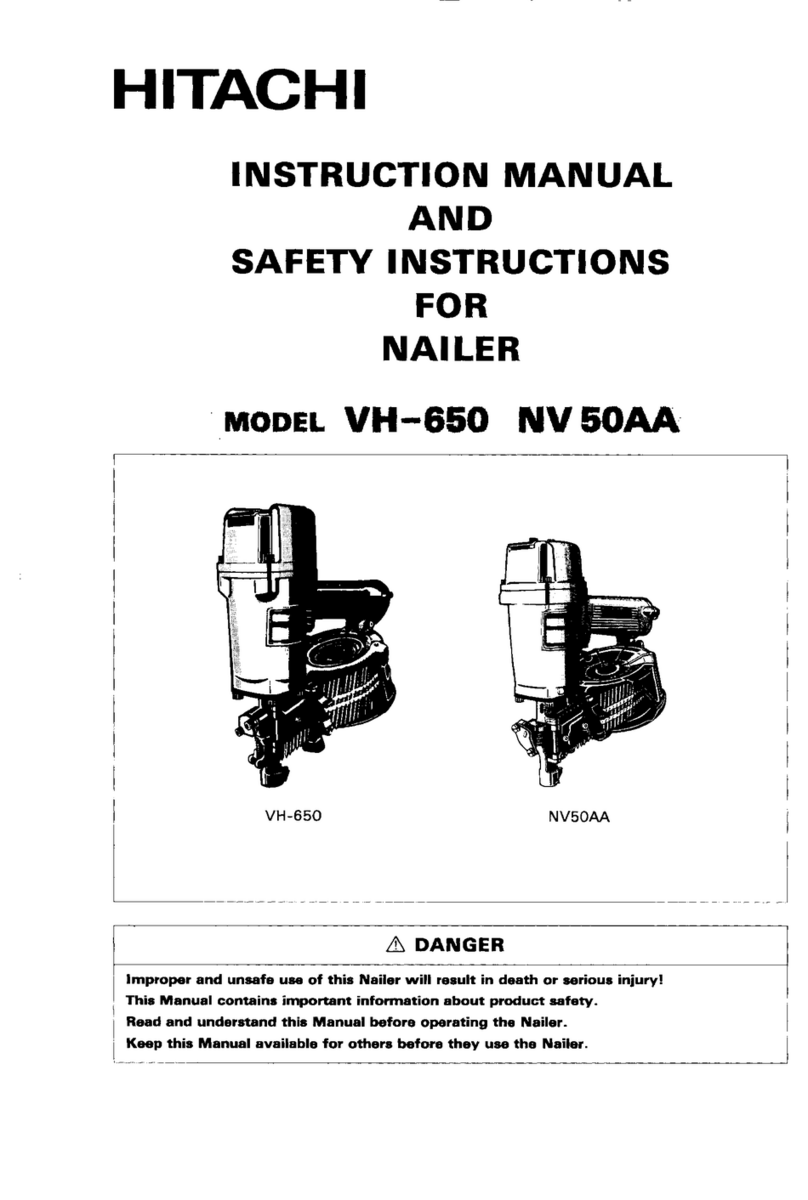
8
INSTRUKCJA ORYGINALNA
Do zasilania narzędzi nie stosowaćtlenu ani innych gazów palnych.
Narzędzia należy podłączaćtylko do takiego układu zasilającego, w którym nie ma możliwości przekroczenia ciśnienia o więcej niż10% wartości maksymalnej. W przypadku
wyższych ciśnieńnależy zastosowaćzawór redukcyjny wraz zainstalowanym za nim zaworem bezpieczeństwa.
Do naprawy narzędzi stosowaćtylko oryginalne części zamienne, podane przez wytwórcęlub jego przedstawiciela. Naprawy powinny byćwykonywane przez specjalistów
upoważnionych przez wytwórcę. UWAGA! Przez specjalistów rozumie sięosoby, które w wyniku szkolenia zawodowego lub doświadczenia posiadajądostatecznąwiedzę
o narzędziach do wbijania elementów złącznych oraz dostatecznąznajomość odpowiednich przepisów bhp, przepisów dotyczących zapobiegania wypadkom, dyrektyw i
ogólnie przyjętych przepisów technicznych (np. norm CEN i CENELEC), aby móc ocenićbezpieczne warunki pracy narzędzi do wbijania elementów złącznych.
