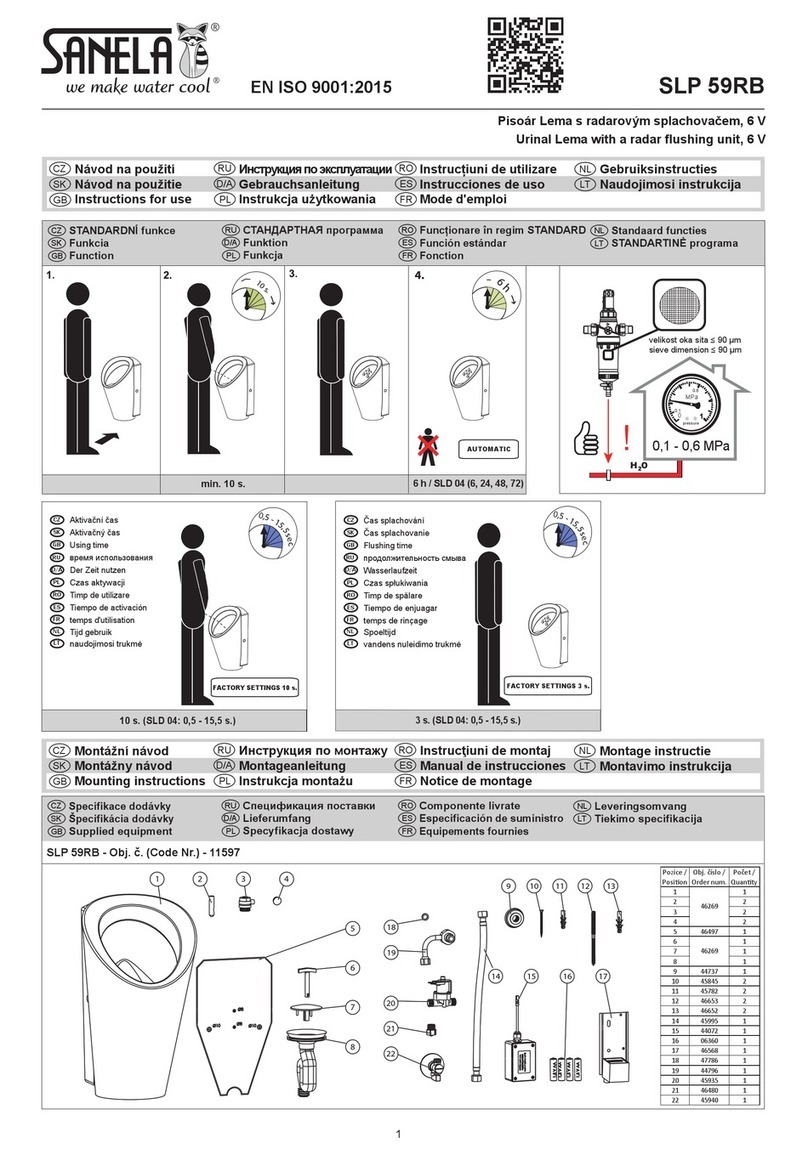
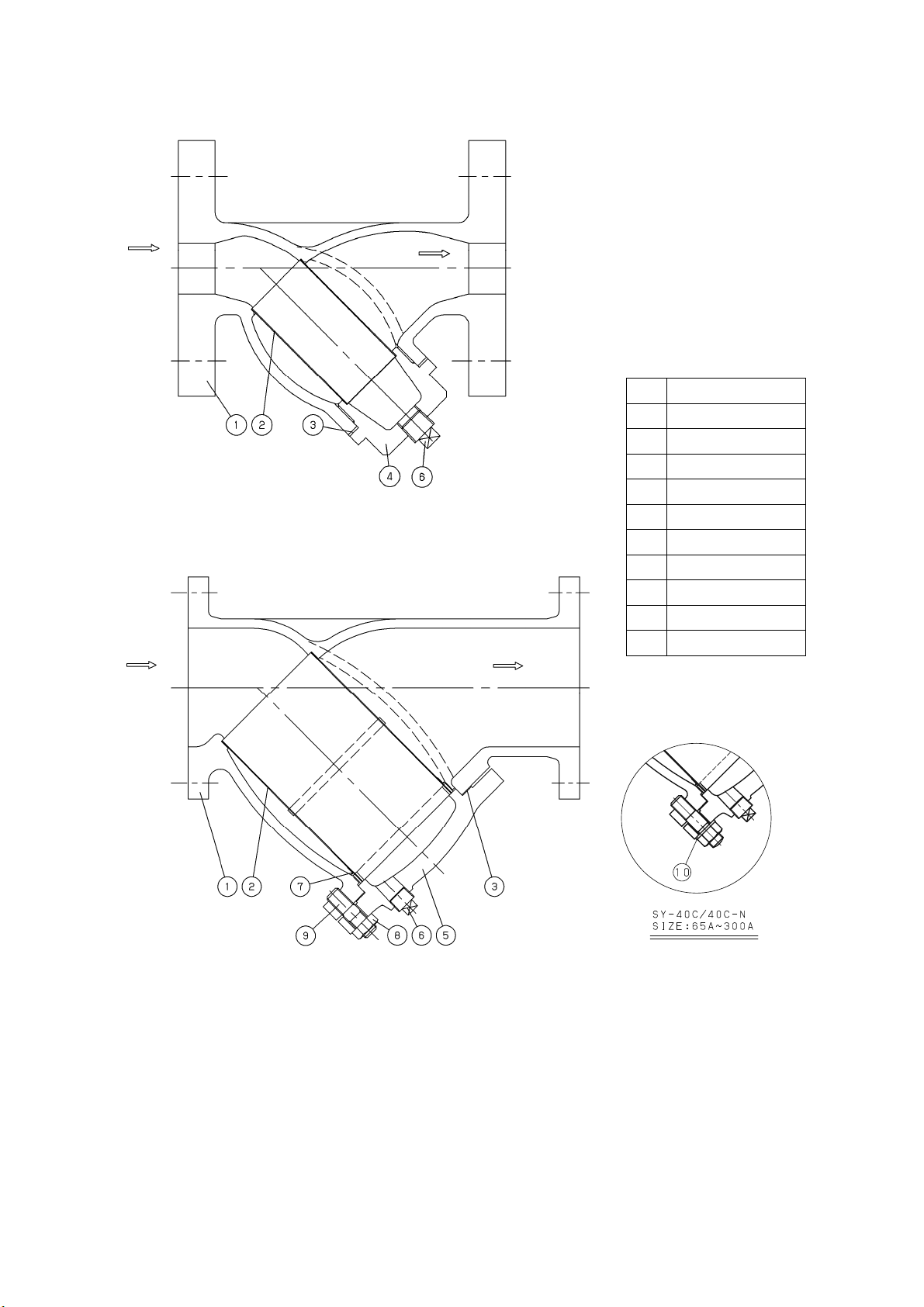
5. Selection of nominal size
To make the best use of the strainer and satisfy the operating requirements to the maximum,
take notice of the following.
The preferred initial pressure loss is 0.02-0.03 MPa.
5.1 Selection of nominal size
Select a nominal size equivalent to that of the pipe (piping nominal size = nominal
size of strainer). Note that the use of a smaller nominal size increases the pressure loss
through the strainer, possibly reducing the machine inlet pressure below the specified limit.
5.2 Selection of piping nominal size
When selecting the piping nominal size, it is necessary to consider the fluid type, maximum
flow rate, permissible pressure loss, piping and equipment cost, etc. With a smaller piping nominal
size, the piping and equipment cost decreases but the pressure loss through the pipe increases to
generate disturbances, possibly resulting in pipe wear, noise and/or vibration. With too large a piping
nominal size, however, not only the piping and equipment cost but also the thermal loss increase. The
standard fluid velocity has been specified in the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) as a guide to
select an appropriate piping nominal size.
<<Standard fluid velocity>>
Fluid Remarks
Standard
flow velocity
Saturated steam
Auxiliary piping for vacuum or small-diameter
piping 15 m/s
(10-20)
Large-diameter piping 30 m/s
(20-40)
Superheated steam Piping diameter: approx. φ75 – φ250 40 m/s
(30-50)
Piping of high-grade material 70 m/s
(65-80)
Inlet of steam coil 0.3-0.7MPa 30 m/s
(25-30)
Air
Higher pressure: 1.0 MPa or more 20 m/s
(20-25)
Lower pressure 15 m/s
( 5-15)
Extremely low pressure: 0.1 MPa or less 10 m/s
( 3-10)
Water or oil 2 m/s
( 2- 4)
* This table shows a standard flow velocity of each type of fluid set based on the
requirements defined in JIS F 7101 (Shipbuilding – Pipes of machinery –
Standard velocity of flow).
- 4 - ■EPDT-167b■