CYC5000 User Guide www.arrow.com
Page | 2 March 2023
Table of Contents
Table of Figures.......................................................................................................................................... 4
CYC5000 IoT / Maker Board ............................................................................................... 5
1.1 About Arrow CYC5000 Board .............................................................................................................................5
1.2 Useful Links ..............................................................................................................................................................5
1.3 Getting Help.............................................................................................................................................................6
Introduction to the CYC5000 Board................................................................................. 7
2.1 Layout and Components ................................................................................................................................... 7
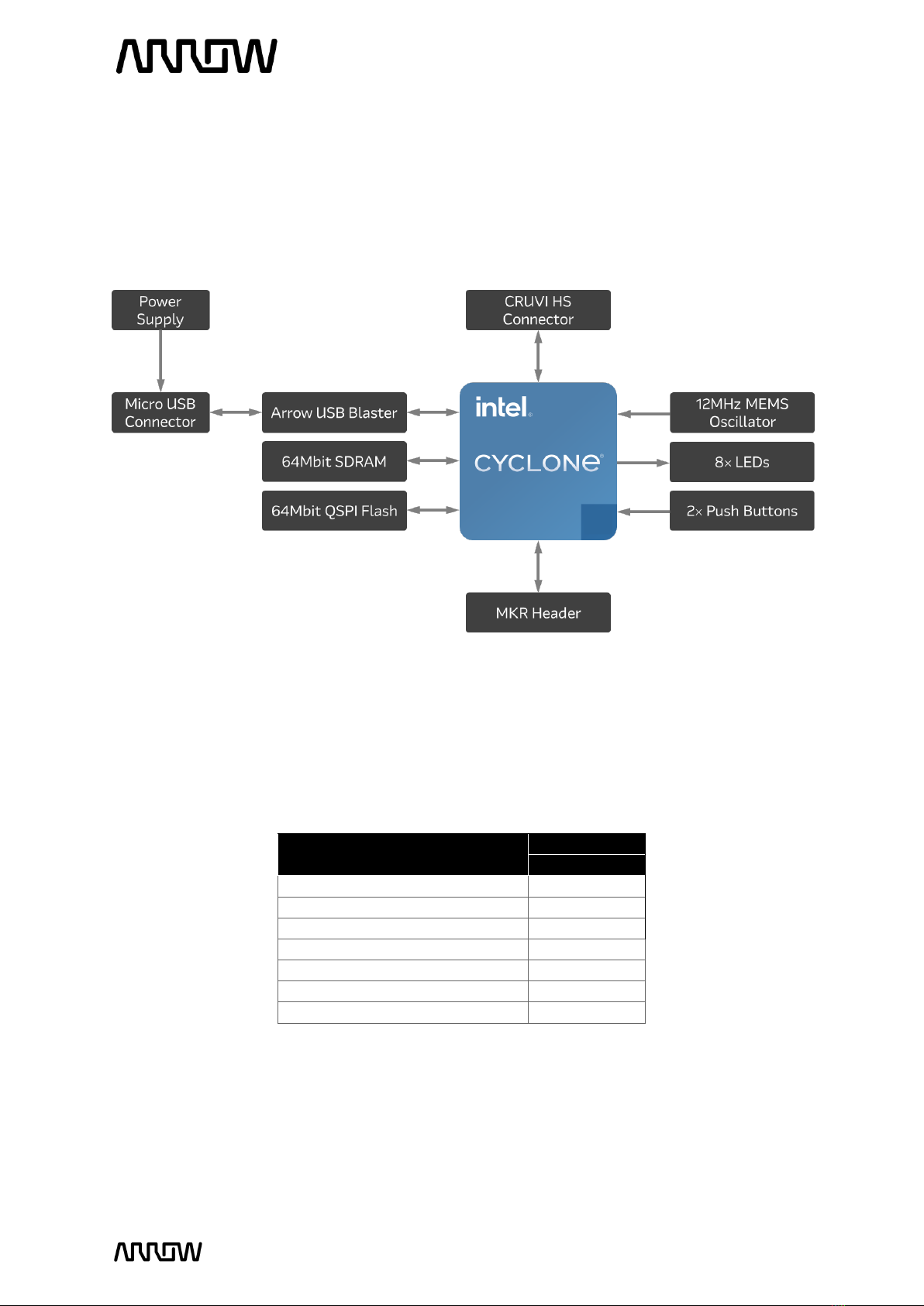
2.2 Block Diagram.........................................................................................................................................................8
Connections and Peripherals of the CYC5000 Board ................................................. 10
3.1 Board Status Elements.....................................................................................................................................10
3.2 Clock Circuitry ......................................................................................................................................................10
3.3 Peripherals Connected to the FPGA ..........................................................................................................11
3.3.1 Communication and Configuration...................................................................................................11
3.3.2 QSPI Configuration Flash Memory ...................................................................................................13
3.3.3 SDRAM Memory.........................................................................................................................................14
3.3.4 CRUVI HS Connector ...............................................................................................................................16
3.3.5 Arduino Header ..........................................................................................................................................18
3.3.6 LEDs .................................................................................................................................................................19
3.3.7 Push Buttons ..............................................................................................................................................20
3.3.8 Power Tree....................................................................................................................................................21
Software and Driver Installation..................................................................................... 23
4.1 Installing Quartus Prime Software............................................................................................................23
4.2 Installing Arrow USB Programmer2..........................................................................................................25
4.3 License ..................................................................................................................................................................... 27
New Project with CYC5000 ..............................................................................................29
5.1 Creating a new Blinky Project with CYC5000 .....................................................................................29
5.2 Building a Blinky Project with CYC5000................................................................................................33
5.2.1 Block Diagram............................................................................................................................................33
5.2.2 Components of the Design .................................................................................................................34
5.2.3 Catalog IP .....................................................................................................................................................34
5.2.4 Create and Configure PLL ....................................................................................................................34
5.2.5 Create and Configure the Counter..................................................................................................36
5.2.6 Create and Configure the Multiplexer...........................................................................................39
5.2.7 Adding the Components to the Schematic..................................................................................41
5.2.8 Connecting the Components .............................................................................................................43