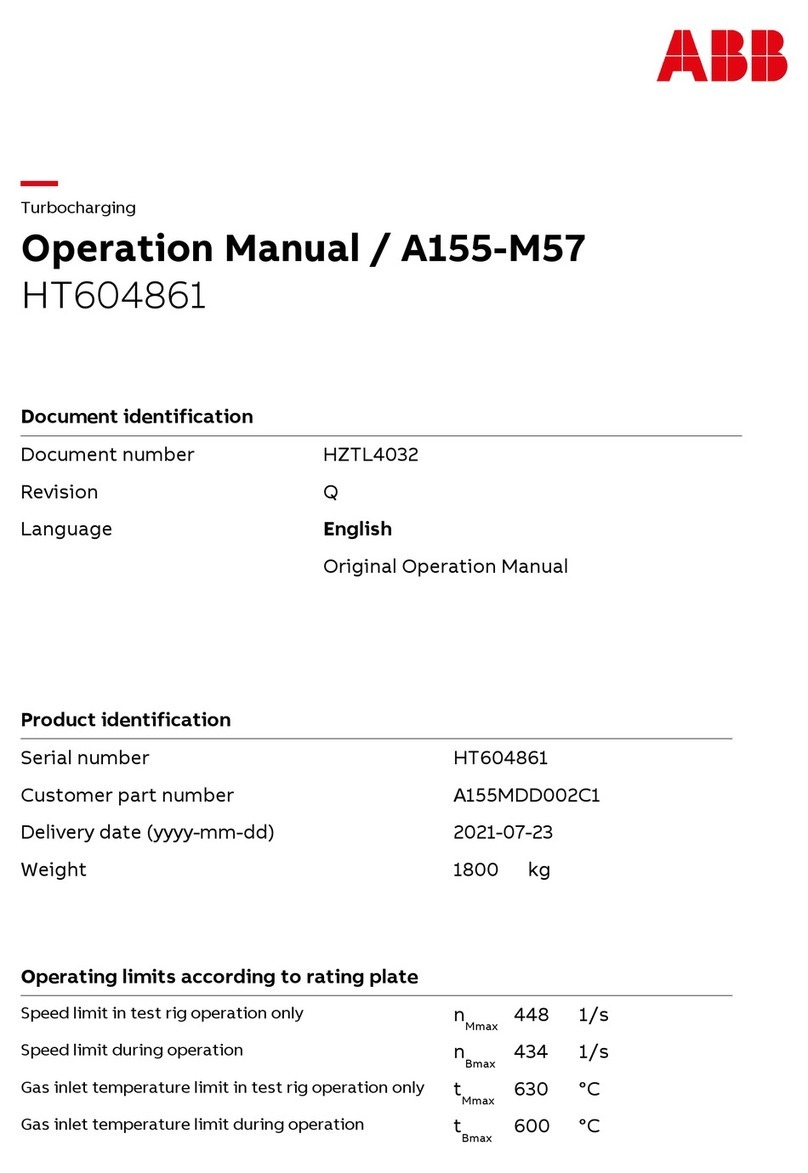
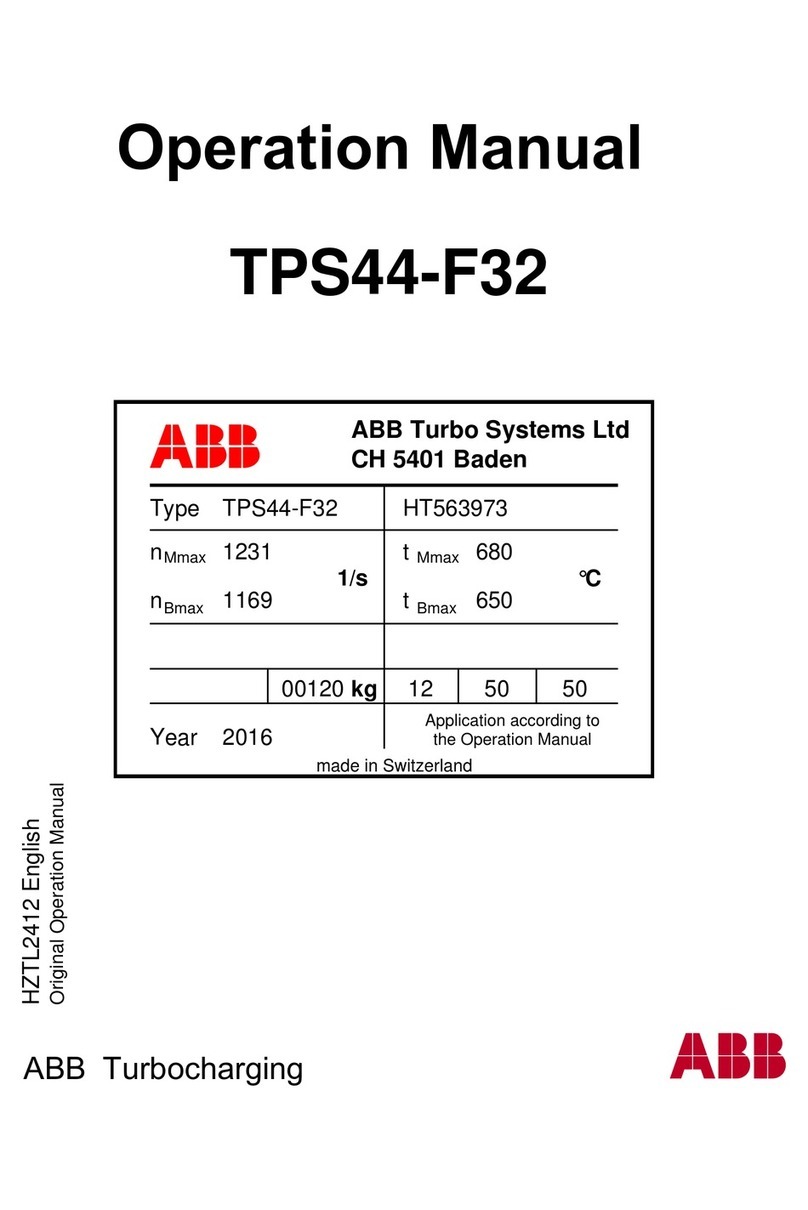
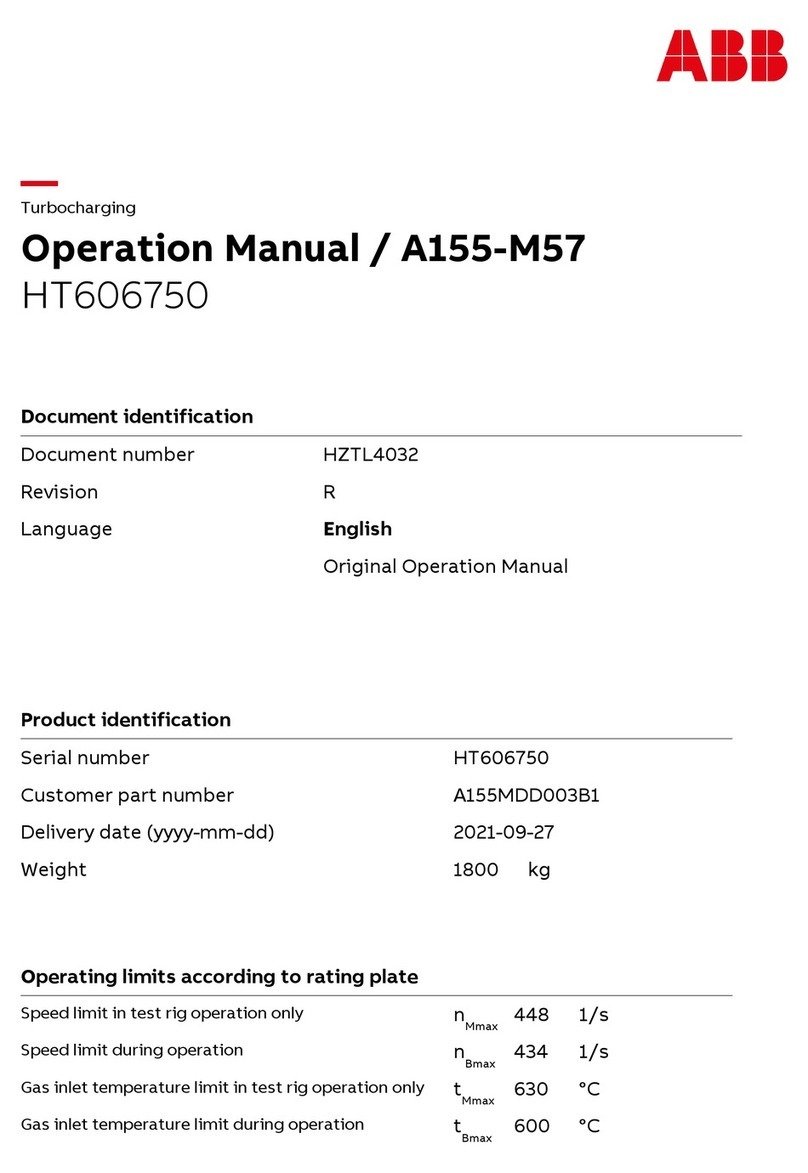
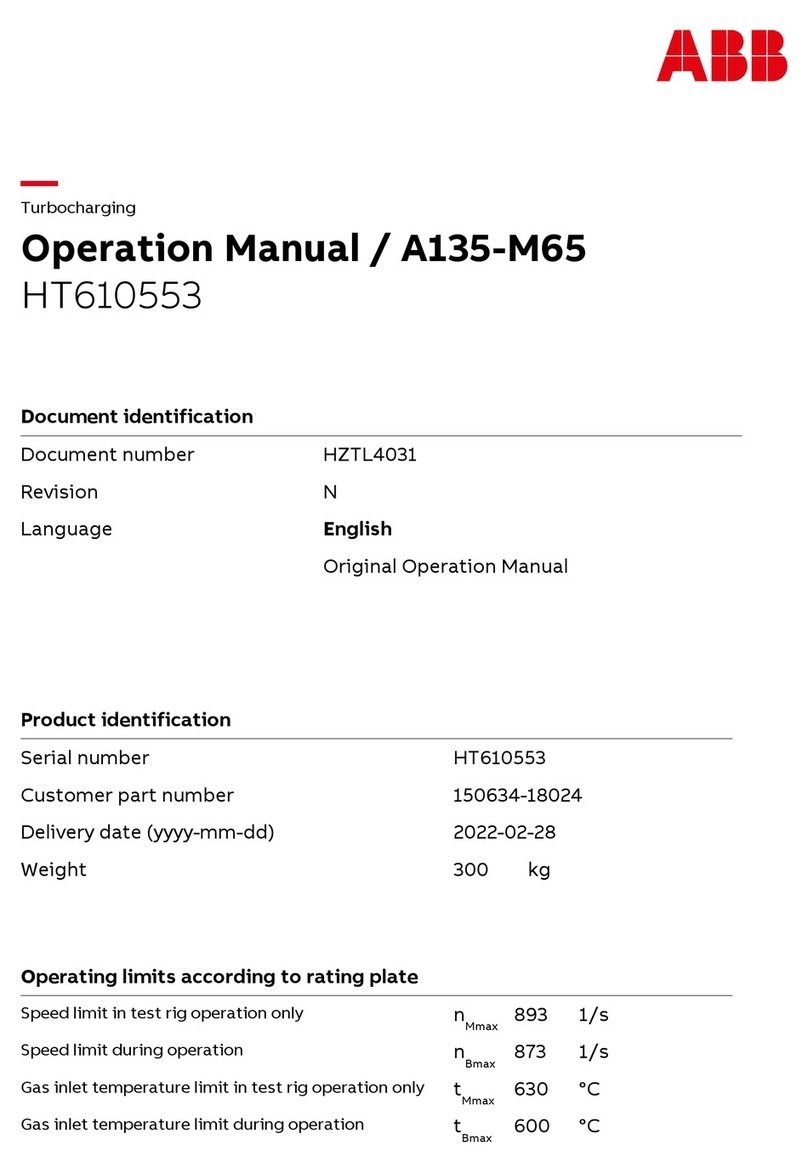
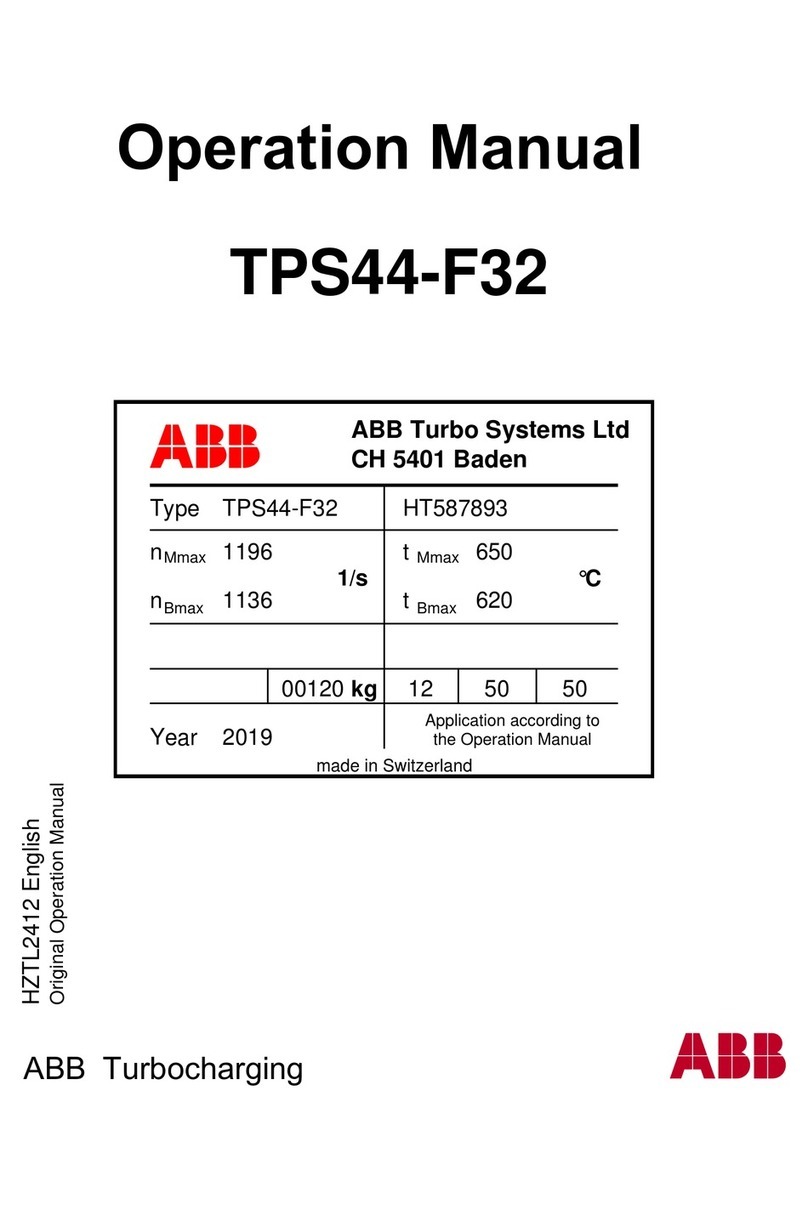
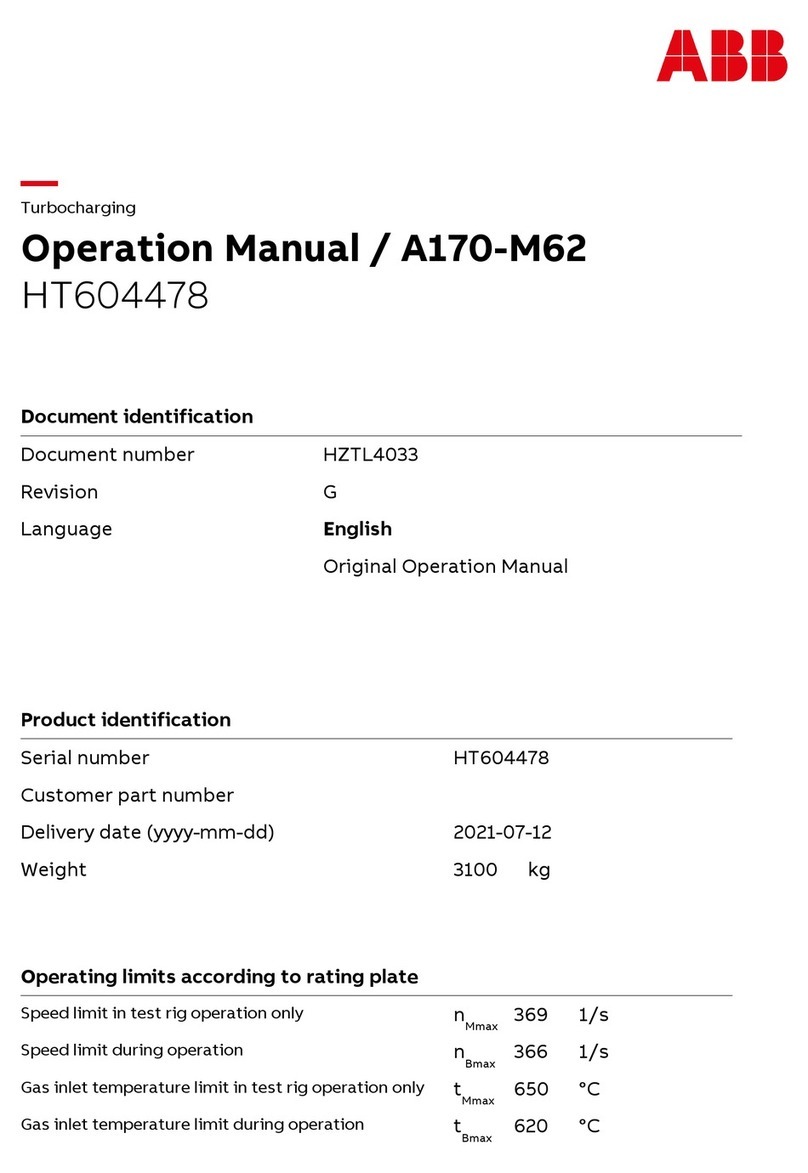
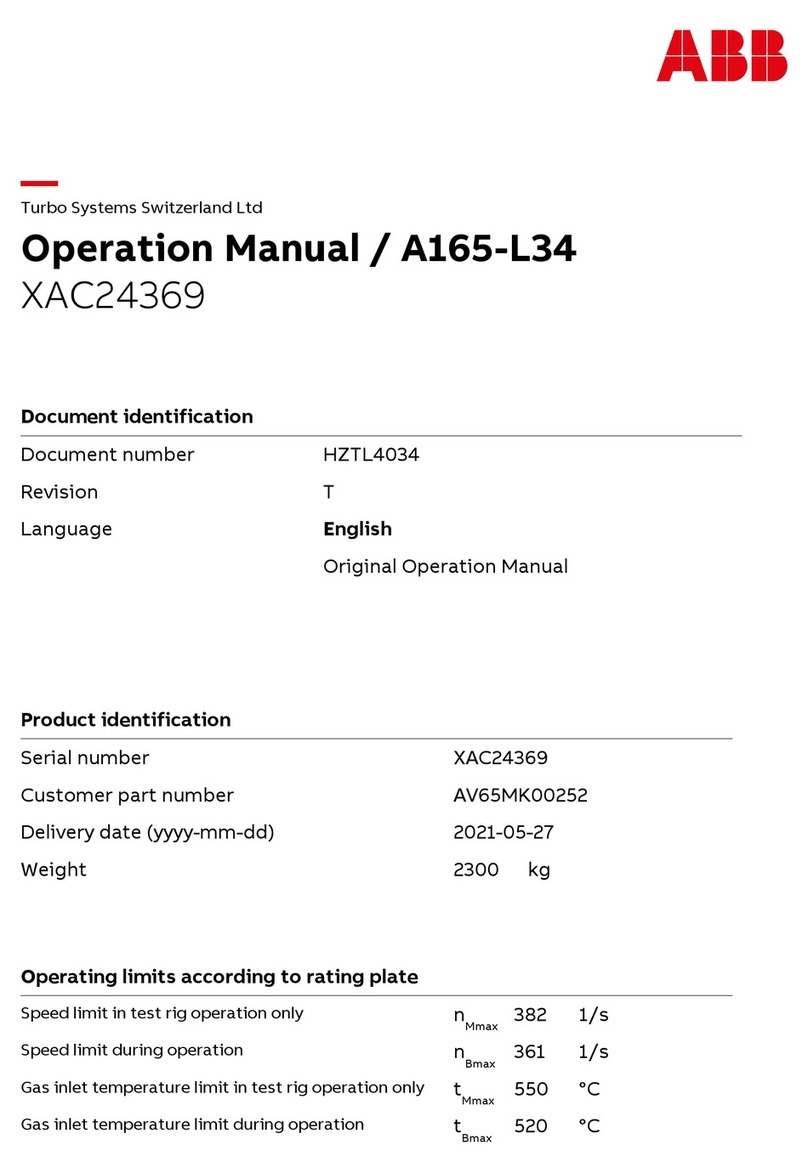
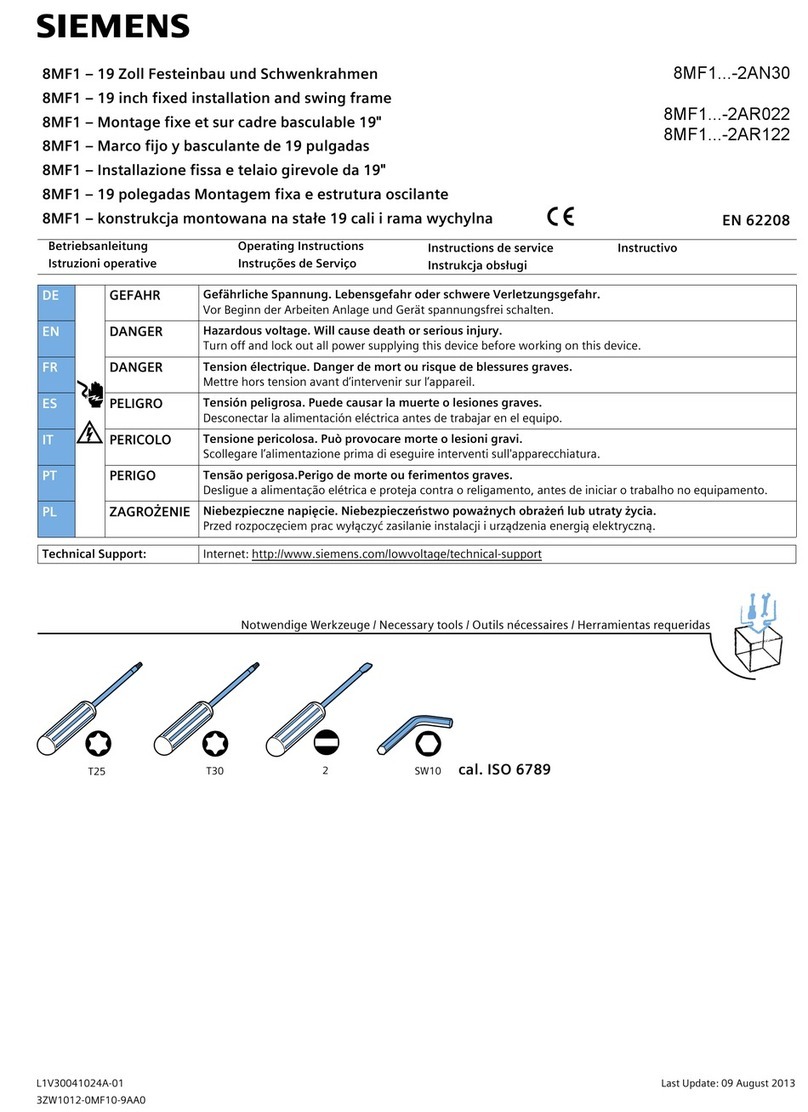
2TLC172287M0201 Rev B 2 www.abb.com/jokabsafety
2015-09-17
Read and understand this document
Please read and understand this document before using the products. Please consult your ABB JOKAB SAFETY
representative if you have any questions or comments.
WARRANTY
