6VD4 - INSTALLATION AND SERVICE INSTRUCTIONS
4.1 General
The VD4 are vacuum circuit breaker for indoor
installation.
For the electrical performances, please refer to the
corresponding technical catalogue code
1VCP000001.
For special installation requirements, please contact
ABB.
The following versions are available:
fixed
withdrawable for UniGear ZS1 switchgear
4.2 Reference Standards
The VD4 circuit breakers conform to the IEC 62271-
100, CEI - VDE - BS Standards are equivalent to IEC
Standards due to harmonization with IEC.
4.3 CLASSIC operating mechanism
VD4 circuit breakers are equipped with modular
CLASSIC spring operating mechanisms. The
operating mechanism is designed to cover the
specific range of 63 kA
4.4 Structure and function
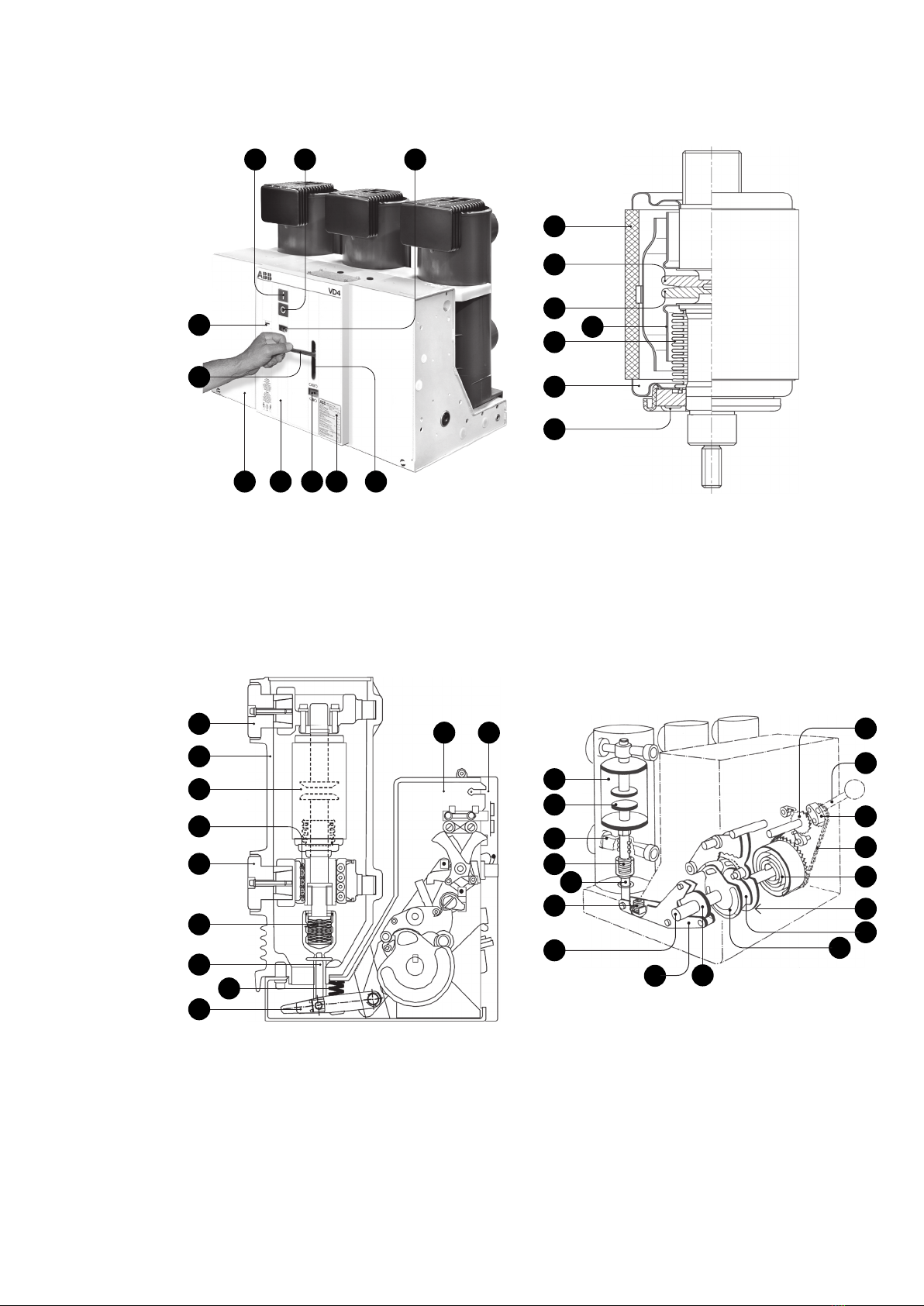
4.4.1 Structure of the breaker poles
(Figures 4/2, 4/3 and 4/4)
The basic structure of a vacuum circuit breaker and
a vacuum interrupter is explained in figures 4/2 and
4/3.
