Beacons
Beacons
Aerohive QuickStart
for the HiveAP 100 Series
This QuickStart guide explains how to set up a HiveAP 100 series device as a managed HiveAP
and how to mount it on a ceiling or wall. To register, get product documentation, and download
software updates, visit www.aerohive.com/support.
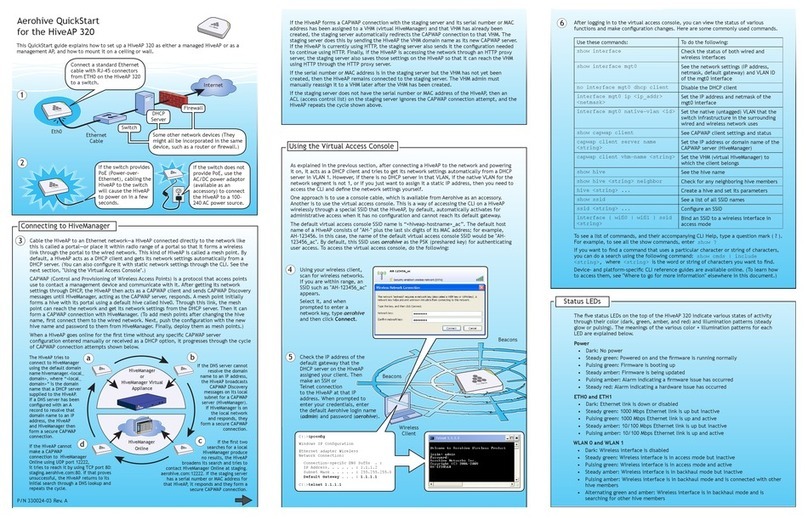
Switch
DHCP
Server
Firewall
Internet
Some other network devices (They
might all be incorporated in the same
device, such as a router or rewall.)
1
Ethernet
Cable
2If the switch provides
PoE (Power-over-
Ethernet), cabling the
HiveAP to the switch
will cause the HiveAP
to power on in a few
seconds.
If the switch does not
provide PoE, use the
AC/DC power adaptor
(available as an
accessory) to connect
the HiveAP to a 100-
240 AC power source.
Eth0
Connect a standard Ethernet
cable with RJ-45 connectors
from ETH0 on the HiveAP to
a switch.
Connecting to HiveManager
3
P/N 330026-05 Rev. A
Using the Virtual Access Console
Using your wireless client,
scan for wireless networks.
If you are within range, an
SSID such as "AH-123456_ac"
appears.
Select the SSID, and when
prompted to enter a
network key, type aerohive,
and then click Connect.
Wireless
Client
As explained in the previous section, after connecting a HiveAP to the network and powering
it on, it acts as a DHCP client and tries to get its network settings automatically from a DHCP
server in VLAN 1. However, if there is no DHCP server in that VLAN, if the native VLAN for the
network segment is not 1, or if you just want to assign it a static IP address, then you need to
access the CLI and dene the network settings yourself.
To do so, you can use the virtual access console. This is a way of accessing the CLI on a HiveAP
wirelessly through a special SSID that the HiveAP, by default, automatically activates for
administrative access when it has no conguration and cannot reach its default gateway.
The default virtual access console SSID name is “<hiveap_hostname>_ac”. The default host
name of a HiveAP consists of "AH-" plus the last six digits of its MAC address; for example,
AH-123456. In this case, the name of the default virtual access console SSID would be "AH-
123456_ac". By default, this SSID uses aerohive as the PSK (preshared key) for authenticating
user access. To access the virtual access console, do the following:
4
5
C:\>ipcong
Windows IP Conguration
Ethernet adapter Wireless
Network Connection:
Connection-specic DNS Sufx . :
IP Address. . . . . . : 1.1.1.2
Subnet Mask . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . : 1.1.1.1
C:\>telnet 1.1.1.1
Status LEDs
6
Bright Soft Dim Off
(a) The HiveAP tries to
connect to HiveManager
using the default domain
name "hivemanager.
<local_domain>",
where “<local_
domain>” is the
domain name that a
DHCP server supplied
to the HiveAP and 12222
is the UDP port number.
If a DNS server has been
congured to resolve
that domain name to an
IP address, the HiveAP and
HiveManager then form a
secure CAPWAP connection
on port 12222. If the HiveAP
cannot make a CAPWAP
connection to HiveManager on port
12222, it tries to reach it by using TCP
port 80: hivemanager.<local_domain>:80.
(b) If the DNS server cannot
resolve the domain
name to an IP address,
the HiveAP broadcasts
CAPWAP Discovery
messages on its local
subnet. If HiveManager
is on the local network
and responds, they
form a secure CAPWAP
connection.
