Automess 6150AD User manual

Contents
1. General
........................................
2
.......
2. Data Outputs
...................................
3
.......
2.1 »Term«
....................................
3
.......
2.1.1 Hardware Characteristics
............
3
.......
2.1.2 Software Characteristics
.............
4
.......
2.2 »Control«
..................................
6
.......
2.3 4.75V
.....................................
7
.......
3. Appendix: Data Inputs
.........................
8
.......
3.1 »PL« and »S/E« Lines
......................
8
.......
3.2 »Ext« Input
................................
10
......
3.3 Probe Characteristics
......................
11
......
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420
Automation und Messtechnik GmbH
23 June 2003
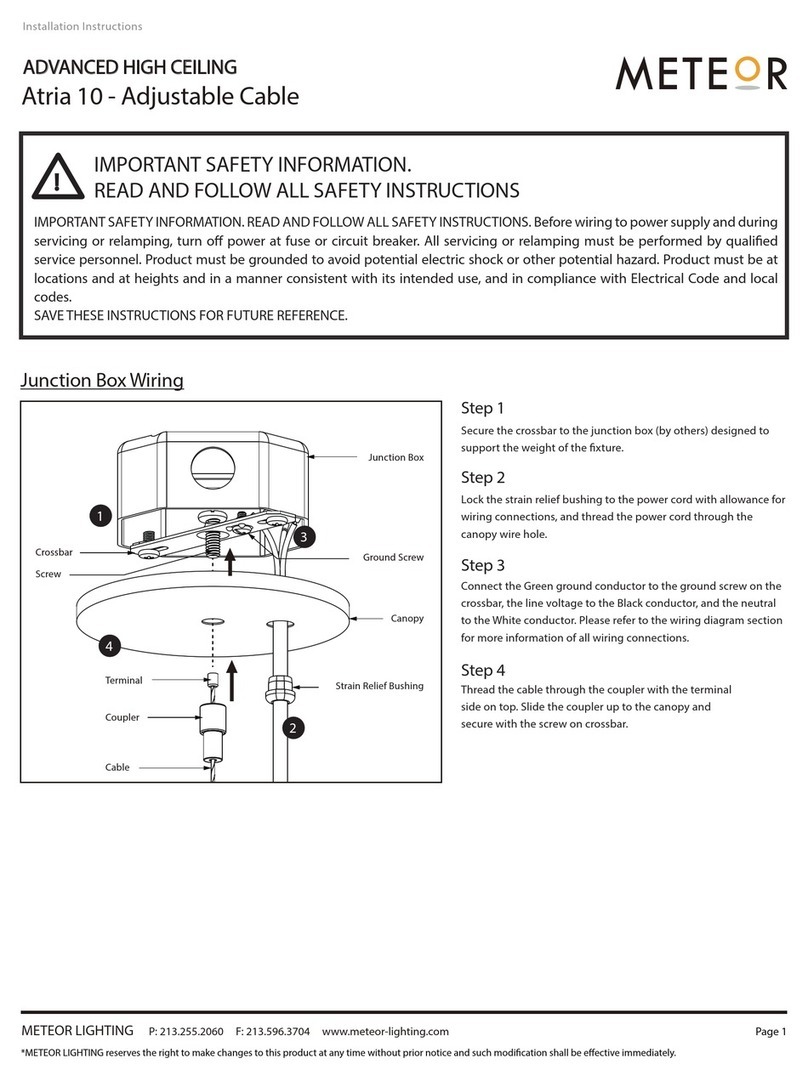
Dose Rate Meter 6150AD:
Probe Connector
Technical Manual

