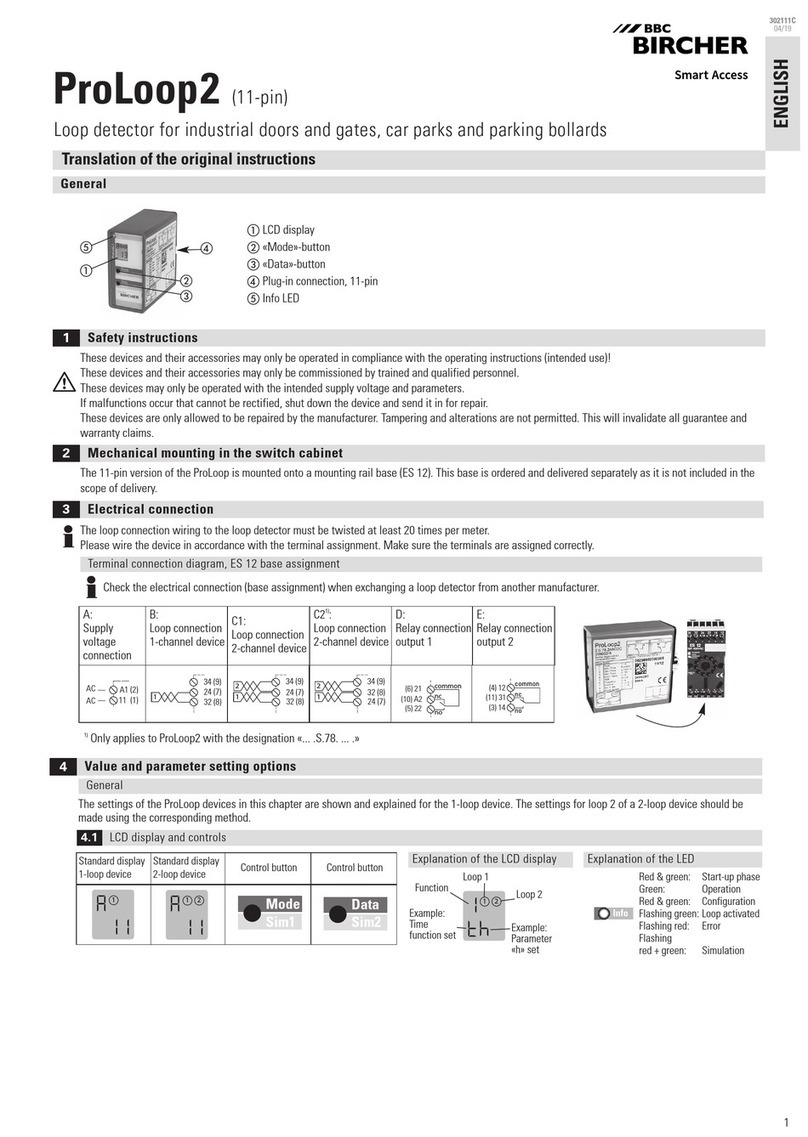
Arcom QAM Snare Snoop User manual

QAM Snare Snoop User
Manual
QS-Snoop-v2.0
2/21/2018
This document details the functions and operation of the QAM Snare Snoop leakage
detector

2
Table of Contents
Overview .............................................................................................................. 5
Screen Navigation ................................................................................................. 6
Settings ................................................................................................................ 6
General................................................................................................................. 7
Information .......................................................................................................7
Sound ...............................................................................................................7
Auto start..........................................................................................................8
Auto Detect Profile ............................................................................................8
Standard ...........................................................................................................9
Exit ...................................................................................................................9
Connection ........................................................................................................... 9
QS Server ..........................................................................................................9
Wi-Fi profile....................................................................................................10
Walk mode -vs-Truck mode............................................................................10
Detector Settings ................................................................................................ 11
Signal Mode........................................................................................................ 11
Channel.............................................................................................................. 11
Channel - Analog detection ................................................................................ 12
Analog channel ...............................................................................................12
Tag confirmation on/off..................................................................................12
Tag frequency .................................................................................................13
Channel - QAM detection.................................................................................... 13
QAM channel...................................................................................................13
Channel – OFDM detection .................................................................................. 13
OFDM channel.................................................................................................14
OFDM detection continuous pilot harmonics ...................................................14
Error CP1 or CP2 .............................................................................................15
Pilot/QAM mode ................................................................................................. 15
Leakage Detector Pilot/QAM mode Channel and Frequency Selection ..............15
Leakage Detector Pilot/QAM mode Code # ......................................................15
Shielding Test mode ........................................................................................... 16
Shielding Test ON/OFF ....................................................................................17
Shielding Test Channels ..................................................................................17
Shielding Test Code ........................................................................................17
Pilot Level .......................................................................................................18

