7835
Hydrazine Monitor Contents
IM/7835–EN Rev. P 1
Contents
1 Safety ...............................................................................2
1.1 Health & Safety ........................................................2
1.2 Electrical Safety – CEI/IEC 61010-1:2001-2 .............2
1.3 Symbols – CEI/IEC 61010-1:2001-2 ........................2
1.4 Product Recycling Information .................................3
1.5 Product Disposal .....................................................3
1.6 Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) ..........3
1.7 Chemical Reagents .................................................3
1.8 Safety Precautions ...................................................3
1.9 Safety Conventions ..................................................3
1.10 Safety Recommendations ........................................4
1.11 Service and Repairs .................................................4
1.12 Potential Safety Hazards ......................................... 4
2 Introduction ..................................................................... 5
2.1 General ....................................................................5
2.2 Sensor Unit ..............................................................5
2.3 Transmitter Unit .......................................................5
3 Mechanical Installation ...................................................6
3.1 Unpacking ...............................................................6
3.2 End of Life Disposal .................................................6
3.2.1 Transmitter ...................................................6
3.2.2 Sensor and Sensor
(Wet Section Assembly) ................................6
3.3 Cleaning ...................................................................6
3.4 Installation Conditions ..............................................6
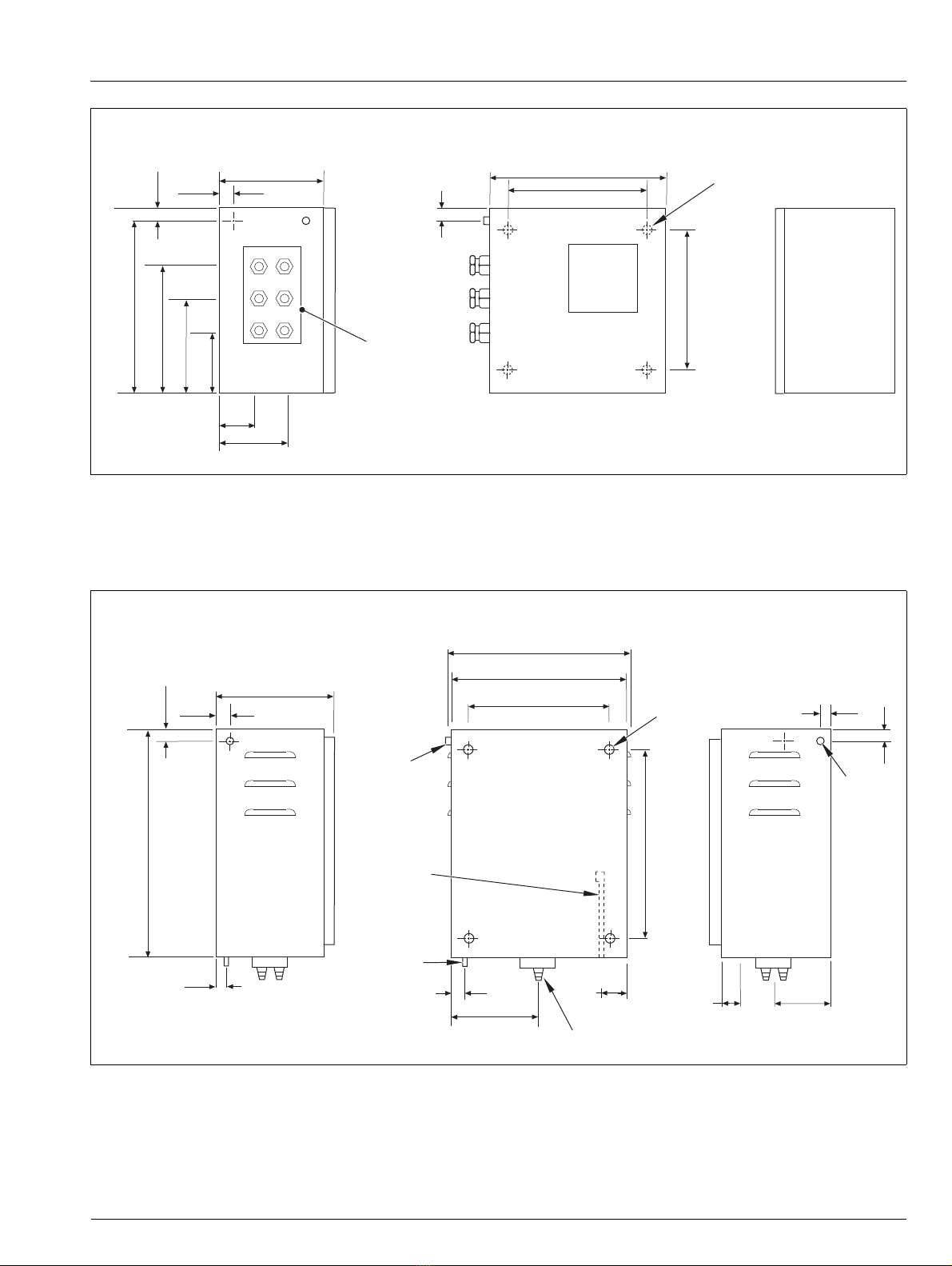
3.5 Overall Dimensions ...................................................6
3.5.1 Transmitter Unit ............................................ 6
3.5.2 Sensor Unit ...................................................7