1
.
General
As implied by its name, the 6150AD probe connector serves for connecting external probes to the
6150AD. However, the probe connector offers additional features, especially to read the 6150AD
instrument by a computer (which is used e.g. by the Automess Dose Rate Acquisition Systems
DES11/12/13). This manual shall provide information to 6150AD users how to use the output signals for
own applications. Throughout this manual it is assumed that the reader is familiar with the operation of
the 6150AD series instruments.
Pin assignment of the probe connector is as follows:
Contrary to e.g. sub-D connectors the pins are not numbered on the body of the connector due to lack of
space. Instead the six pins were given the names indicated above (which are names taken from the
schematics of the 6150AD). All further discussions of the signals will refer to these names. The colours in
parentheses are those of the wires in the Automess standard probe cable. So the easiest way to access the
signals for testing or for connecting some user equipment would probably be to cut a standard probe cable
into two equally sized pieces, which would give two test cables at a time.
The purpose of the signals is listed below an will be discussed in more detail later:
GND
Ground potential. Note that there is no pin for GND. The cable shield serves both as shield
and as ground connection. The aluminium housing of the 6150AD and the AD probes is
electrically equal to GND.
4.75V
Supply voltage for external probes. Identical to supply of 6150AD internal electronics.
PL, S/E
Signals needed for serial readout of probe data (probe type and calibration parameters). PL
(»parallel load«) is an output used to load these data into a shift register. S/E
(»Senden/Empfangen« = »transmit/receive«) is a tri-state bidirectional line used to clock
and read the shift register.
Ext
Pulse input from external probes. External pulses will only be counted if an external probe
was recognized through lines PL and S/E.
Term
Serial output similar to RS232 (»terminal«) for a periodic readout of dose rate by a
computer.
Control
Output to switch between the two GM counters in the telescopic probe AD-t.
External probes require all lines except Control and Term. The two detector probe AD-t additionally
requires the Control line. Term is not required by any probe.
Term (pink)
Control
(gray)
GND (shield)
4.75V (green)
Ext
(brown)
PL (white)
S/E (yellow)
06/2003
Technical Manual 6150AD Probe Connector
Page
2
of
14
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420

Lines Term, Control, and 4.75V are data and power outputs, respectively. They will be discussed in the
next section »Data Outputs«. Lines PL, S/E, and Ext can be regarded as data inputs when using the
6150AD as a ratemeter for external probes. Data inputs will be covered in the appendix »Data Inputs«.
However, this appendix contains confidential information and will be added to this document only on
special request.
2
.
Data Outputs
2
.
1
»Term«
The 6150AD calculates a new dose rate value approximately every second and outputs this value as a
string of characters through the Term line. This can be used to read the 6150AD by a computer through a
serial RS232 interface. Output characters are binary and thereby not suitable to be viewed directly on a
serial terminal or printer. The time between two subsequent output strings may vary slightly due to
varying microprocessor load. Nevertheless, counting strings may also be used for time measurement,
since the average time between two strings is exactly equal to 1.049 seconds (2
20
µs) as derived from the
internal quartz.
Term acts purely as a transmitter, there is no way to feed data into the 6150AD or to request a repeat in
case of transmission errors. Also, there are no handshake signals to control the Term output.
2
.
1
.
1
Hardware Characteristics
The Term line is a CMOS gate output with an impedance of several hundred Ohms. Its driving
capability is therefore at least equivalent to RS232 interfaces. Nevertheless, cables should be restricted to
maximum lengths as with RS232 interfaces (15m at 9600Bd, 30m at 4800Bd, etc.). Contrary to RS232
lines the Term output is not short circuit proof and swings between GND and 4.75V because there is no
negative voltage available in the 6150AD.
Term output
RS232 output specs
RS232 input specs
logical »0«:
+4.75V
+5...+15V
> +3V
logical »1« (marking state):
GND
-5...-15V
< -3V
Although the positive Term level of 4.75V does not completely meet the RS232 specification of +5V
minimum, it should be properly recognized by any RS232 device, since any voltage above +3V has to be
recognized as the positive level. The GND level however lies in the undefined range from -3V...+3V.
Fortunately almost all RS232 devices recognize GND level as the negative level. So far we only met one
exception in a many years old IBM serial/parallel adapter using a 75154 input buffer. This input buffer
changes and stores its state only if its input level is outside the -3V...+3V range. If this rare case should
occur, the remedy would be to feed Term through a 1 nF capacitor into the RS232 interface. This
capacitor will differentiate GND to +4.75V and +4.75V to GND transitions to positive and negative
spikes, which will be recognized and stored by the 75154.
06/2003
Technical Manual 6150AD Probe Connector
Page
3
of
14
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420