3
Next Band .......................................................................................................18
Leak Alarms........................................................................................................ 18
Signal alarms ..................................................................................................19
SE Test alarms.................................................................................................19
Calibration.......................................................................................................... 19
Detector Mode .................................................................................................... 20
Detector Mode – when configured for QAM detection........................................... 20
Detection channel displayed on screen............................................................21
Indication of leaks detected at bands other than displayed..............................21
Switch to different band ..................................................................................21
Fix detection to one frequency ........................................................................21
Leakage Display Level Indicator .......................................................................22
Detector Mode – Analog...................................................................................... 22
Detector Mode – OFDM ....................................................................................... 23
Detector Mode – Pilot/QAM ................................................................................. 23
Detector Mode – Shielding Test ........................................................................... 23
Screen navigation in Shielding Test mode........................................................24
Shielding effectiveness indication....................................................................24
Noise Floor Level Indication................................................................................. 25
Auto shutdown counter....................................................................................... 25
Other battery saving features .............................................................................. 25
GPS status indicator ............................................................................................ 25
Error Messages and Troubleshooting................................................................... 27
No GPS lock.....................................................................................................27
No Wi-Fi connection........................................................................................27
No Data...........................................................................................................28
No response from Server .................................................................................28
Headend Signal Processor offline.....................................................................28
No GPS at Headend Signal Processor ...............................................................29
Setup correct QAM channels............................................................................29
Unable to connect to Q-browser .....................................................................29
Changes made in Q-browser are not saved in detector....................................30
Shut Down.......................................................................................................... 30
Antennas ............................................................................................................ 30
GPS antenna....................................................................................................30
RF walk mode antenna ....................................................................................30

4
Wi-Fi antenna..................................................................................................31
Frequency Setup of QAM Snare Pilot transmitter .................................................. 31
Turning the Pilot transmitter on ......................................................................32
Battery charging ................................................................................................. 32
Patents ............................................................................................................... 32

5
Overview
The QAM Snare Snoop is designed with the
fulfillment technician in mind for troubleshooting
within the home or at the drop. It is a multi-
modulation format, multi-channel detector that is
extremely flexible for the user. It will operate in
QAM, Analog, Pilot/QAM, OFDM and Shielding Test
detector modes. The device does not provide the
ability to record drive-outs, and does not report
detected leaks to the QAM Snare server database.
However, when the Snoop Auto Detection profile is
configured, the Snoop Time and GPS coordinates are
captured at the server to log activity each time the
detector is activated.
When not being used, it is stored in its cradle, where
is receives power as well as the GPS from the roof
antenna which attaches to the cradle. It is designed
to remain powered while cradled such that it
establishes GPS lock and is always ready to be used
without wait time for the technician. When the
technician needs to use the detector, it is pulled
from the cradle and the technician can freely move
to the leak source. The Snoop is a Wi-Fi device that
requires Wi-Fi connectivity when used in the QAM
detector mode. When used in Analog detector,
Pilot/QAM detector, Shielding Test detector and
OFDM detector modes it does not require Wi-Fi
connectivity nor does it require GPS lock.
The Snoop Shielding Test detector mode is intended to be used in conjunction with
the QAM Snare Pilot Transmitter, to quickly troubleshoot locations in the home and
MDU’s where poor shielding effectiveness results in forward ingress issues related to
close proximity LTE transmitters. Others have referred to this testing technique as
‘Pressure Testing’.
The device contains no maps and provides the user with no feedback as to the
flagged leak location. If it is desired to utilize this product as a find and fix tool at leak
locations previously identified by other QAM Snare devices having drive-out capability,