4 Electrical Installation .......................................................8
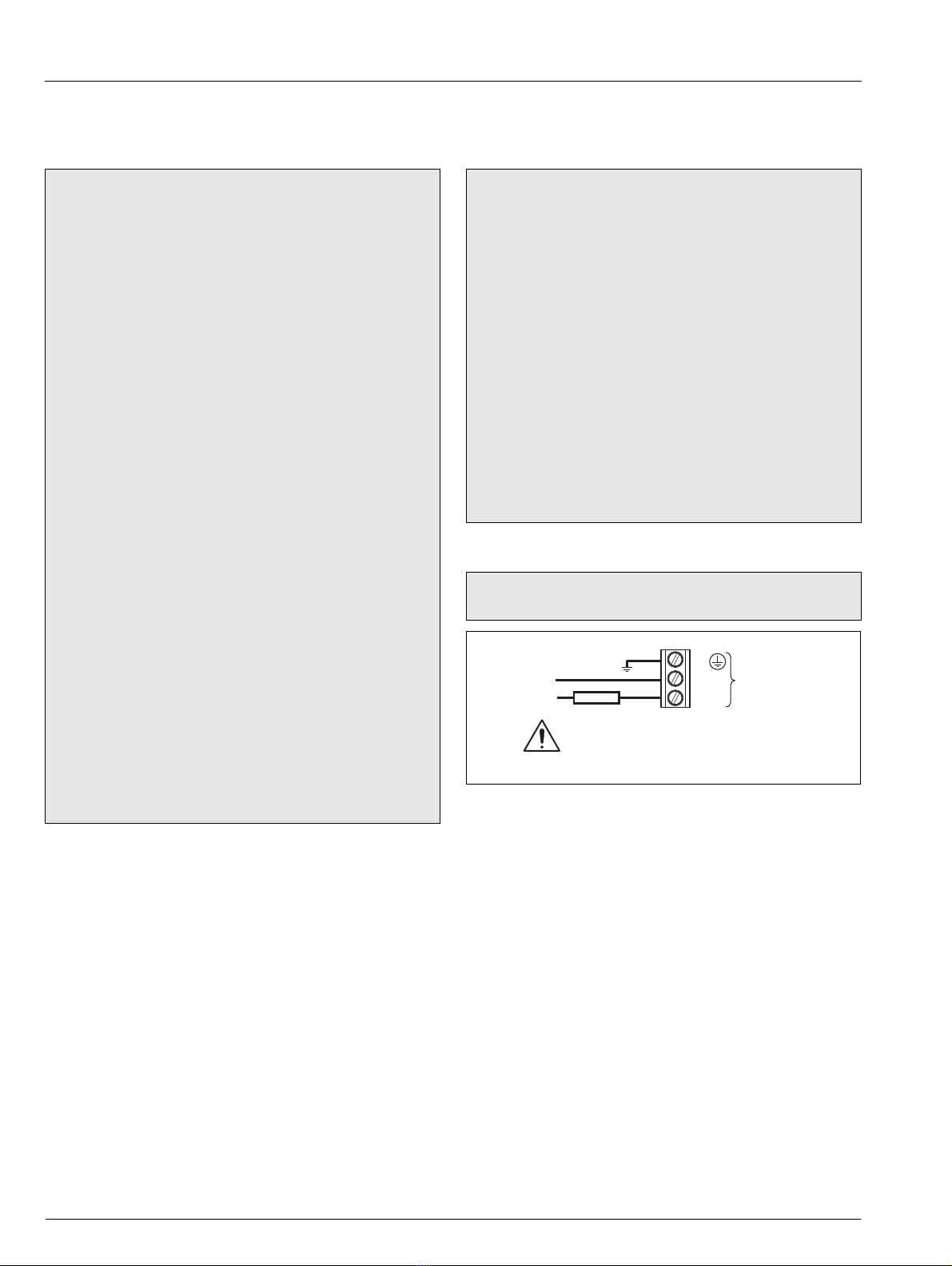
4.1 Electrical Safety ........................................................8
4.1.1 Power Supply Connections ..........................8
4.2 Transmitter Unit – Access to Terminals ....................9
4.3 Transmitter Unit –
Cable Gland Entries and Connections ......................9
4.4 Transmitter Unit – Ancillary Equipment ...................10
4.4.1 Recorders ................................................... 10
4.4.2 Range Indication .........................................10
4.5 Sensor Unit – Access to Terminals .........................10
4.6 Sensor Unit – Cable Gland Entries
and Connections ....................................................11
4.7 Sensor Unit – Sample Requirements ......................12
4.8 Sensor Unit – External Pipe Connections ...............12
4.8.1 Inlet Pipe .....................................................12
4.8.2 Drain Pipe ...................................................12
5 Commissioning .............................................................13
5.1 Start-Up .................................................................13
5.2 Sensor Unit ............................................................13
5.3 Setting Flowrates ..................................................13
5.3.1 Standard Solution Flowrate .........................14
5.3.2 Sample Flowrate ........................................ 14
5.3.3 Sample Temperature .................................15
6 Programming ................................................................ 16
6.1 Operator Page and Keys ....................................... 16
6.1.1 Access Level and Entering Passwords .................. 16
6.2 Menus ................................................................... 17
6.2.1 Calibrate .................................................... 17
6.2.2 Device Setup .............................................. 17
6.2.3 Input/Output ............................................. 18
6.2.4 Device Info ................................................. 18
7 Calibration ..................................................................... 19