Stojaki do podpierania narzędzia mocowane na przykład do stołu roboczego, powinny byćzaprojektowane i wykonane przez wytwórcęstojaka w taki sposób, aby można
było bezpiecznie zamontowaćnarzędzie, odpowiednio do jego przeznaczenia i aby nie dopuścićdo jego uszkodzenia, odkształcenia lub przemieszczenia.
Do konserwacji stosowaćtylko środki smarne wymienione w instrukcji.
Narzędzi do wbijania elementów złącznych z uruchamianiem stykowym lub ciągłym uruchamianiem stykowym, oznakowanych symbolem „Nie stosowaćna rusztowaniach,
drabinach” nie należy stosowaćdo określonych zastosowań. Na przykład, gdy zmiana miejsca wbijania wymaga skorzystania z rusztowań, schodów, drabin lub konstrukcji
podobnych do drabin np. łat dachowych. Do zamykania skrzyńczy klatek. Do mocowania układów bezpieczeństwa transportowego, np. na pojazdach i wagonach.
Podane wartości hałasu sąwartościami charakterystycznymi dla narzędzia i nie dotycząhałasu emitowanego w miejscu zastosowania. Hałas w miejscu zastosowania bę-
dzie zależałnp. od środowiska pracy, obrabianego przedmiotu, podparcia obrabianego przedmiotu. W zależności od warunków na stanowisku pracy i kształtu obrabianego
przedmiotu, może zachodzićpotrzeba zastosowania indywidualnych środków tłumienia hałasu. Takich jak umieszczenie obrabianych przedmiotów na podporach tłumiących
hałas, dociskanie lub przykrywanie obrabianych przedmiotów. Regulacja ciśnienia do minimalnej wartości wystarczającej do wykonania pracy. W specjalnych przypadkach
konieczne jest noszenie ochronników słuchu.
Podane wartości drgańsącharakterystyczne dla narzędzia i nie oznaczająoddziaływania na układ ręka - ramiępodczas używania narzędzia. Każde oddziaływanie na układ
ręka - ramięprzy posługiwaniu sięnarzędziem będzie zależećnp. od siły chwytu, siły docisku, kierunku pracy, wyregulowania zasilania energią, przedmiotu obrabianego
czy podparcia przedmiotu obrabianego.
Przed każdąoperacjąsprawdzić, czy mechanizm bezpiecznika i mechanizm spustowy działająprawidłowo i czy wszystkie śruby i nakrętki sądokręcone.
Nie dokonywaćżadnych zmian w narzędziu bez upoważnienia wytwórcy.
Nie demontowaćżadnych części narzędzia, takich jak bezpiecznik, ani nie spowodować, aby nie działały.
Nie wykonywaćżadnych „nagłych napraw” bez właściwych narzędzi i wyposażenia.
Zaleca się, aby narzędzie przechodziło odpowiedniąkonserwacje, w regularnych odstępach czasu zgodnie z instrukcjąwytwórcy.
Unikaćosłabienia lub uszkodzenia narzędzia, na przykład przez: dziurkowanie lub grawerowanie, wprowadzanie zmian nie zatwierdzonych przez wytwórcę, prowadzenie
po szablonach z twardego materiału, np. stali, upuszczanie lub popychanie po podłodze, używanie urządzenia w charakterze młotka, przykładanie nadmiernej siły jakie-
gokolwiek rodzaju.
Nigdy nie należy kierowaćdziałającego narzędzia w kierunku swoim ani innej osoby.
W czasie pracy narzędzie trzymaćw taki sposób, aby nie dopuścićdo możliwości obrażeńgłowy lub ciała w przypadku ewentualnego odskoku, powodowanego zakłóce-
niami w zasilaniu energiąlub twardymi przestrzeniami wewnątrz obrabianego przedmiotu.
Nigdy nie uruchamiaćnarzędzia w kierunku wolnej przestrzeni. Dzięki temu unika sięzagrożenia powodowanego przez swobodnie latające elementy złączne, a także
zagrożenia wynikającego z nadmiernych naprężeńw narzędziu.
W czasie przenoszenia należy odłączyćnarzędzie od układu zasilającego, szczególnie, gdy konieczne jest skorzystanie z drabin lub przyjęcie nietypowej pozycji przy
poruszaniu się. W miejscu pracy przenosićnarzędzie trzymając je tylko za uchwyt i nigdy z wciśniętym spustem.