2 | P a g e
Table of Contents
Specifications .............................................................................................................................................. 4
Unboxing the Printer................................................................................................................................... 5
Box Contents ........................................................................................................................................... 5
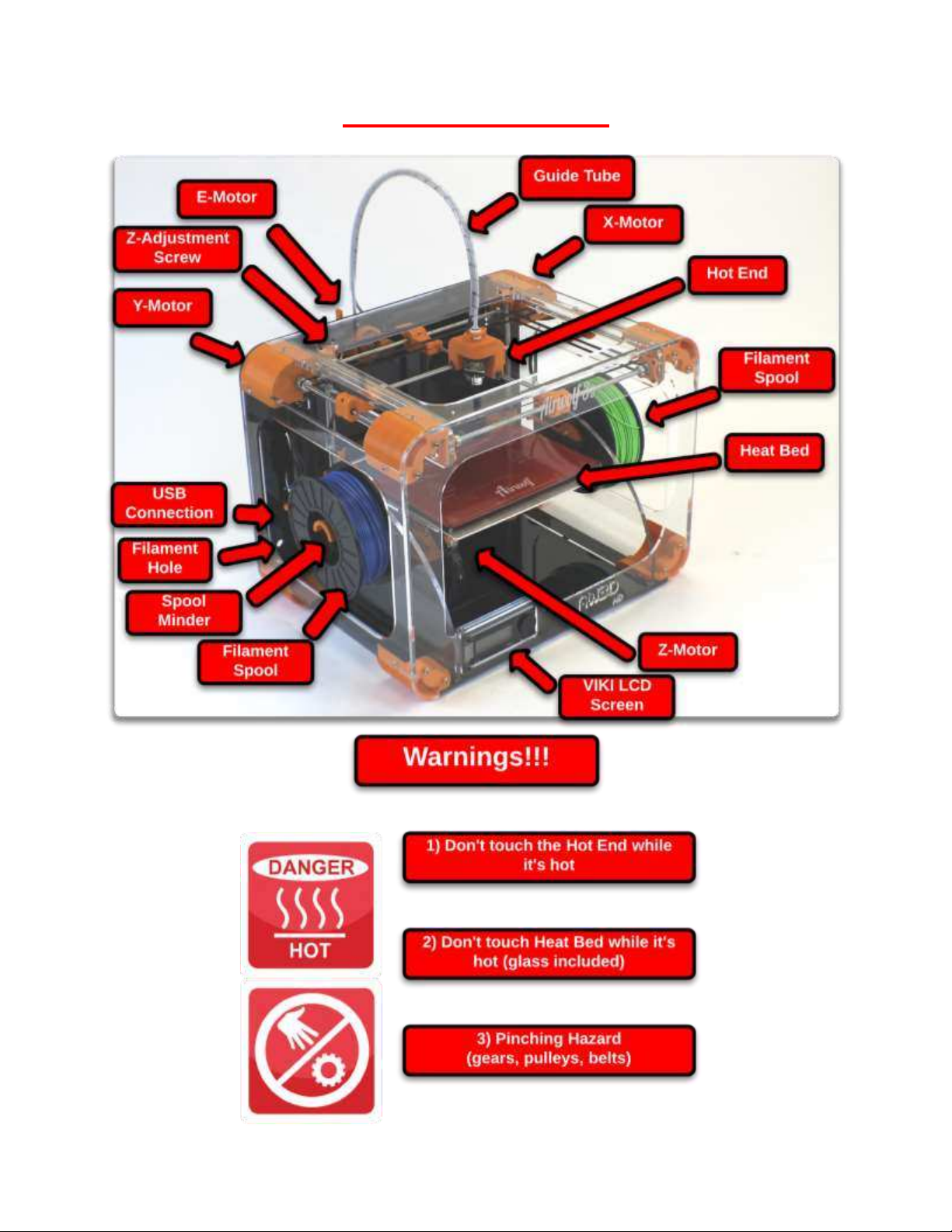
Part Directory.............................................................................................................................................. 6
How it Works............................................................................................................................................... 7
Extruder Assembly .................................................................................................................................. 7
Hot End and Heat Bed Motion ................................................................................................................ 7
Plug In & Turn On........................................................................................................................................ 8
Pre-Printing Steps ....................................................................................................................................... 9
Quick Start Guide .................................................................................................................................... 9
Quick Start Guide (contd.)..................................................................................................................... 10
1) Leveling the Heat Bed ....................................................................................................................... 11
First Print & Calibration......................................................................................................................... 12
First Print & Calibration (contd.) ........................................................................................................... 13
2) Loading Filament............................................................................................................................... 14
E G O‘ GOO........................................................................................................................ 15
4) The First Layer ................................................................................................................................... 15
5) LED Lights .......................................................................................................................................... 15
VIKI LCD Screen ......................................................................................................................................... 16
VIKI: Introduction .................................................................................................................................. 16
VIKI: Home Screen................................................................................................................................. 16
VIKI: Layout............................................................................................................................................ 17
VIKI: How To .......................................................................................................................................... 18
RAMBo Driver ........................................................................................................................................... 19
Setup (Windows 8 Only)........................................................................................................................ 19
Installation (PC Only)............................................................................................................................. 20
5 Steps to Printing..................................................................................................................................... 23
1) Download or Design a 3D Model ...................................................................................................... 24
2) Convert to STL File Type.................................................................................................................... 25
3) Netfabb: Layout (STL Clean Up) ........................................................................................................ 25
3) Netfabb: How To (STL Clean Up)....................................................................................................... 26
4) Slicing ................................................................................................................................................ 27