V300ATA VoIP User Manual
- ii -
Tables Of Content
1. INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................ 1
1.1 MAIN FEATURES........................................................................................................ 2
2. YOUR ANALOG TELEPHONE ADAPTOR (ATA) AT A GLANCE.................. 3
2.1 PORTS AND BUTTONS ................................................................................................. 3
2.2 LED DESCRIPTION ..................................................................................................... 3
3. INSTALLING YOUR ATA........................................................................................ 4
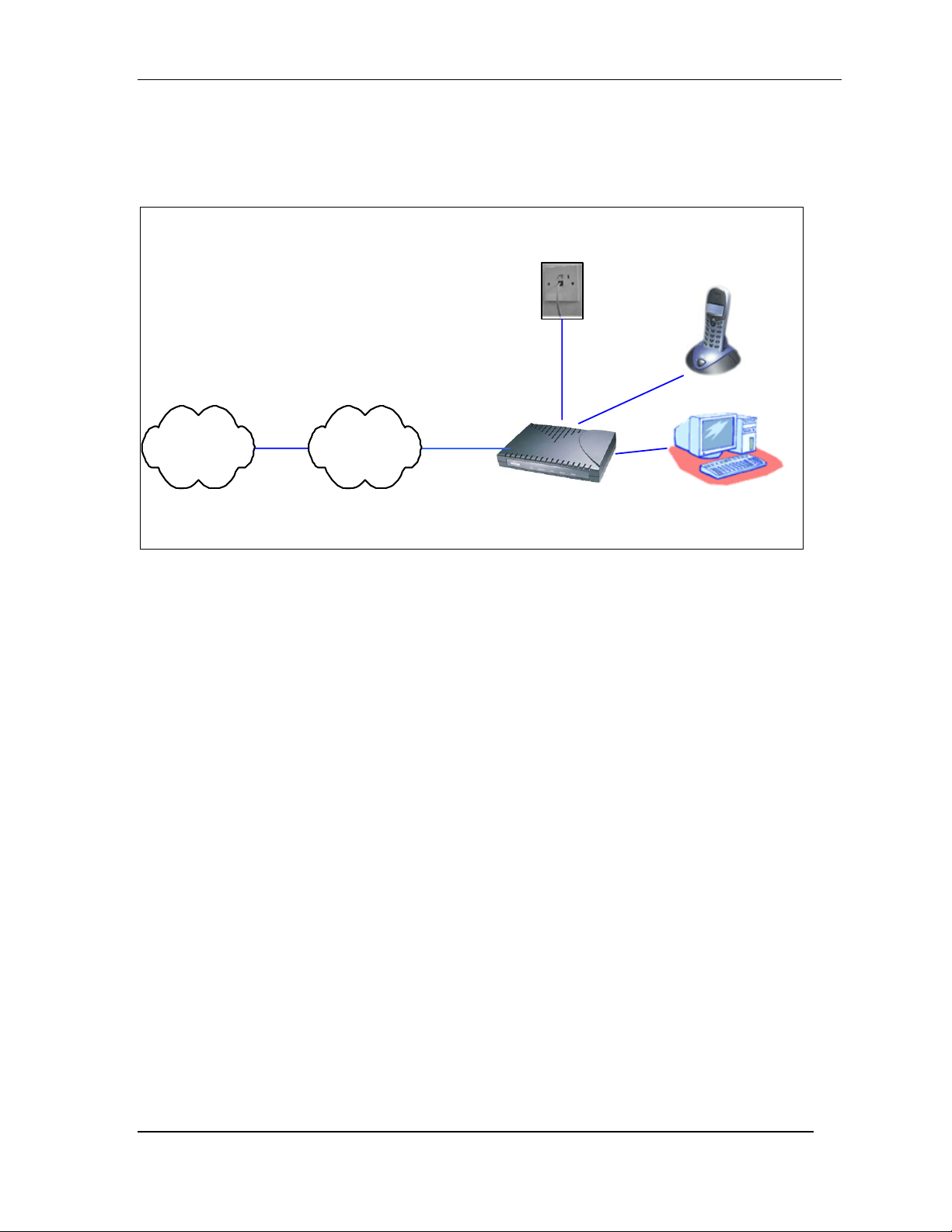
3.1 FOR SINGLE-USER CONNECTION .............................................................................. 4
3.2 FOR MULTIPLE-USERS CONNECTION........................................................................ 5
3.3 FOR COMPANY NETWORK CONNECTION.................................................................... 6
4. SETTING UP YOUR V300ATA ROUTER FUNCTIONALITY VIA GUI .......... 7
4.1 ACCESS TO V300ATA GUI....................................................................................... 7
4.2 SETUP MODE.............................................................................................................. 7
5BASIC MODE........................................................................................................... 8
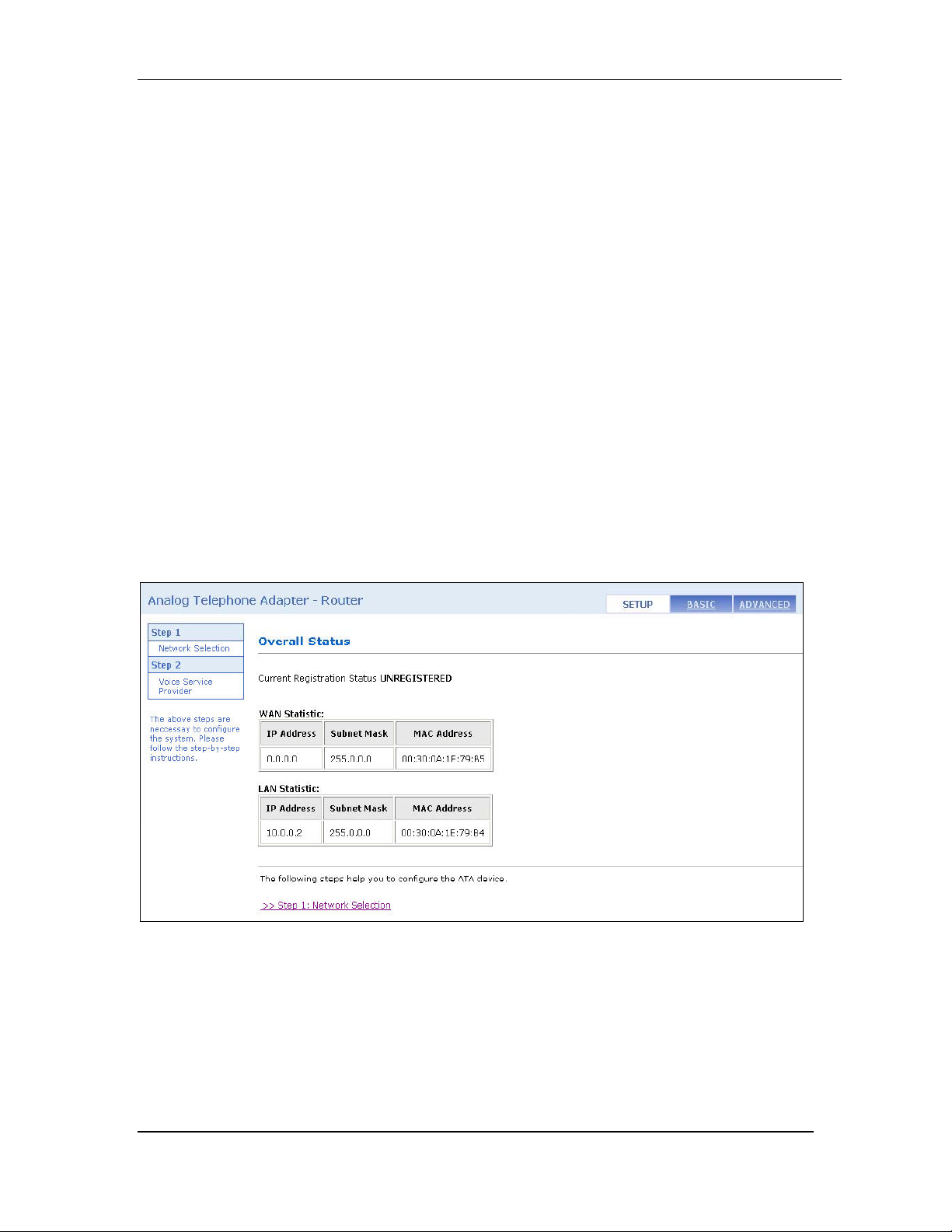
5.1 OVERALL STATUS.................................................................................................... 9
5.2 LAN STATUS......................................................................................................... 10
5.3 DHCP CLIENT STATUS.......................................................................................... 11
5.4 PPP STATUS .......................................................................................................... 12
5.5 TCP STATUS.......................................................................................................... 13
5.6 SYSTEM LOG.......................................................................................................... 14
6 BASIC CONFIGURATIONS................................................................................... 15
6.1 WAN CONFIGURATION.......................................................................................... 15
6.2 LAN & DHCP CONFIGURATION........................................................................... 18
6.3 NAT CONFIGURATION........................................................................................... 20
6.4 PORT FORWARDING CONFIGURATION.................................................................... 22
6.5 BRIDGE FILTERING................................................................................................ 23
6.6 DNS CONFIGURATION........................................................................................... 24
6.7 SAVE SETTINGS / REBOOT ..................................................................................... 25
7. ADVANCED MODE................................................................................................. 27
7.1 ATA CONFIGURATION............................................................................................. 27
7.2 SIP SERVICE PROVIDER CONFIGURATION................................................................ 28
7.2.1 SIP Service Provider........................................................................................ 28
7.3 ATA LOGIN ACCOUNT CONFIGURATION................................................................. 30
7.4 ATA TIMER CONFIGURATION.................................................................................. 32
7.5 COUNTRY SPECIFIC RING & TONES CONFIGURATION............................................ 33
7.6 ATA MISC CONFIGURATION ................................................................................. 35
8. ADMIN PRIVILEGE................................................................................................ 38