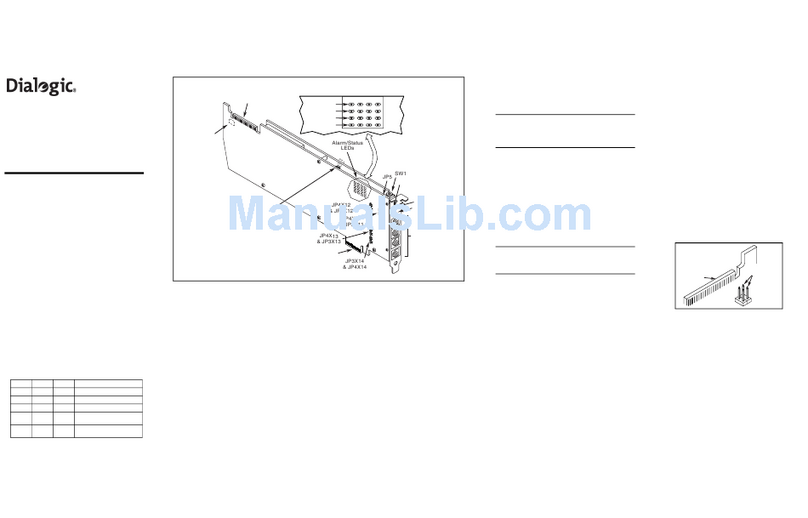
Introduction
3
Introduction
section
1
2
3
4
5
6
2. Avoid Obstacles and Interference
Avoid placing your wireless router (or access point) near devices that
may emit radio “noise”, such as microwave ovens. Other objects that
can inhibit wireless communication can include:
• Refrigerators
• Washers and/or dryers
• Metal cabinets
• Large aquariums
• Metallic-based, UV-tinted windows
If your wireless signal seems weak in some spots, make sure that
objects such as these are not blocking the signal’s path between your
computers and wireless router (or access point).
3. Cordless Phone Placement
If the performance of your wireless network is impaired after attending
to the above issues, and you have a cordless phone:
• Try moving cordless phones away from the wireless router
(or access point) and your wireless-enabled computers.
• Unplug and remove the battery from any cordless phone
that operates on the 2.4GHz band (check manufacturer’s
information). If this fixes the problem, your phone may
be interfering.
• If your phone supports channel selection, change the
channel on the phone to the farthest channel from your
wireless network as possible. For example, change the
phone to channel 1 and move your wireless router (or
access point) to channel 11. (Your channel selection will vary
depending on your region.) See your phone’s user manual for
detailed instructions.
• If necessary, consider switching to a 900MHz or 5GHz
cordless phone.
Placement of your Wireless Networking Hardware for
Optimal Performance
Your wireless connection will be stronger the closer your computer
is to your wireless router (or access point). Typical indoor operating
range for your wireless devices is between 100 and 200 feet. In the
same way, your wireless connection and performance will degrade
somewhat as the distance between your wireless router (or access
point) and connected devices increases. This may or may not be
noticeable to you. As you move farther from your wireless router (or
access point), connection speed may decrease. Factors that can
weaken signals simply by getting in the way of your network’s radio
waves are metal appliances or obstructions, and walls.
If you have concerns about your network’s performance that might be
related to range or obstruction factors, try moving the computer to a
position between five and 10 feet from the wireless router (or access
point) in order to see if distance is the problem. If difficulties persist
even at close range, please contact Belkin Technical Support.
Note: While some of the items listed below can affect network
performance, they will not prohibit your wireless network from
functioning; if you are concerned that your network is not operating at
its maximum effectiveness, this checklist may help.
1. Placement of your Wireless Router (or Access Point)
Place your wireless router (or access point), the central connection
point of your network, as close as possible to the center of your
wireless network devices.
To achieve the best wireless network coverage for your “wireless
clients,” (i.e. computers enabled by Belkin Wireless Notebook Cards,
Wireless Desktop Cards, and Wireless USB Adapters):
• Ensure that your wireless router’s (or access point’s) antennas
are parallel to each other, and are positioned vertically (toward
the ceiling). If your wireless router (or access point) itself is
positioned vertically, point the antennas as much as possible in
an upward direction.
• In multistory homes, place the wireless router (or access point) on a
floor that is as close to the center of the home as possible. This may
mean placing the wireless router (or access point) on an upper floor.
• Try not to place the wireless router (or access point) near a
cordless 2.4GHz phone.