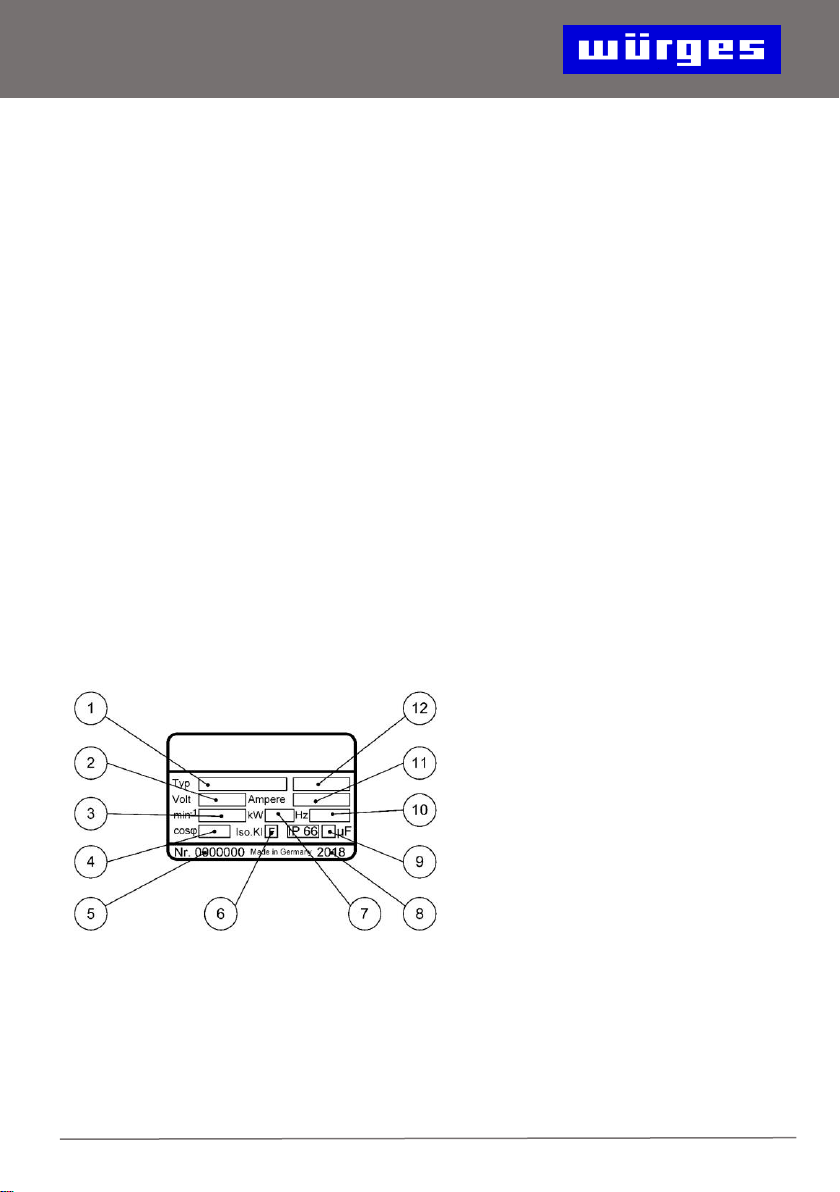
9
4.3. Design and Function
The electric drive of the series is an asynchronous motor.
The exception is the type HV 2 GL, where it is driven by a permanent magnet-
excited direct current motor with carbon brushes.
There are eccentric unbalance discs on the two shaft ends of the motor.
This is understood to mean a rotating body, the mass of which is not distributed
rotationally symmetrically, and which thus generates vibration.
This vibration can be dosed by adjusting the weights.
You can find construction details from p. 25.
4.4. Further Technical Features
Voltage 3 ~ 230 / 400V 50Hz, 1 ~ 230V 50Hz
Special voltages from 3 ~ 42V - 3 ~ 700V 50Hz, 60Hz and 200Hz are available.
Special designs with PTC thermistors (standard for HV 75 - HV 200), anti-
condensation heating available
2-, 4-, 6, - and 8-pole versions (10- and 12-pole on request)
Low power consumption with high starting torque
The windings of sizes HV 1 & HV 2 are completely encapsulated with the housing
under vacuum. In the other sizes, the complete vibration-proof winding is vacuum
impregnated twice with special resin, not just the winding head.
All windings are equipped with phase insulation, so operation on frequency
converters is possible without hesitation.
Each winding is checked twice in our factory: 1.) after delivery and 2.) after
installation in the motor.
Tropical insulation as standard
Insulation class F (155 ° C), on request insulation class H (180 ° C)
Ambient temperature -20 ° C to + 40 ° C, with some types up to + 55 ° C