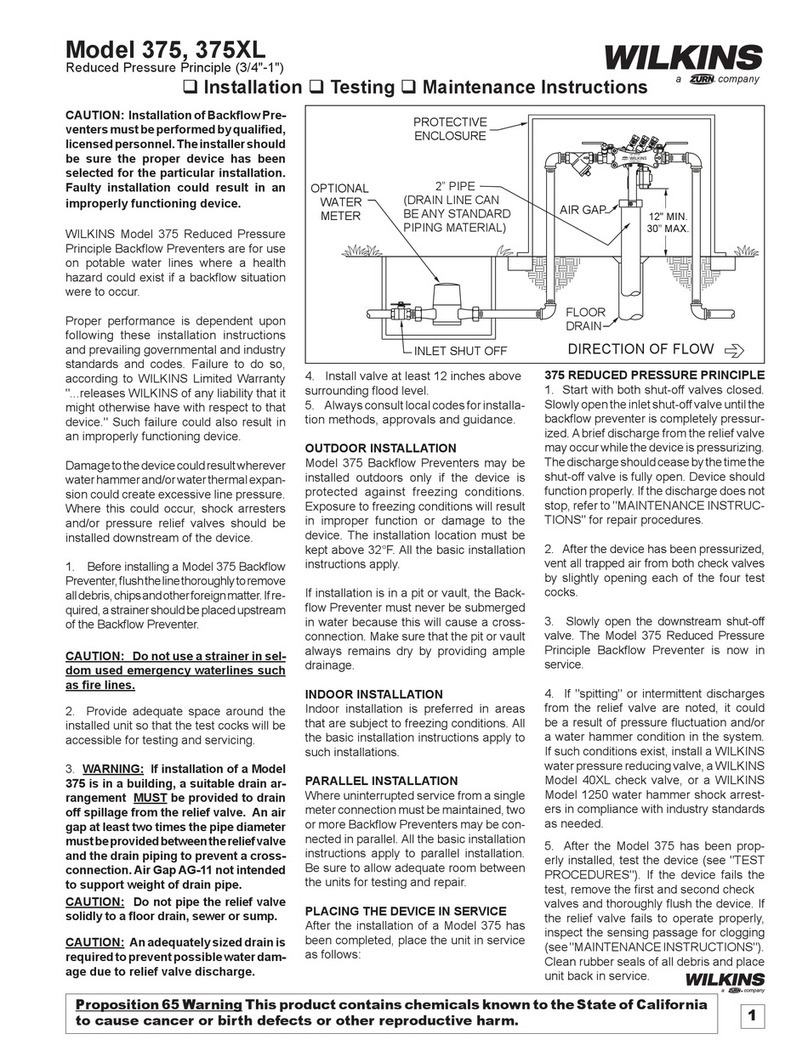
WILKINS, a ZURN company
1747 Commerce Way, Paso Robles, CA 93446 Phone:805-238-7100 Fax:805-238-5766
3
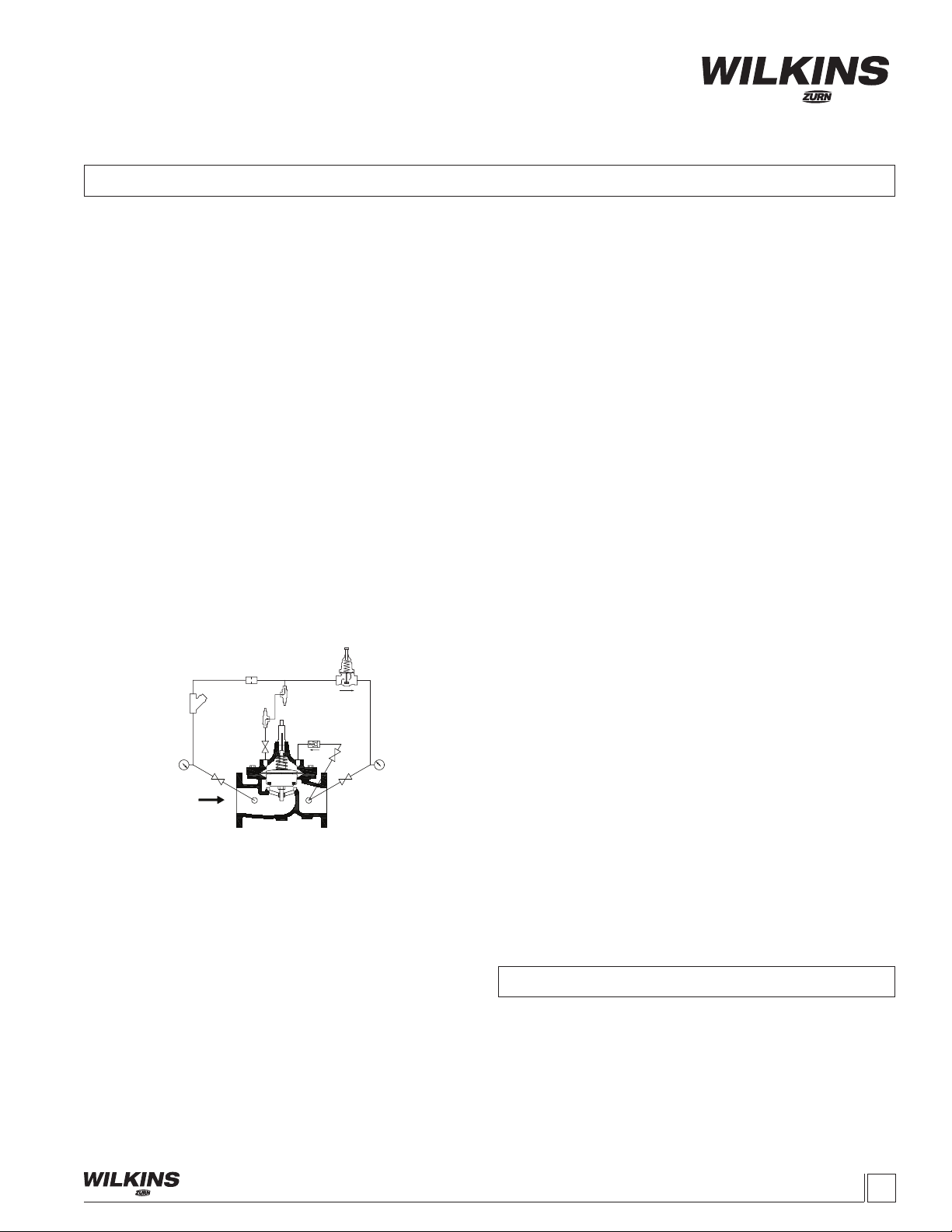
DIAPHRAGM MOVEMENT CHECK
1. The diaphragm movement check can be determined during
the diaphragm check or it can It can also be performed with the
use of a valve position indicator model ZPI.
2. Replace cover plug and open pilot ball valves on inlet and cover.
3.Closingtheoutletisolationballvalveswilldirecttheowto
the cover causing it to close. NOTE: Slow or delayed closing
of main valve is normal and is due to the time requirements
to ll, pressurize cover, and stretch the diaphragm into the
closed position. This normal delay is not mechanical bind-
ing of the valve assembly.
4. Using the valve position indicator, make note of the closed
position on the indicator. Compare distance of the open mark to
the close mark and compare to Table 3.