The poles, which are constructed in column form,
are mounted on the bracket-shaped rear part of
mechanism enclosure 1. The live parts of the breaker
poles are located in the insulating material pole
tubes 12 and protected from impacts and other
external influences.
With the breaker closed, the current path leads from
the upper breaker terminal 13 and a chamber holder
fixed in the pole tube to the fixed contact 15.2 in the
vacuum interrupter 15, then via the moving contact
15.3 and the roller contact 16.2, to the lower breaker
terminal 14. The switching motion is effected by
means of the insulated coupling rod 18 with internal
contact force springs 17.
4.4.2 Structure of the breaker operating
mechanism (Figures 4/1, 4/4 and 4/5)
The operating mechanism is of the stored-energy
spring type and acts on the three breaker poles. The
necessary operating energy is stored ready for
activation by charging the spring energy store.
The stored-energy spring mechanism essentially
consists of drum 33 containing the spiral spring, the
charging system, the latching and operating
mechanism and the linkages which transmit the
force to the breaker poles. In addition, there are
supplementary components such as the charging
—
4. Description
motor, releases, auxiliary switches and the controls
and instruments located on the front of the
mechanism enclosure 1.
The basic structure of a stored-energy spring
mechanism is explained in figure 4/4.
The operating mechanism is fundamentally suitable
for auto-reclosing and, due to the short charging
times, also for multi-shot auto-reclosing.
In the basic version of the circuit breaker, the spring
energy store is charged manually. The operating