A typical setup to read the 6150AD by a PC (optionally with a probe connected) would be:
The cable EB84-0193 is basically a probe extension cable with a »T« connection making the GND and
Term signals available at the 9 pin sub-D connector.
2
.
1
.
2
Software Characteristics
Interface settings are
4800 Bd (9600 Bd for special 6150AD1-BiZa version)
8 data bits
no parity
1 stop bit
The character string sent approximately every second consists of the following six bytes:
1
.
STX (02H) as the start of text character
2
.
type of detector/6150AD
3
.
dose rate mantissa (low byte)
4
.
dose rate mantissa (high byte)
5
.
dose rate exponent
6
.
block check character
The second byte (type of detector/6150AD) contains:
Bit 0-5:
detector in use:
0 = probe 6150AD-0
7 = probe 6150AD-b
15 = probe 6150AD-15
17 = probe 6150AD-17
18 = probe 6150AD-18
19 = probe 6150AD-19
20 = 6150AD internal tube
21 = probe 6150AD-t, low range tube
22 = probe 6150AD-t, high range tube
Bit 6:
type of internal tube:
0 = ZP1200 (6150AD2/4/6)
1 = ZP1310 (6150AD1/3/5)
Bit 7:
measuring quantity:
1 = 6150AD »/E« model (6150ADx/E)
0 = other (6150ADx or 6150ADx/H)
PC
standard probe cable
probe (optional)
connecting cable »PC - 6150AD - probe«
DB-9
Automess part number EB84-0193
6150AD
06/2003
Technical Manual 6150AD Probe Connector
Page
4
of
14
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420

Bytes 3-5 contain the current dose rate reading in floating point notation, where bytes 3 and 4 contain
the 16 bit positive mantissa and byte 5 is the signed (-128...+127) 2-based exponent. The unit is µSv/h
(pulses per second for pulse rate indicating probes like 6150AD-k, AD-17, AD-19).
Byte 6 is the XOR (exclusive OR) of Bytes 2-5 and is intended to be used as a block check character to
detect transmission errors.
The following QBASIC program gives an example how to decode the string:
' Variable Types
DEFINT A-W
DEFSNG X-Z
' Constant Expressions
CONST STX = 2
CONST DEVERR = 57
' ---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Main Program
' ---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Open COM: 4800 Bd, no parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop,
no handshake
OPEN "com1:4800,n,8,1,rs,cs,ds,cd" FOR INPUT AS #1
ON ERROR GOTO RecvErr
' Main Loop: read and decode string
(6 characters including STX),
' display result, exit on any key.
MainLoop:
DO
WHILE ASC(INPUT$(1, #1)) <> STX: WEND 'wait for STX
sonde = ASC(INPUT$(1, #1)) 'type of detector/6150AD
bc = sonde
mantlo = ASC(INPUT$(1, #1)) 'low order mantissa
bc = bc XOR mantlo
manthi = ASC(INPUT$(1, #1)) 'high order mantissa
bc = bc XOR manthi
expon = ASC(INPUT$(1, #1)) 'exponent
bc = bc XOR expon
IF expon > 127 THEN expon = expon - 256
bc = bc XOR ASC(INPUT$(1, #1)) 'block check
IF bc <> 0 THEN ERROR DEVERR 'block check error
mant = manthi * 256 + mantlo '16 bit mantissa
xdl = mant * 2 ^ (expon - 15) 'dose rate as floating point number
GOSUB GetProbe 'set ger$, det$ and unit$
PRINT TIME$; " Device: 6150"; ger$; " Detector: "; det$;
PRINT USING " Reading=########.### "; xdl;
PRINT unit$
LOOP WHILE LEN(INKEY$) = 0 'exit on any key
PRINT "End."
END
' ---------------------------------------------------------------------
' set ger$ / det$ / unit$ according to
'sonde'
' ---------------------------------------------------------------------
GetProbe:
flag
$ = ""
IF sonde >= 128 THEN
flag
$ = "/E": sonde = sonde - 128
ger$ = "AD2/4/6" +
flag
$
IF sonde >= 64 THEN ger$ = "AD1/3/5"
+
flag
$
: sonde = sonde - 64
det$ = "unknown"
unit$ = "µSv/h"
SELECT CASE sonde
CASE 0
det$ = "Probe AD-0"
unit$ = "cps"
CASE 7
det$ = "Probe
AD-b"
CASE 15
det$ = "
Probe
AD-15"
CASE 17
06/2003
Technical Manual 6150AD Probe Connector
Page
5
of
14
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420