6
as a time saver it is recommended to use the QAM Snare Web Client on a mobile device
to have visibility to the GPS calculated flagged leak location which provides an accurate
starting point for the final search. This process is much more effective than blindly
walking around, but marginally more time consuming as compared to the Navigator
Plus device which contain maps integrated within the device display.
Screen Navigation
Upon startup the user can either select Detector mode,
where the unit will function as a leakage detector – or the
user can select Settings, where various changes to the
operating parameters are made.
Screen navigation is performed with a simple three
button scheme. The left and right arrows move the
highlighted cursor to the desired item to be selected, and
the middle circular enter button is used to confirm the
selected menu item. The circular middle button also
functions as a power button and turns the unit on by
pressing and holding for two seconds.
Settings
The Settings button is used to select all the various
configuration options. To access this mode, use the left or
right arrow to highlight the Settings mode and press enter.
Settings related to the QAM Snare server and the Wi-Fi
profiles that the device attaches to MUST be configured
through the Q-browser software program.

7
General
The General settings button provides for access to several
miscellaneous configuration items which are detailed below.
Information
The Information selection item provide the user with
information on the Device ID (which by default is the MAC
address) and Technician ID that was assigned to the unit
through Q-browser. It provides information on the Firmware
revision, the QAM Snare Server name it is configured to
connect to, and the device MAC address. For security
reasons, the Wi-Fi configuration is not displayed – but this
information is available through the Q-browser.
Sound
The Sound button allows the user to turn the audio alarm
and button feedback on or off. Naviagate to Sound and
press enter, then use the right or left arrow to select on or
off, then press enter to confirm the selection. The threshold
setting for high and low leak alarms is configured in the Leak
alarms menu item, and the sound off setting configured here
will override the Leak alarm setting.

8
Auto start
The Auto Start/Stop setting allows the unit to turn on and
establish GPS lock automatically when power is applied, as
when the vehicle is started. It will NOT automatically enter
detector mode, as it is not intended to detect leaks while
cradled. This setting also controls an Auto Off counter
feature, which powers the device down when power is
disconnected, as the vehicle is turned off.
Auto Detect Profile
The Auto Detect Profile turns on and off the ability to
automatically switch between detection profile (Analog, QAM,
Pilot/QAM, and OFDM) based on GPS coordinates. Different
sections of the cable network can have different channel
lineups and can utilize different modulation format, or can
be in R-PHY node areas. Since the detection schema can be
different in different areas, the Auto Detection Profile feature provides a means to for
the detector to automatically switch to the correct detection profile without user
involvement. The QAM Snare Server communicates with the detector and based upon
its GPS location tells it which mode it should be in. Additionally, when Auto Detection
Profile is ON, and Wi-Fi & QS Server credentials have been entered, the Snoop will
connect to a selected server to send GPS Time and coordinates to the server. This is
used to log Snoop usage activity only, and no leakage data is recorded. “GPS SYNC” is
required when Auto Detect Profile is turned “ON”.
When Auto Detection Profile is ON, the main menu will indicate this by adding
“AUTO” to the detector menu option.

9
Standard
This allow to change the television standard between
NTSC, PAL B/G, and PAL D/K so the proper channel listing
can be selected. It is a one-time setup parameter.
Exit
Exit returns to the higher-level menu screen. Select and
press enter.
Connection
The connection menu item is used to select the QAM
Snare server and Wi-Fi devices the Snoop connects to.
Specifics related to these connections must be entered using
the Q-browser software program by connecting a PC to the
device through the USB port on the cradle. Multiple profiles
may be entered, and the connection setting allows the user to select from previously
entered profiles, but it will not allow profiles to be entered directly into the Snoop.
QS Server
The QAM Snare Server which the
device needs to connect to is
selected here. Press enter and the
profiles of servers previously
configured through the Q-browser
are displayed, with the server name
and IP address displayed. To select a different server press next server. If the required
server is not displayed it must be configured through the Q-browser. Multiple server

