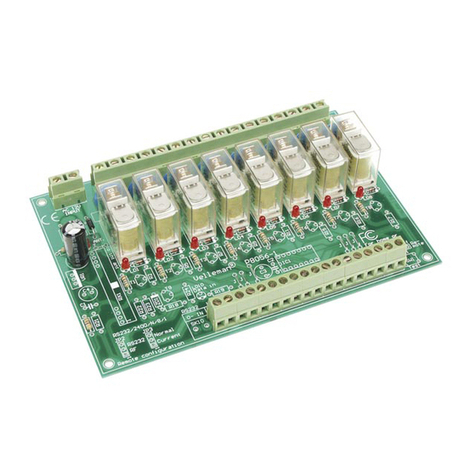
20. Addressing the K8056 card through RS232 commands.
Addressing