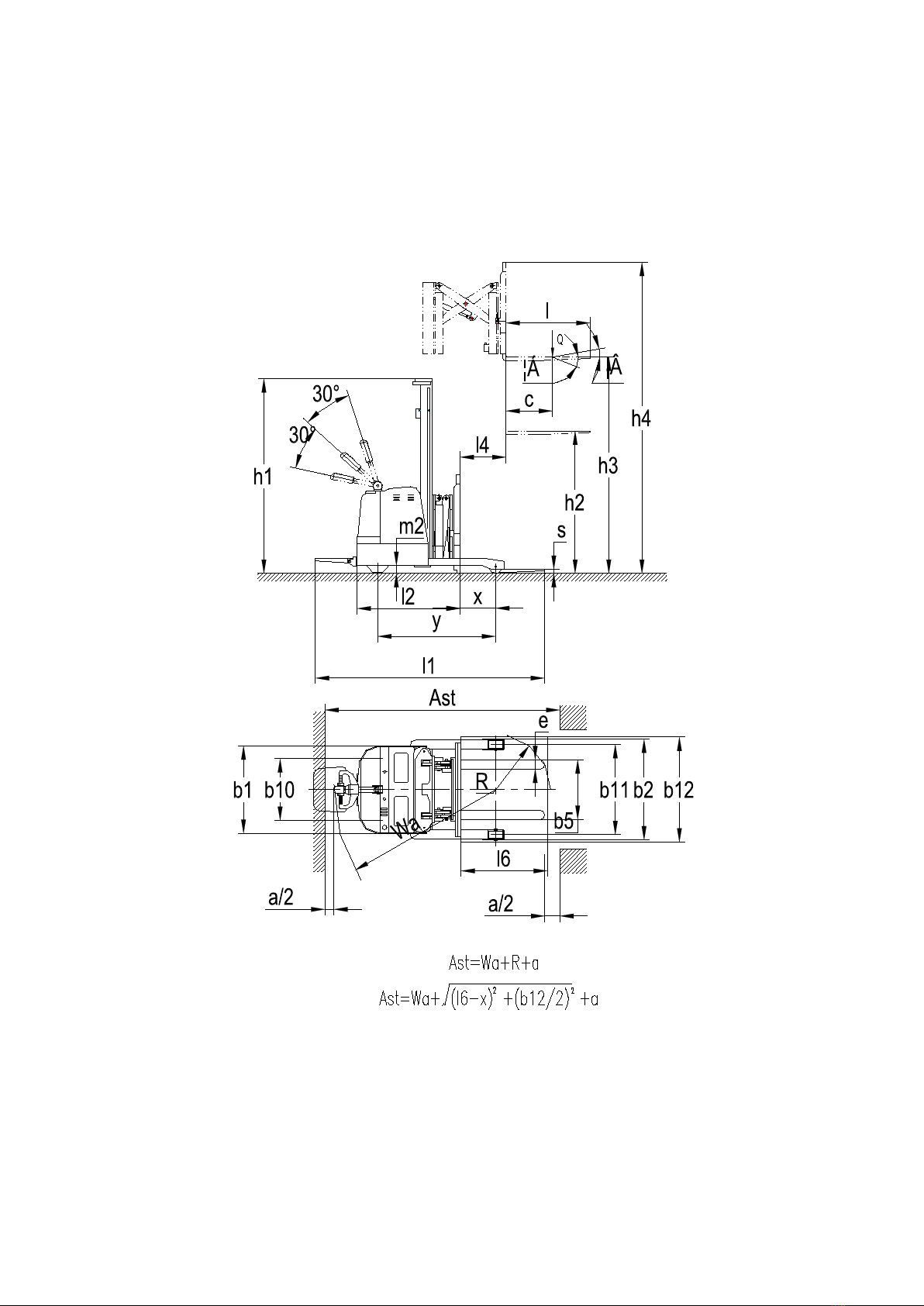
5.2.2 Operation of handling and stacking
As indicated in Fig. I, pull out the general power supply switch, unlock the electric door lock, and drive the stacker to
goods pile nearby (the tip of the fork is 30cm from the goods pile). Turn lifting-lowering handle of multi-way valve so
as to adjust the height of the fork to a proper position; turn fork reach handle to insert the fork slowly and as deep
as possible into the goods pallet. Turn the lifting-lowering handle of multi-way valve to lift the fork until it is 20-30cm
from the ground. Turn extension handle of multi-way valve to return the fork. Drive the truck to the location of the
goods shelf and slowly stop until the tip of the fork (or the front end of goods) is 20cm from the goods shelf. Turn
lifting-lowering handle until the fork rises to a proper height of the shelf (The bottom of the pallet is about 10cm
higher than the shelf). Move the goods slowly to the accurate position of the shelf and turn fork reach handle to
move the fork forward slowly to a proper position. Turn lowering handle of multi-way valve to put the goods
carefully on the shelf. Turn extension handle of multi-way valve to return the fork inside the truck to lower the fork
until it is about 30mm from the ground to drive the stacker away from the goods shelf. During operation, please pay
attention to obstacles around and slow down when turning around.