5. Verify that the main valve is closed, by opening a down-
stream source (not the outlet isolation ball valve on the main
body).Ifwatercontinuouslyows,thenthemainvalveisnot
sealing properly. Double check the valve movement matches
the values in Table 3 and refer to the disassembly procedures
section if it does not. This is an indication that the main valve
is not sealing due to an obstruction between the seat and
thesealoradamagedseal.Ifwaterdoesstopowingand
the measured valve movement does not match Table 3, then
there is possible damage under the cover. Remove cover to
identify obstruction and replace parts as necessary
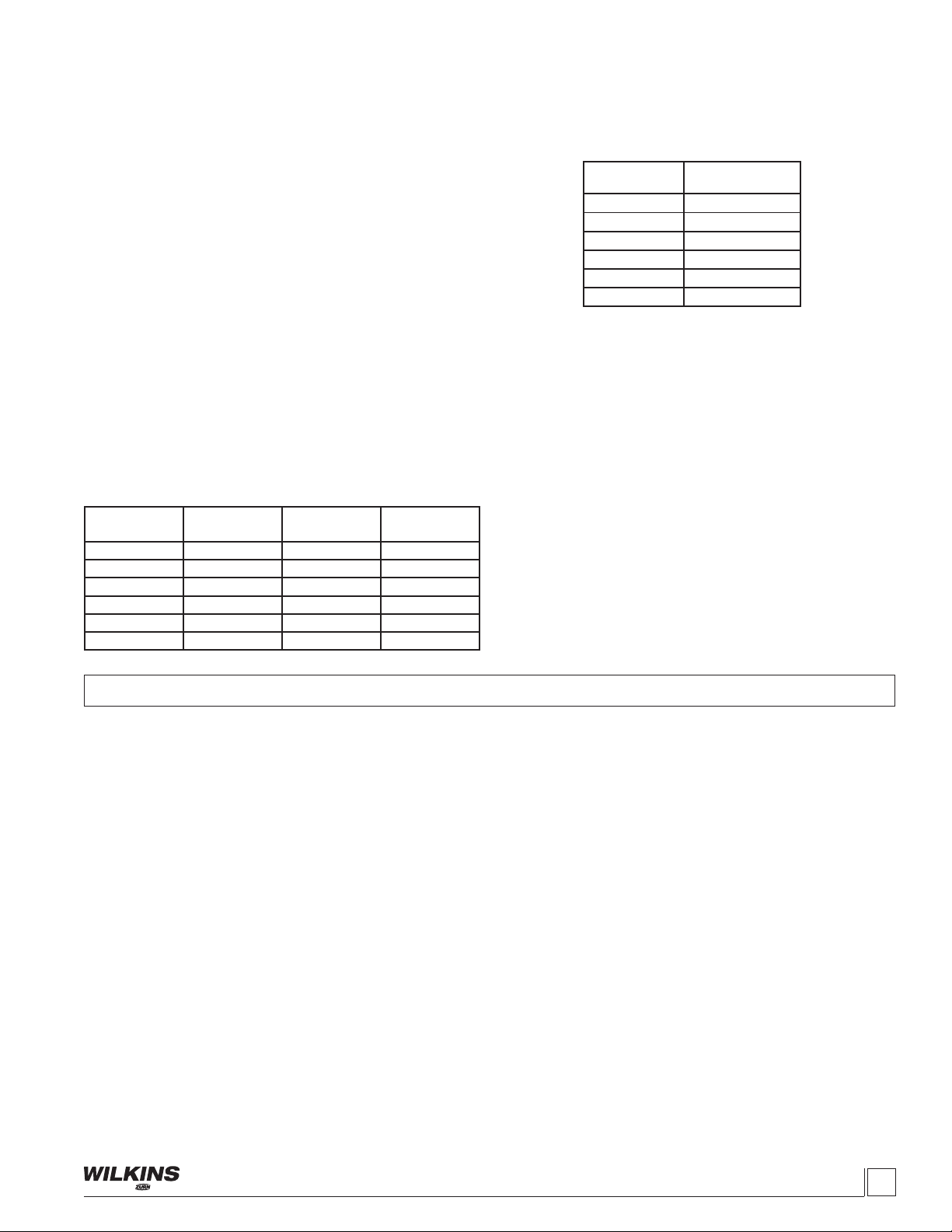
TABLE 3. VALVE STEM TRAVEL
VALVE SIZE
(in)
VALVE SIZE
(mm)
STEM TRAVEL
(in)
STEM TRAVEL
(mm)
2" 50 0.7 18.0
2-1/2" 65 0.8 21.3
3" 80 0.9 23.4
4" 100 1.1 28.8
6" 150 1.7 43.4
8" 200 2.4 59.7
6. For smaller valves (6” and below) diaphragm checks can
be performed by hand with the use of a valve stem tool. The
valve stem tool can be made using Table 4 to create a “T” bar
handle with the appropriate threads on the opposite end of the
“T” handle.