(c) If the rst two searches
for a local HiveManager
produce no results, the
HiveAP tries to contact
HiveManager Online at
redirector.aerohive.com:12222.
If the Aerohive redirection
server has a serial number for
that HiveAP in its ACL (access control
list), it responds and they form a secure
CAPWAP connection. If the HiveAP cannot make a
CAPWAP connection to HiveManager Online on UDP port
12222, it tries to reach it on TCP port 80. If that proves
unsuccessful, the HiveAP returns to its initial search
through a DNS lookup and repeats the cycle.
HiveManager
or
HiveManager Virtual
Appliance
HiveManager Online
ab
c
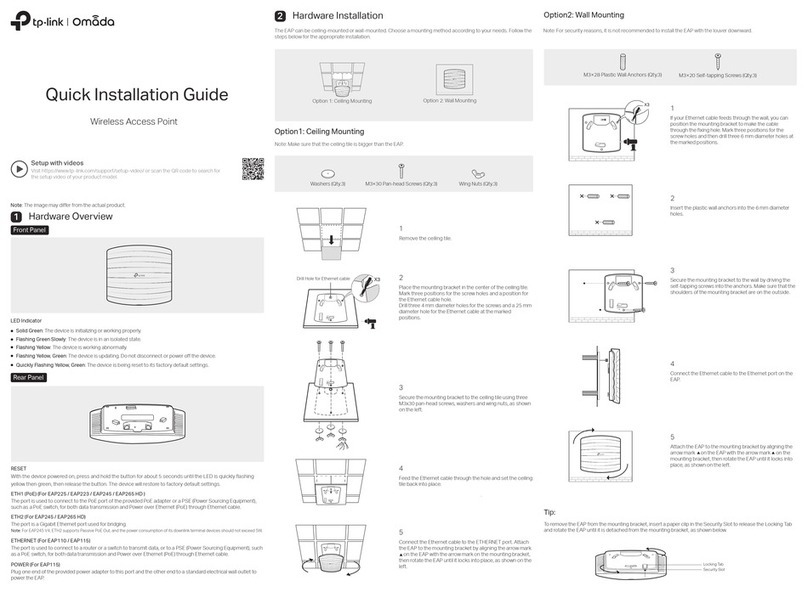
After you cable the HiveAP to an Ethernet network and power it on, it automatically
attempts to get its network settings through DHCP and contact HiveManager. The process
typically takes about ve minutes to complete. If you see the HiveAP listed on the Monitor >
Access Points > HiveAPs page in the HiveManager GUI, the initial setup is complete and you
can now begin managing the HiveAP through HiveManager.
If the HiveAP does not appear in the HiveManager GUI after about ten minutes, read the
rest of this guide to understand how the HiveAP attempts to contact HiveManager and what
you can do to help establish a connection between the two devices.
By default, a HiveAP acts as a DHCP client and gets its network settings automatically from a
DHCP server. (You can also congure it with static network settings through the CLI. See the
next section, "Using the Virtual Access Console".) After a HiveAP has its network settings, it then
acts as a CAPWAP client and sends CAPWAP Discovery messages until HiveManager, acting as
the CAPWAP server, responds. CAPWAP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points) is a
protocol that access points use to contact a management device and communicate with it.
When a HiveAP goes online for the rst time without any specic CAPWAP server conguration
entered manually or received as a DHCP option, it progresses through this cycle of CAPWAP
connection attempts:
A HiveAP connected directly to the network is called a portal. You can also place a HiveAP
within radio range of a portal so that it forms a wireless link through the portal to the wired
network. This kind of HiveAP is called a mesh point. A mesh point initially forms a hive with
its portal using a default hive called hive0. Through this link, the mesh point can reach the
network and get its network settings from the DHCP server. Then it can form a CAPWAP
connection with HiveManager. (To add mesh points after changing the hive name, rst
connect them to the wired network. Next, push the conguration with the new hive name and
password to them from HiveManager. Finally, deploy them as mesh points.)
If the HiveAP forms a CAPWAP connection with the Aerohive redirection server and its serial
number has been entered in an ACL, the redirection server automatically redirects the
CAPWAP connection to the corresponding HiveManager Online VHM (virtual HiveManager).
The redirection server does this by sending the HiveAP the HiveManager domain name or IP
address as its new CAPWAP server and the name of the appropriate VHM. If the HiveAP is
currently using HTTP, the redirection server includes the conguration needed for the HiveAP
to continue using it. Similarly, if the HiveAP is congured to access the public network through
an HTTP proxy server, the redirection server saves the relevant settings on the HiveAP so it
will continue using the HTTP proxy server when connecting to HiveManager.