10
profiles would only be necessary for the technician that works in areas covering more
than one server.
For clarification, a typical QAM Snare installation will have multiple hubs connected
to one server that covers a broad area. One signal processor hardware device is
required in each hub, and the signal processors communicate with the QAM Snare
server when in QAM Detector mode. The server monitors the GPS location of each
connected field device and coordinates that each device receives signal samples
appropriate for the hub the field device is currently located. This setting has nothing
to do with signal processors as that is managed by the server – just multiple server
addresses.
Wi-Fi profile
The Snoop is a Wi-Fi enabled device that requires
connectivity to operate in QAM detector mode. Profiles that
were previously entered into the device through the Q-
browser are selected through this menu item. Multiple
profiles may be stored in device, and selected when desired.
Walk mode -vs-Truck mode
Other QAM Snare products such as the Navigator Plus utilize a Truck mode and
Walk mode concept for how the device operates when it is cradled and when it is used
by the technician moving around. Since the Snoop is designed to be used only while
moving around outside the vehicle, it inherently operates in Walk mode, as has no
Truck mode capability.

11
Detector Settings
QAM Snare Snoop is very flexible as to how it operates.
Specifics related to the desired detector settings are
configured here.
Signal Mode
Signal mode is the terminology used to describe the leakage
detector operating in Analog, QAM, Pilot/QAM or OFDM
modes. If it desired to use any of these modes - then Signal
mode needs to be turned to On. When Signal mode is turned
off, the unit will only operate in Shielding Test mode (used in
conjunction with a Pilot transmitter device for in-home
troubleshooting) and the unit will automatically go into Shielding Test mode when the
Detector setting is selected.
If the unit will not allow you to select QAM, analog, or
OFDM modes and that is what you would like to do, then the Signal mode needs to be
turned on.
Channel
This is where the leakage detector channel and channel
format is selected for QAM, Analog, Pilot/QAM and OFDM
modes.
Snoop can operate simultaneously at two frequencies one
above and one below 650MHz. The channels below 650MHz
are considered to be the low band and the channels above
650MHz is considered to be the LTE band. Low band allows selection of OFDM, QAM,
Pilot/QAM, Analog, or OFF. LTE band allows selection of OFDM, QAM, or off.
To configure, the logic is to select the desired band and press enter. The arrow
buttons will cycle between available modulation formats or off – press enter for the
desired selection.

12
The next step is to select the desire channel or frequencies for the selected
modulation format within the selected band, and then configure for the specifics and
details related to the selected modulation format as described below.
After one frequency band is configured, navigate to the Next band line and press
enter, then repeat the process for the second band. When Auto Detection is enabled,
the QS server will control the detection channel and will over-ride any channel settings
configured on the local detector.
Channel - Analog detection
When Analog detection is selected, in addition to the
channel configuration, an option to use analog tagging is
available. From the Low band line, press enter, then use the
arrow keys to select Analog.
Analog detection option is not available as a selection
option for the LTE band.
Analog channel
To select the channel, navigate to the Channel line, press
enter, and then use the right and left arrow keys to select the
desired channel.
If the channels displayed are different from the television
standard utilized in your network, go to the General settings
page, select Standard, and change to the appropriate desired television standard.
Tag confirmation on/off
If utilizing an existing AM tagging system is desired, then
the TAG confirm option needs to be set to ON. Navigate to
the TAG confirm line, press enter, use the arrow keys to
toggle ON/OFF.

13
Tag frequency
The TAG frequency must be configured to match the
frequency of the utilized tag system. Default is 20 Hz. To
change to a different frequency, navigate to the TAG
frequency line, press enter, and use the arrow keys to select
desired modulation frequency. Selectable options range
from 10 – 30 Hz.
Channel - QAM detection
From either the Low band or LTE band selection line,
press enter, use the arrows to select QAM, then press
enter.
QAM channel
To select the QAM channel, navigate down to the Channel
line, press enter, and use the arrows to select the desired
frequency.
After selecting the channel, navigate down to Next band
and repeat the process to configure the second channel.
For QAM detection, it is recommended to use only channels configured as Global
Channels in the QAM Snare Manager Program to avoid channel contention issues. Each
server is only able to process four different channels, and all users connected to the
server must operate only on those four channels.
Channel – OFDM detection
From either the Low band or LTE band selection line,
press enter, use the arrows to select OFDM, then press enter.

