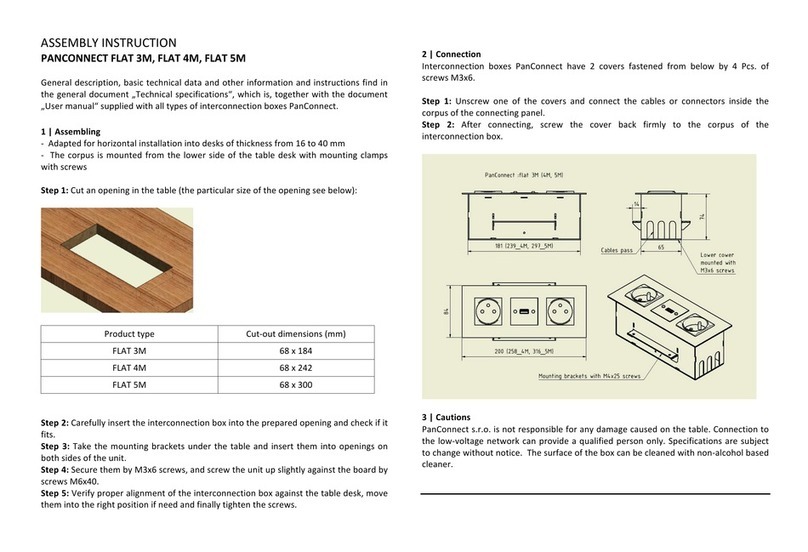
1. Description
Transformer protection IED RET650
RET650 provides fast and selective
protection, monitoring and control for all
types of transformers, such as two and three-
winding transformers, autotransformers,
shunt reactors and step-up transformers in
power stations.
2. Application
RET650 provides fast and selective
protection, monitoring and control for two-
and three-winding transformers,
autotransformers, generator-transformer units
and shunt reactors. The transformer IED is
designed to operate correctly over a wide
frequency range in order to accommodate
power system frequency variations during
disturbances and generator start-up and shut-
down.
A very fast differential protection function,
with automatic CT ratio matching and vector
group compensation, makes this IED the
ideal solution even for the most demanding
applications. RET650 IED has very low
requirements on the main CTs, no
interposing CTs are required. The differential
protection function is provided with 2nd
harmonic and wave-block restraint features to
avoid tripping for magnetizing inrush, and
5th harmonic restraint to avoid tripping for
overexcitation.
The differential function offers a high
sensitivity for low-level internal faults.
RET650 IED's unique and innovative sensitive
differential protection feature, based on well-
known theory of symmetrical components
provide best possible coverage for winding
internal turn-to-turn faults.
Low impedance restricted earth-fault
protection functions are available as
complimentary sensitive and fast main
protection against winding earth faults. This
function includes a directional zero-sequence
current criterion for additional security.
Tripping from Pressure relief / Buchholz and
temperature devices can be done through the
IED where pulsing, lock-out contact output
etc. is performed. The binary inputs are
heavily stabilized against disturbance to
prevent incorrect operations at e.g. dc system
capacitive discharges or dc earth faults.
Versatile phase, earth, negative and zero
sequence overcurrent functions, which can be
made directional, provide further alternative
backup protection. Thermal overload with
two time-constants, volts per hertz, over/
under voltage are also available.
Built-in disturbance and event recorder
provides valuable data to the user about
status and operation for post-fault
disturbance analysis.
Breaker failure protection allow high speed
back-up tripping of surrounding breakers.
Disturbance recording is available to allow
independent post-fault analysis after primary
disturbances.
Three packages has been defined for
following applications:
• Two winding transformer in single
breaker arrangements (A01)
• Three winding transformer in single
breaker arrangements (A05)
• Tap changer control (A07)
The packages are configured and ready for
direct use. Analog and tripping IO has been
pre-defined for basic use. Other signals need
to be applied as required for each application.
The graphical configuration tool ensures
simple and fast testing and commissioning.
Transformer protection 1MRK 504 110-BEN -
RET650
Product version: 1.0 Issued: September 2009
Configured Revision: -
ABB 3