TABLE 4. VALVE STEM THREAD SIZE
VALVE SIZE
(in)
THREAD SIZE
UNF INTERNAL
2" 10 - 32
2-1/2" 10 - 32
3" 1/4 - 20
4" 1/4 - 20
6" 3/8 - 20
8" 3/8 -16
7. To perform the diaphragm check using the vale stem tool,
rstremoveallpressureinthesystemandventthecover.
Then remove the center plug on the cover and insert tool into
the top of the stem threads. Once the tool is inserted, the
valve can be lifted up and the valve movement can be mea-
sured by creating marks on the tool in the opened and closed
positions. The distance between marks is the valve stem
travel. Replace or repair any parts as necessary.
SEAL CHECK
1. To check the seal of the valve disc, an additional pressure
gauge will be needed downstream of main valve.
2.Withthevalveowing,slowly,closepilotoutletballvalves
to apply pressure to cover and allow to close.
3. Open downstream source and monitor the pressure on the
inlet and installed outlet gauge, for one min. The pressure on
the outlet side should remain zero. If the pressure matches inlet
pressure or increases, the main valve is leaking or the outlet
ball valve on the pilot system is allowing pressure to creep by.
Either way it is recommended that the valve be disassembled
and inspected (refer to “Disassembly” section).
Maintenance Instructions
PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
The Zurn Wilkins ZW200 models require minimal maintenance.
However, it is highly recommended to schedule annual inspec-
tions and to have a repair kit on hand before work begins.
DISASSEMBLY
Warning: Because of the ability to perform inspections and
maintenance without removal from the system, it is very
important that all shut off valves be closed and all pressure
relieved in the valve before beginning disassembly. Failure
to do so can result in personnel injury or equipment damage.
1. Verify that all pressure sources are closed up and down-
stream of valve.
2.Removepressureinpilotsystembylooseningthetubet-
tings to the valve body and cover. When all pressure has been
vented, continue to disassemble the pilot control valve and
cover tubing. NOTE: Taking a picture before tear down can help
with re-assembly of pilot system.
3. Next remove the cover by loosening and removing the
cover bolts. If the cover does not come off easily it may be nec-
essary to loosen the cover using a brass chisel and rubber mal-
let. Apply the chisel under the cover pointing upward away from
valve body and tap bottom of cover with the chisel and mallet to
loosen the cover. Once the cover is loose, pull cover straight up
to avoid damaging the stem and stem bearing in the cover. On
larger valves 8” and up, eye bolts and a hoist are recommended
due to the weight of these larger covers.
4. With the cover removed the diaphragm assembly can be
removed. To avoid damaging the seat bushing, grab the stem
and lift straight up. For larger valves 8” and up it is recommended
that an eye bolt with the proper stem threads be used with a
hoist to lift the assembly out of the valve (see Table 4 for ap-
propriate stem threads).
5. Next it is recommended that the diaphragm assembly be
placed in a vise with the bottom hex nut secured. Once secured
remove the spring and stem nut. While removing the nut inspect
the stem threads. Clean stem with a wire brush if mineral de-
posits or corrosion are present.
6. After inspecting the stem and removing the nut the diaphragm
assembly can be dismantled. If the valve has not been serviced
in awhile it is possible that the assembly will require the use of a
rubber mallet or pry bars to dismantle the assembly. If this is the
case gently tap or pry the components until the components are
free to move. When disassembling be sure to clean, inspect, and
save all components. Replace any damaged components as
necessary.
7. The last component to inspect is the seat which is in the body
of the main valve. During inspection of the seat, clean and polish
asnecessarywithnegritwet/drysandpaper(400gritorhigher).
Typically, if after cleaning there is no visual damage or excessive
wear the seat should not require removal. If damage is present
or the seat is excessively worn the seat should be replaced.