14
OFDM channel
To select the OFDM channel, navigate down to the
Channel line, press enter, and use the arrows to select the
desired frequency.
OFDM detection continuous pilot harmonics
Two harmonics of the OFDM continuous pilots are utilized
for OFDM detection. The two harmonic frequencies MUST
both we within the bandwidth of the selected OFDM channel,
and for optimum performance the two harmonics should be
selected at the maximum spacing within the channel. The
EXACT frequency of each pilot harmonic must be entered. It
is recommended that the device is configured to enable the
Auto Detection Profile such that exact harmonic frequencies
do not need to be loaded into the detector, and the detector
acquires the information from the QS Server. The method to
determine the pilot harmonic frequency is beyond the scope
of this document, consult with your supervisor to get the proper frequency
information.
If it is required to add this information manually to the detector, once the frequency
information is acquired, first navigate to the CP1 line item and press enter. The cursor
will move to the first frequency digit. If this digit needs to be changed, press enter,
then use the left and right arrow to increment or decrement the digit. Press the enter
button to confirm the selection. The use the right arrow to move to the next digit that
needs to be changed and repeat the process. The right arrow can also be used to skip
digits if they do not need to be changed. Once this process is finished, continue to
press the right arrow to highlight MHz, and the entire line as entered will be accepted.
Then for the next CP2 line, repeat the process for the second harmonic of the
continuous pilot within the selected channel bandwidth – press the right arrow to move
the cursor to the far right to accept changes. Frequencies can also be configured using
the Q-browser, and it is recommended to do so such that the exact frequency can be

15
cut and pasted as a more foolproof configuration process – if Auto Detection is not
being used.
Error CP1 or CP2
If you receive this error message after selecting the two
harmonic frequencies, it indicates that the selected
frequency is outside of the bandwidth of the selected
channel. Repeat the configuration step and ensure the
selected frequencies are within the channel.
Pilot/QAM mode
The Pilot/QAM option is used to detect a leakage test
signal comprised of a pair of low-level CW carriers separated
by 6 MHz, with one of the carriers injected at the channel
boundary on the lower edge of the Single Carrier QAM (SC-
QAM) signal, and the second CW carrier injected at the
channel boundary on the upper edge of the same SC-QAM
signal. The Pilot/QAM carriers are precisely placed at the QAM band edge, ± 5 kHz.
This setting is typically utilized in Remote-PHY systems.
Leakage Detector Pilot/QAM mode Channel and Frequency Selection
Once Pilot/QAM mode has been selected it is necessary adjust frequency and level
parameters for detection. Using the Arrows and Enter keys, select “Channel” and press
Enter. Select the desired leakage detection channel using the Arrow and Enter Keys.
Leakage Detector Pilot/QAM mode Code #
To simplify the setup of specific pilot frequencies the Snoop presents codes for the
operator to select a desired pair of frequencies. To set the Pilot/QAM detector
frequency use the Arrows and Enter keys to select “Code” and press Enter. Now
continue with the Arrow keys to select the desired leakage detection code
(frequencies). Press Enter again and you will see the channel you selected, Pilot Level,
and Frequency code.

16
There are four possible channel codes for every detection channels used by Arcom,
intended to provide flexibility in overbuild situations. Table 1 below illustrates those
frequencies. To select the desired code, simply select Code# and use the Up and Down
arrows to select the desired frequency code.
Table 1: Code # vs Pilot Carrier Frequencies
As illustrated above, the Pilot Carriers are typically offset
-30 dBc with respect to the channel level. However, if the
pilot carriers are above or below -30 dBc then the Snoop
Pilot Level requires adjustment so the detected leakage levels
are accurate. To adjust the Pilot Level offset, select the “Pilot
Lev, dB:” options and use the right and left arrows and the
enter button to set the offset accordingly.
Shielding Test mode
To quickly and easily troubleshoot difficult ingress problems in the home, Snoop is
able to operate as a Shielding Efficiency (SE) detector. Operation in this mode requires
the use of a QAM Snare Pilot transmitter device.
The transmitter is connected at the grounding block in place of the home coax feed
(the home is disconnected from the cable network when the transmitter is used) or at
the tap. The transmitter places a high level, easy to find signal at the frequency which
is programmed into the transmitter when setting up. The process of how to configure