det$ = "
Probe
AD-17"
unit$ = "cps"
CASE 18
det$ = "
Probe
AD-18"
CASE 19
det$ = "
Probe
AD-19"
unit$ = "cps"
CASE 20
det$ = "internal GM"
CASE 21
det$ = "AD-t low DR"
CASE 22
det$ = "AD-t high DR"
END SELECT
RETURN
' ---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Handler for transmission errors
' ---------------------------------------------------------------------
RecvErr:
IF ERR = DEVERR THEN PRINT TIME$; " Transmission Error": RESUME MainLoop
ON ERROR GOTO 0
2
.
2
»Control«
This output switches between the two GM counters in the telescopic probe AD-t, where Control = high
(4.75V) selects the low dose rate GM counter, and Control = low (GND) selects the high dose rate GM
counter. If any other or no probe is connected, Control will always be high.
Certain software versions of the 6150AD (e.g., the Swedish version V-36.04) make additional use of the
Control output: With the AD-t probe, Control will operate as described above. With any other or no probe
the Control output will signal dose rate alarm: Control = high indicates that dose rate alarm is off, and
Control = low indicates that dose rate alarm is on. This allows triggering of external alarming devices.
However, one has to consider that the Control output can only drive very small loads due to its internal
structure:
The microprocessor port can sink only a few mA and can source almost no current, because the high state
is achieved through a weak pull-up resistor of 10-100 kOhms depending on the manufacturer of the
microprocessor. The Control output can therefore only drive high impedance low capacity inputs like
CMOS gates as shown in the drawing above. Such buffering is strongly recommended before connecting
some external device.
micro-
processor
port
1 kOhm
6150AD
4.75V
Control
GND
buffered
output
(e.g. 4049, 4069, 40106)
(inverted)
CMOS gate 4000 series
06/2003
Technical Manual 6150AD Probe Connector
Page
6
of
14
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420