If the redirection server does not have the HiveAP serial number, the ACL ignores the CAPWAP
connection attempts, and the HiveAP repeats the connection cycle shown previously.
Check the IP address of the
default gateway that the
DHCP server on the HiveAP
assigned your client. Then
make an SSH or Telnet
connection to the HiveAP
at that IP address.
(Note that the Telnet
connection is protected by
WPA2 security mechanisms.)
When prompted to enter your
credentials, enter the default
Aerohive login name (admin)
and password (aerohive).
After logging in to the virtual access console, you can view the status of various
functions and make conguration changes. Here are some commonly used commands:
Use these commands: To do the following:
show interface Check the status of both wired and
wireless interfaces
show interface mgt0 See the network settings (IP address,
netmask, default gateway) and VLAN
ID of the mgt0 interface, which is the
management interface of the HiveAP
no interface mgt0 dhcp client Disable the DHCP client
interface mgt0 ip <ip_addr>
<netmask>
Set the IP address and netmask of the
mgt0 interface
interface mgt0 native-vlan <id> Set the native (untagged) VLAN that the
switch infrastructure in the surrounding
wired and wireless network uses
interface mgt0 vlan <id> Set the VLAN for management and
control trafc
show capwap client See CAPWAP client settings and status
show hive See the hive name
show hive <string> neighbor Check for any neighboring hive members
hive <string> ... Create a hive and set its parameters
show ssid See a list of all SSID names
ssid <string> ... Congure an SSID
interface { wi0 | wi1 } ssid
<string>
Bind an SSID to a wireless interface in
access mode
save cong Save the conguration to ash
reboot Reboot the HiveAP
Only set the following command when managing HiveAPs through HiveManager or
HiveManager Virtual Appliance. Do not use it with HiveManager Online.
capwap client server name
<string>
Set the IP address or domain name of the
CAPWAP server (HiveManager)
To see a list of commands, and their accompanying CLI Help, type a question mark ( ? ).
For example, to see all the show commands, enter show ?
If you want to nd a command that uses a particular character or string of characters,
you can do a search using the following command: show cmds | include
<string>, where <string> is the word or string of characters you want to nd.
Device- and platform-specic CLI reference guides are available online. (To learn how to
access them, see "Where to go for more information" elsewhere in this document.)
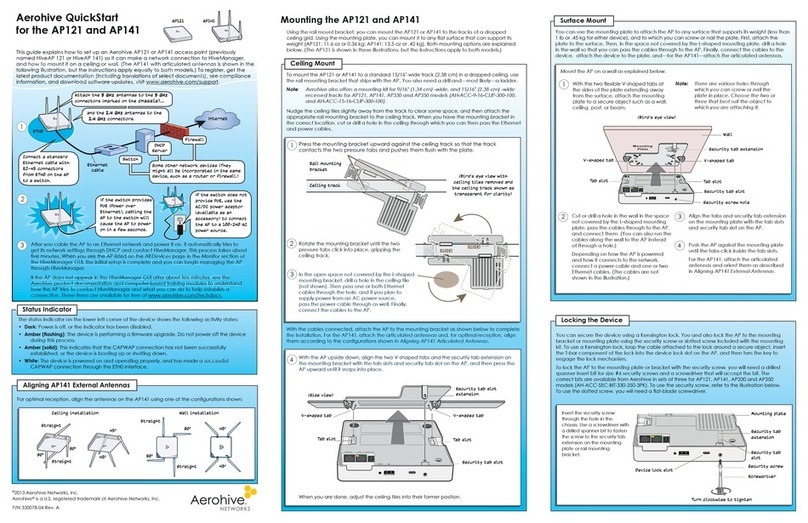
The status indicator has been incorporated into the Aerohive logo on the top of the HiveAP
110 and 120. It is illuminated by various colors to indicate different states of activity. The
meanings of the colors are explained below.
• Dark: There is no power or the status indicator is disabled.
• Blue: (solid) The device is booting up or there is no backhaul link; (ashing) the
device is shutting down
• Green: The default route is through the backhaul Ethernet interface, but not all
conditions for normal operations (white) have been met.
• Yellow: The default route is through a backhaul wi interface, but not all conditions
for normal operations (white) have been met.
• White: The device is powered on and the rmware is operating normally; that is, a
wireless interface in access mode is up, a wired or wireless backhaul link is up, and
the HiveAP has a CAPWAP connection to HiveManager.
• Purple: A new image is being loaded from HiveManager.
• Orange: An alarm indicating a rmware or hardware issue has occurred.
You can adjust its brightness level from bright (the default) to soft to dim, or turn it off
completely. In HiveManager, the setting is on the Conguration > Management Services >
Management Options page. CLI: [ no ] system led brightness { soft | dim | off }.