17
the transmitter is described in a later section of this manual. Shielding Test Pilots can
be used in either the LOW band, LTE band, or both.
The Pilot Transmitter generates two carriers in each band at frequencies equivalent
to the Pilot/QAM detection scheme described above at one selectable channel in each
of the LOW and LTE bands. Two pilot carriers are utilized in both the aeronautical and
LTE bands to minimize multipath effects and to make the product easier to use. When
using this mode, since the transmitter is located at the grounding block – there is no
visibility to leaks in the drop between the multi-tap and the grounding block. Because
of this, and because of the extra time required to install and to retrieve the transmitter,
it is only recommended to use this test mode when troubleshooting specific problems.
Shielding Test ON/OFF
To turn Shielding Test mode on, navigate to the
Shielding Test: On/Off line, press enter and change the
setting to ON.
If you do not plan on using this option, turn it to OFF
such that it does not appear as a menu option when you
enter the Detector screen.
Shielding Test Channels
To configure the Shielding Test channels, navigate to the
“Channel” option and press enter. The LOW band of
frequencies will appear first. Select the line titled “Channel”
and use the right and left arrows, and the enter button to
select the desired Low Band channel
Shielding Test Code
Select the desired Code (as described in Table I above).

18
Pilot Level
The Transmitter RF output level is +46 dBmV, but there are many scenarios where
the test pilot signal level will be lower. For example, if a
splitter is connected after the grounding block, the
transmitter signal will be attenuated 7 to 8 dB. So, an
adjustment to the receiver will be necessary. Assuming the
splitter is 3 or 4-way, the Test Pilot RF output of the splitter
will be +39 dBmV. In this situation the Snoop Pilot Level
setting should be set to +39 dBmV. (+46 dBmV pilot out – 7.5 dB splitter attenuation).
Next Band
To configure the LTE pilot, select Next Band and the select the channels, code and
Pilot Level as done in the Low band
Remember that prior to using the Pilot transmitter, the transmitter needs to be
connected to the cradled Snoop via USB such that the pilot settings configured in
Snoop can automatically be transferred to the Pilot transmitter. After initial setup this
connection process is only required when a change is made to the Snoop pilot settings.
Leak Alarms
The Snoop can be configured to provide low and high
level audio alarms based upon the amplitude of the detected
leak, for both bands of operation in Signal alarm mode (QAM,
OFDM, or Analog) and in Shielding Test alarm mode. The
alarm is based upon the leak level at the detector.

19
Signal alarms
To change the alarm value for both the low and LTE
bands, use arrow keys to navigate to the item you would like
to change, press enter and then use the arrow keys to
increase or decrease the number.
SE Test alarms
The Shielding Test alarms also display a shielding
effectiveness indicator, which equates the detected signal to
shielding effectiveness. From this setting, one can see that it
is possible to locate very small leaks which could be the
source of forward ingress from close proximity transmitters
such as LTE devices.
To change the alarm value, navigate to the alarm level
indicator and use the arrows to increase or decrease the
alarm setting.
Calibration
The calibration setting is used to normalize the setup to a
known leak with a known level, and to compensate for
antenna variations, and other internal variations. Calibration
Factors” are factory set for the type of antenna supplied with
each Snoop.

20
Changes to calibration are password protected, and
should only be done by users familiar with the process. This
process is minimally important for Snoop since leak
detection results are not updated to the server.
Detector Mode
The detector mode is used when the user wants the leak
detector to locate leaks. When the device is placed in
detector mode, if both Signal and Shielding Test are turned
on, it will ask which mode the user would like to enter.
Select the desired Signal or Shielding Test Mode.
If the device is configured for only one mode, either
Signal or Shielding Test – the detector will directly enter the
configured mode and not ask this question.
Detector Mode – when configured for QAM detection
QAM detector mode is only available when the device is pulled from the cradle and
when GPS-Hold is indicated on the display. When the unit is placed back in the cradle
it will automatically exit QAM detector mode. Typically,
Snoop will be configured for single or dual frequency
detection at either the LTE and/or Aeronautic band. The user
needs to ensure that the correct antenna is connected to the
antenna input for the selected frequency and band. When
operating in one frequency band the Snoop will sample the
selected channel two times per second. A screen sample
showing single channel detection is shown to the right.
Snoop can simultaneously detect leaks at two channels,
one each within the low and the LTE band. This mode should
Table of contents