2
.
3
4.75V
This section describes line and load characteristics of the 4.75V output which may be used to supply
external devices. As will be shown, up to 50 mA may be drawn from this output. This seems a reasonable
limit when keeping in mind that battery life with an external device should still amount to several hours.
The 4.75V output voltage is generated inside the 6150AD out of the battery voltage by means of a
switched regulator. It is individually tested in serial production to be in the range of 4.65V to 4.90V with a
typical value of 4.75V (at an input battery voltage of 7.0V).
no load
RL = 82.5 Ohm
U
in
V
U
out
V
I
in
mA
U
out
V
I
out
mA
efficiency
%
5.0
4.782
52.0
4.320
52.4
87
5.5
4.785
55.0
4.651
56.4
87
6.0
4.789
52.5
4.683
56.8
84
7.0
4.795
46.5
4.724
57.3
83
8.0
4.801
42.0
4.744
57.5
81
9.0
4.807
38.0
4.758
57.7
80
9.5
4.810
37.0
4.765
57.8
78
Note that at input battery voltages below 5.5 volts the 6150AD will issue battery warning.
End of »Data Outputs« section.
Appendix with »Data Inputs« section is only supplied on special request.
in
I
I
out
U
in
U
out
RL
6150 AD
4.75V
GND
06/2003
Technical Manual 6150AD Probe Connector
Page
7
of
14
Daimlerstrasse 27
Telefon
+49(0)6203-9503-00
http://www.automess.de
USt.-ID-Nr. / VAT ID No.
D-68526 Ladenburg
Telefax
+49(0)6203-9503-29
eMail: [email protected]
DE 144 458 420
Table of contents
Popular Cables And Connectors manuals by other brands
Philips
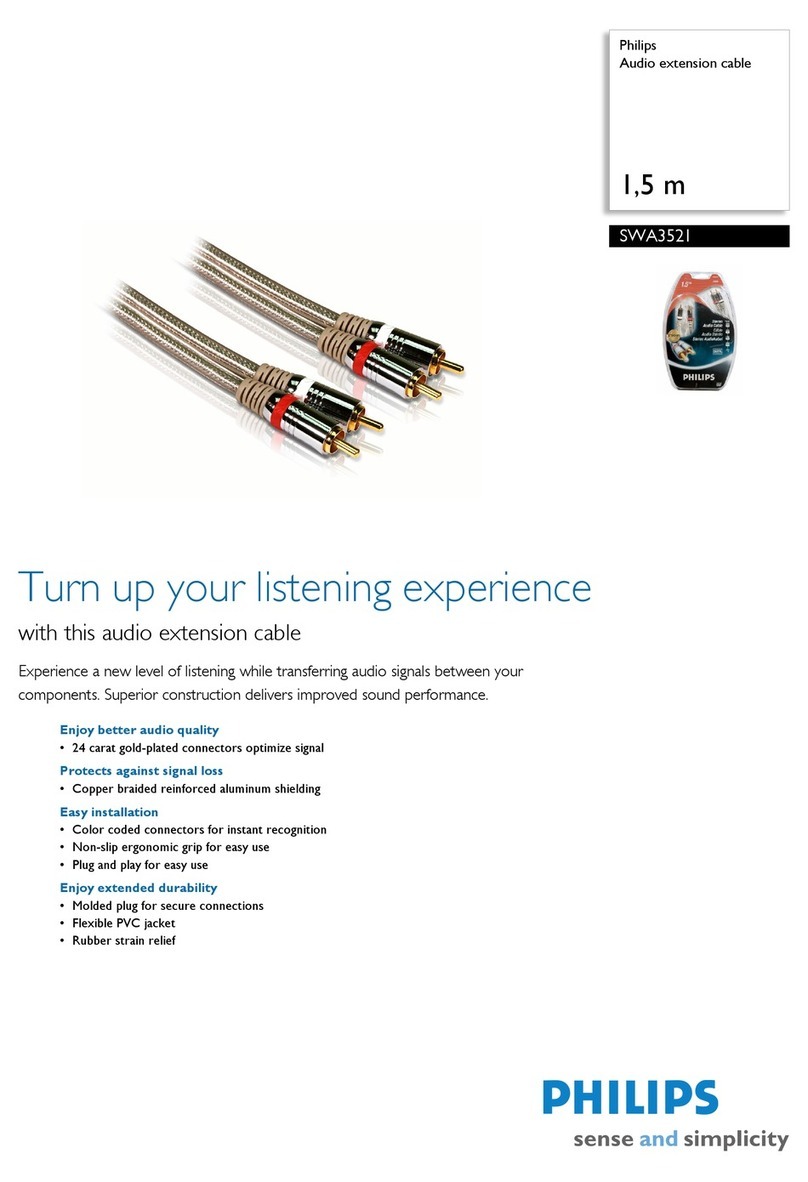
Philips SWA3521 Specifications

Cairn
Cairn OptoSplit II Troubleshooting
Roxtec
Roxtec R Series installation instructions

ATEN
ATEN VS-132 user guide

Tyco Electronics
Tyco Electronics 58062-1 instruction sheet
Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation Allen-Bradley Kinetix 2090 Series installation instructions