7.1 Calibrating the System – General Tasks ................. 19
7.2 Sensor Calibration ................................................. 19
7.3 Setting the Standard Solution Value ....................... 19
7.4 Restoring Calibration Defaults ................................ 19
8 Troubleshooting ............................................................ 20
8.1 Diagnostics Classification Codes .......................... 20
8.2 Diagnostics Messages .......................................... 20
9 Maintenance ................................................................ 21
9.1 Chemical Solutions ................................................ 21
9.1.1 Reagent Solution – 5m (20% W/V) .................
Sodium Hydroxide ...................................... 21
9.1.2 Standard Solution ...................................... 21
9.2 Scheduled Servicing .............................................. 21
9.2.1 Weekly ....................................................... 21
9.2.2 Six-Monthly ................................................ 21
9.2.3 Yearly ......................................................... 22
9.3 Shut-down Procedures .......................................... 23
9.3.1 Sensor Unit ................................................ 23
9.3.2 Transmitter Unit .......................................... 23
9.4 Unscheduled Servicing .......................................... 24
9.4.1 Monitor Malfunction ................................... 24
9.4.2 Calibration Fail Alarm .................................. 24
9.4.3 Cleaning The Platinum Anode and
Sensor Ceramic ......................................... 25
9.4.4 Sensor Check ............................................ 25
9.4.5 Refurbishing The Sensor ............................ 25
9.4.6 Simple Electronic Check ............................ 26
10 Spares List .................................................................... 27
10.1 Refurbishment Spares ........................................... 27
10.2 Strategic Spares .................................................... 27
11 Specification ................................................................. 28