5.2.3 Operation of taking goods down from shelves
As indicated in Fig. I, pull out the general power supply switch, unlock the electric door lock, drive the truck to the
goods shelf nearby (the tip of the fork is 30cm from the goods shelf). Turn lifting-lowering handle of multi-way valve
so as to adjust the height of the fork to a proper position. Turn extension handle of multi-way valve to insert the fork
slowly and as deep as possible into the goods pallet. Turn lifting-lowering handle of multi-way valve to lift the
goods (the bottom of pallet is 10mm from the goods shelf). Turn extension handle of multi-way valve to move the
goods slowly from goods shelf. Turn lifting-lowering handle of multi-way valve to lower the fork until it is 20mm
to 30mm from the ground. Drive the stacker away from the goods shelf until it reaches a desired position and then
slowly stop it. Turn the extension handle of multi-way valve to reach the goods wholly outside the fork leg. Turn the
lifting-lowering handle of multi-way valve to make the fork completely away from the goods. Turn extension handle
of multi-way valve and move the fork slowly out of the goods pallet.
5.3 Abnormal situation handling in operation
5.3.1 When the handle of multi-way valve returns to the middle position from some working position, if it is still during
operation, press down the general power supply switch to cut off the power supply at once. Meanwhile move the
stacker to a safe place and lower the goods manually so as to repair the stacker.
5.3.2 If the brake is out of function when the stacker is in operation, the operation must be stopped at once and repair the
truck.
5.3.3 When the truck is moving backward and pushing the operator against a wall or other objects, press the emergency
reverse button on top of the control handle and the stacker will automatically move forward to avoid injuring the
operator.
5.4 After operation
After operation, the stacker should be parked in a fixed parking position and routine maintenance should be
conducted according to the stipulations in clause 6 and charging should be carried out.
6. Maintenance
Note: It is prohibited for untrained personnel to maintain the truck.
6.1 Whether the truck can operate satisfyingly depends on the efficient maintenance. When maintenance is ignored, the
truck may pose a threat to human lives and cause property damage. Routine inspection should be conducted, when
the truck is in operation, to eliminate abnormal conditions in time. Never use a faulty truck to ensure safety and to
prolong the service life of the stacker.
6.2 Maintenance: The maintenance of the truck is divided into three levels, i.e. routine maintenance, level I
maintenance and level II maintenance.
Routine maintenance: Daily maintenance is to clean the surface of the stacker body and the surface of the
storage battery and to examine the firmness of the power supply line and whether the elasticity of the chain is
normal.
Level I maintenance: Level I maintenance should be performed once every week. Besides what should be done
in daily maintenance, the operation situation of all the parts should be carefully inspected to see whether the
operation is normal; whether there is any loose of the fasteners; whether the elasticity of the chain is appropriate;
whether the connecting pin of the chain connection is bending or twisting; whether the up and down movement of