ABB JOKAB SAFETY’s exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials and workmanship for
a period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of sale by ABB JOKAB SAFETY.
ABB JOKAB SAFETY MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, REGARDING
NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE PRODUCTS,
ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS DETERMINED THAT THE
PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OR THEIR INTENDED USE. ABB JOKAB SAFETY
DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
ABB JOKAB SAFETY SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES, LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS,
WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR STRICT LIABILITY.
In no event shall responsibility of ABB JOKAB SAFETY for any act exceed the individual price of the product on which
liability asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL ABB JOKAB SAFETY BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS
REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS ABB JOKAB SAFETY’S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS
WERE PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO ABUSE,
MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
SUITABILITY FOR USE
ABB JOKAB SAFETY shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to
the combination of products in the customer’s application or use of the product. At the customer’s request,
ABB JOKAB SAFETY will provide applicable third party certification documents identifying ratings and limitations of
use that apply to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a complete determination of the suitability
of the products in combination with the end product, machine, system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must be given. This is not intended to
be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses listed may be suitable
for the products:
Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions or uses
not described in this document.
Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation systems, medical equipment,
amusement machines, vehicles, and installations subject to separate industry or government regulations.
Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR PROPERTY
WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND
THAT THE ABB JOKAB SAFETY PRODUCT IS PROPERLY RATED AND INSTALLED FOR THE INTENDED USE
WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PERFORMANCE DATA
While every effort has been taken to ensure the accuracy of the information contained in this manual
ABB JOKAB SAFETY cannot accept responsibility for errors or omissions and reserves the right to make changes and
improvements without notice. Performance data given in this document is provided as a guide for the user in
determining suitability and does not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of ABB JOKAB SAFETY’s test
conditions, and the users must correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is subject to the
ABB JOKAB SAFETY Warranty and Limitations of Liability.