mechanism can optionally be fitted with a charging
motor.
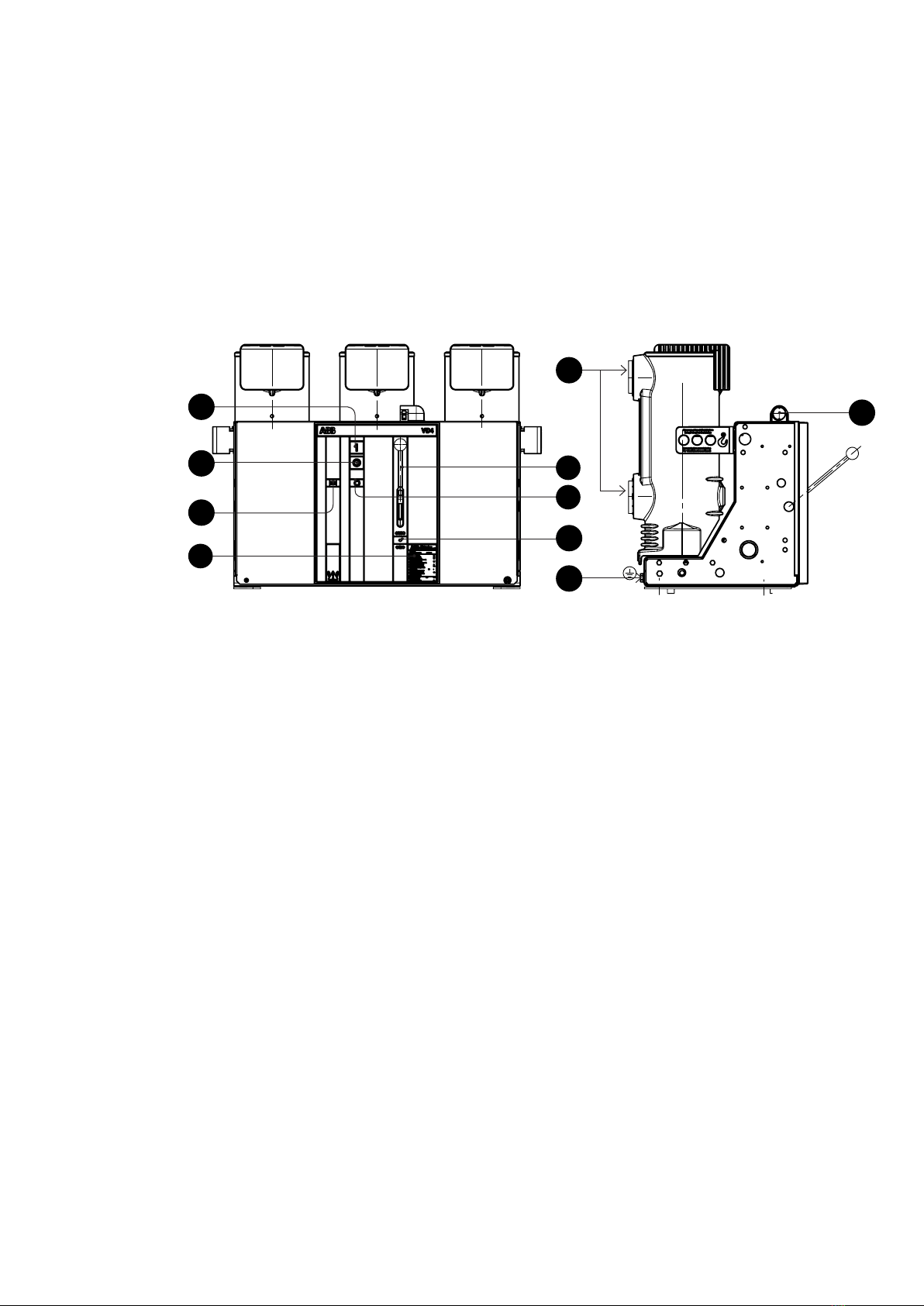
There is one rating plate with the main data of the
switch equipment on front plate 1.1, and another at
the lower front right in mechanism enclosure 1.
The basic version of the stored-energy spring
mechanism is fitted with the following auxiliary
equipment:
Shunt release OFF -MBO1
Five-pole auxiliary switch -BGB2 for annunciation
purposes 38
Auxiliary switch -BGB4 for fault annunciation
Mechanical ON push-button 2
Mechanical OFF push-button 3
Mechanical position indicator 4
Charging condition indicator 8 for the spring
energy store
Mechanical operating cycle counter 5
The following additional equipment can be installed:
Blocking magnet -RLE1 with auxiliary switch -BGL1
Shunt release ON -MBC
Second shunt release OFF -MBO2
Indirect overcurrent release -MBO3
Undervoltage release -MBU
Five-pole auxiliary switches -BGB1 and -BGB3
Charging motor -MAS 36
Five-pole auxiliary switch -BGS1 to switch the
charging motor.
4.4.3 Releases, blocking magnet and auxiliary
switches (Figures 4/1, 4/5, 9/1, 9/2, 9/3)
The releases and the blocking magnet are
mounted at the top left on the spring operating
mechanism.
The allocation of the auxiliary switches can be
seen in the wiring diagram.
The five-pole auxiliary switch -BGS1 is operated by
the charging condition indicator 8. It controls the
charging motor -MAS, serves as an electrical
interlock for shunt release ON -MBC when the
spring mechanism is not sufficiently charged, and
also provides an electrical switching readiness
signal.
Operation of the five-pole auxiliary switches
-BGB1, -BGB2 and -BGB3 is dependent on the
switching position of the circuit breaker.