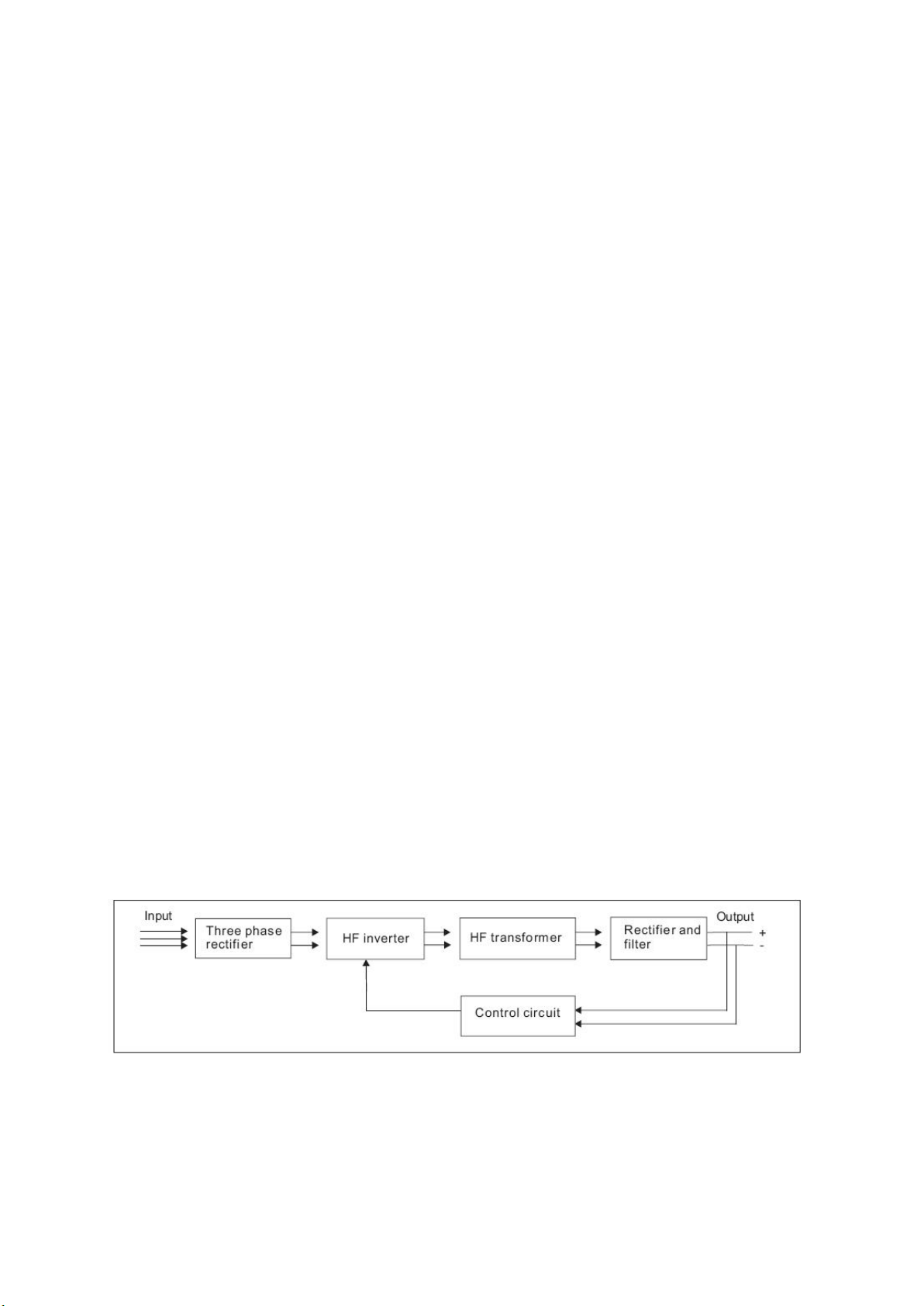
3
-Equipotential bonding
-Workpiece grounding (earthing)
-Shielding
Shield the entire welding equipment and other equipment nearby.
ARC rays can burn
•Visible and invisible rays can burn eyes and skin.
•Wear an approved welding helmet or suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material
(leather, heavy cotton, or wool) to protect your eyes and skin from arc rays and sparks when welding
or watching.
•Use protective screens or barriers to protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose themselves to the arc rays or to hot
spatter or material.
Fumes and gases can be dangerous
•Welding may produce fumes and gases, breathing these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your
health.
•When welding, keep your head out of the fume. If inside, ventilate the area at the arc to keep fumes
and gases away from the breathing zone. If ventilation is not good, wear an approved air-supplied
respirator.
•Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while wearing an air-supplied respirator.
•Welding fumes and gases can displace air and lower the oxygen level causing injury or death. Always
use enough ventilation, especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
Welding and cutting sparks can cause fire or explosion
•When not welding, make sure the electrode circuit is not touching the work or ground. Accidental
contact can cause sparks, explosion, overheating, or fire. Make sure the area is safe before doing
any welding.
•Welding and cutting on closed containers, such as tanks, drums, or containers, can cause them to
blow up. Make sure proper steps have been taken.
•When pressure gas is used at the work site, special precautions are required to prevent hazardous
situations.
•Connect work cable to the work as close to the welding zone as practical to prevent welding current
from passing too long and creating fire hazards or overheat.
•Wear oil-free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuffless trousers, high shoes,
and a cap. Wear ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear safety
glasses with side shields when in a welding area.
•Be attention that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas and start a fire. Remove fire hazardous from the welding area, if not
possible, cover them thoroughly. Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material and
where the atmosphere may contain flammable dust, gas, or liquid vapors (such as gasoline).
•Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and hot metal. Remove any combustibles from
operator before perform any welding.
•Keep a fire extinguisher readily available.
•Empty containers, tanks, drums, or pipes which have combustibles before perform welding.
•Remove stick electrode from electrode holder or cut off welding wire at contact tip when not in use.
•Apply correct fuses or circuit breakers. Do not oversize or bypass them.
Cylinder can explode if damaged
•Pressure gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode. Since
gas cylinders are normally part of the welding process, be sure to treat them carefully.
•Cylinders should be located away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to physical
damage. Use proper equipment, procedures, and sufficient number of persons to lift and move
cylinders.
•Always install cylinders in an upright position by securing to a stationary support or cylinder rack to
prevent falling over or tipping.
•Keep a safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and any other source of heat, sparks, or
flame.
•No touching cylinder by welding electrode, electrode holder or any other electrically “hot” parts. Do
not drape welding cables or welding torches over a gas cylinder.
•Use only correct compressed gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and fittings designed for the process
used; maintain them and associated parts in good condition.
•Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct shielding gas for the and properly
operating regulators designed for the gas and pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be
suitable for the application and maintained in good condition.
•Open the cylinder valve slowly and keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet.
•Valve protection caps should be kept in place over valve expect when the cylinder is in use or
connected for use.
Hot parts can burn
•Do not touch hot parts with bare hand or skin.
•Ensure equipment is cooled down before perform any work.