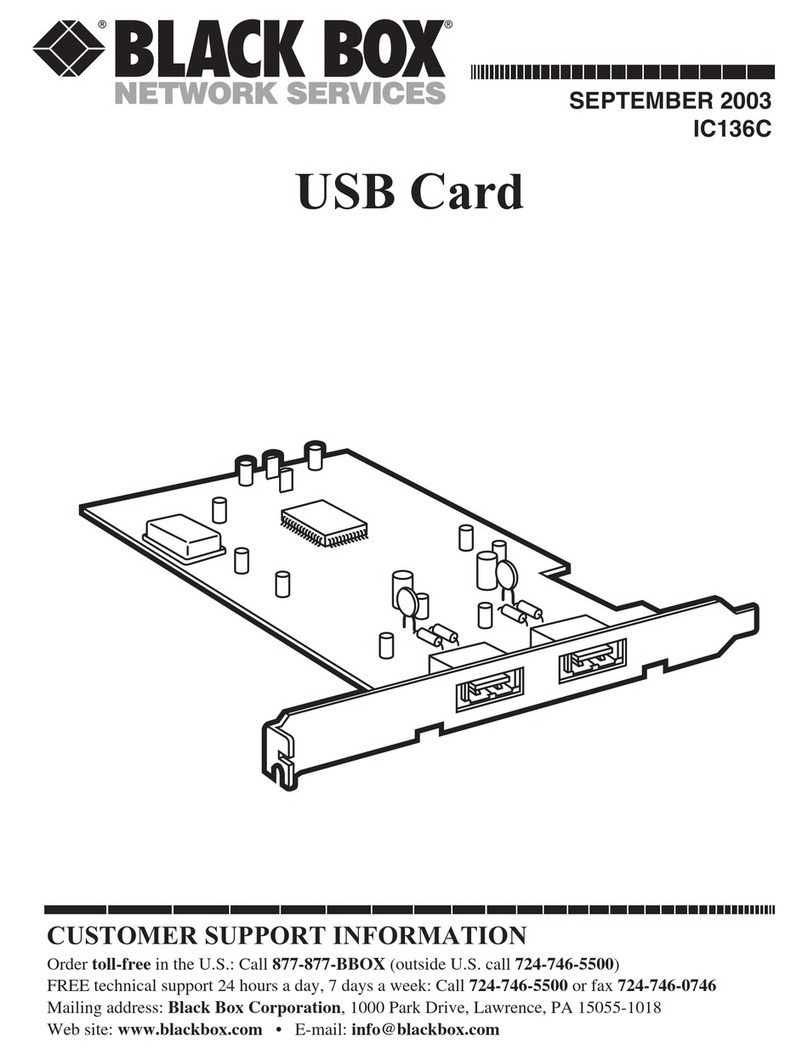
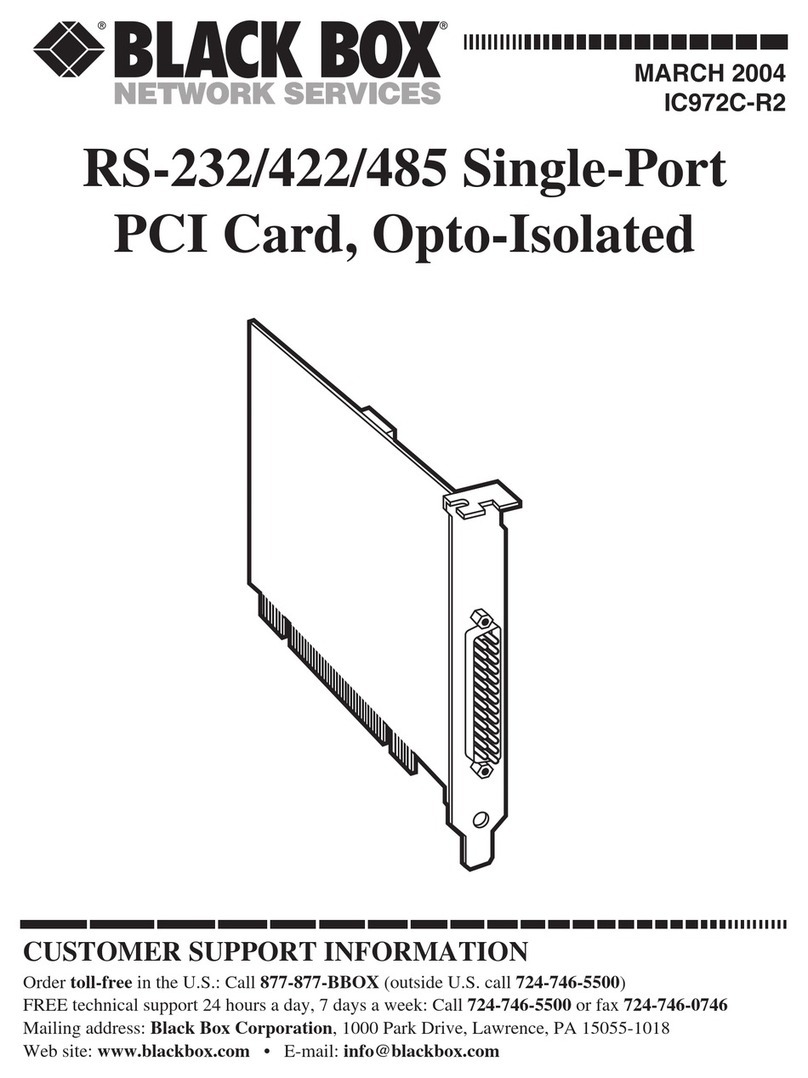
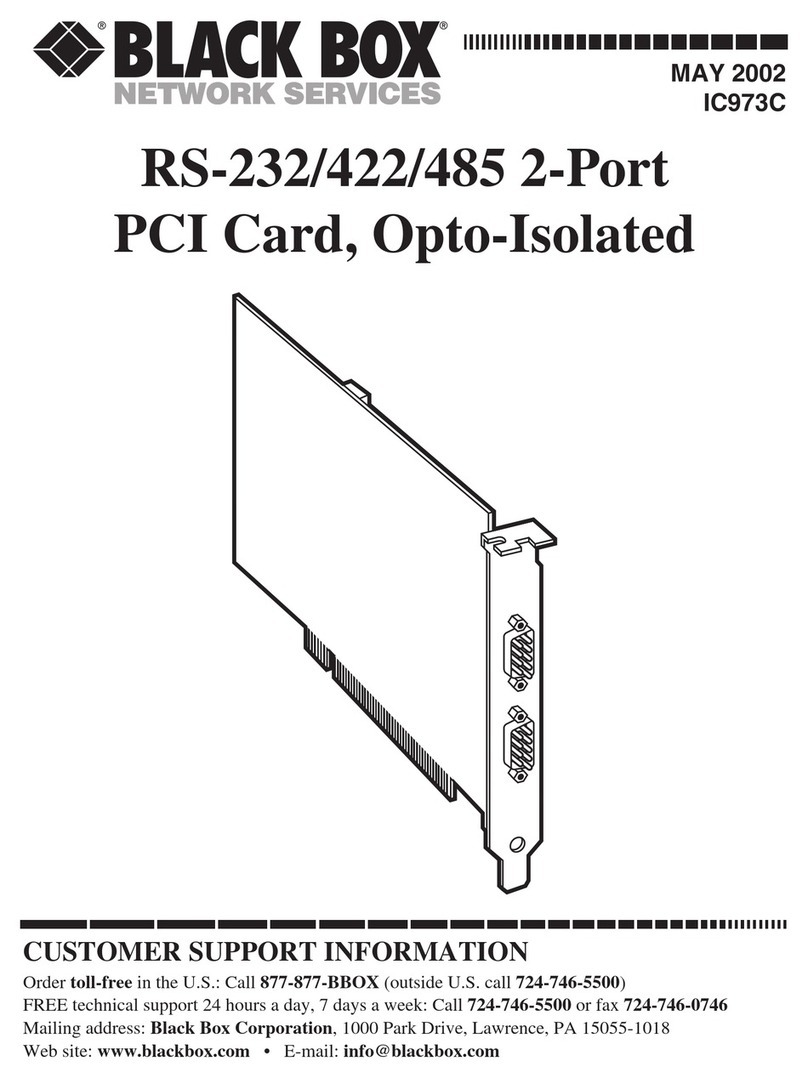
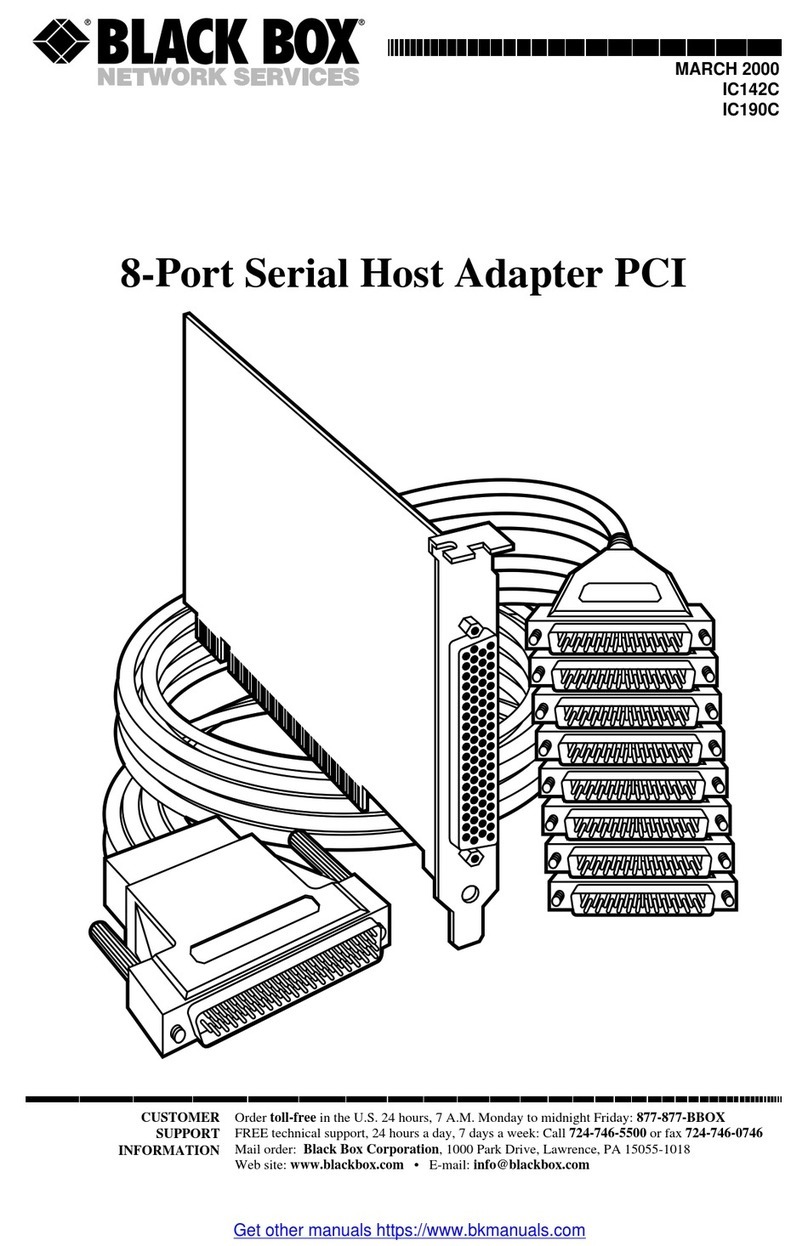
3
NOM STATEMENT
NORMAS OFICIALES MEXICANAS (NOM)
ELECTRICAL SAFETY STATEMENT
INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
1. Todas las instrucciones de seguridad y operación deberán ser leídas antes de
que el aparato eléctrico sea operado.
2. Las instrucciones de seguridad y operación deberán ser guardadas para
referencia futura.
3. Todas las advertencias en el aparato eléctrico y en sus instrucciones de
operación deben ser respetadas.
4. Todas las instrucciones de operación y uso deben ser seguidas.
5. El aparato eléctrico no deberá ser usado cerca del agua—por ejemplo, cerca
de la tina de baño, lavabo, sótano mojado o cerca de una alberca, etc..
6. El aparato eléctrico debe ser usado únicamente con carritos o pedestales que
sean recomendados por el fabricante.
7. El aparato eléctrico debe ser montado a la pared o al techo sólo como sea
recomendado por el fabricante.
8. Servicio—El usuario no debe intentar dar servicio al equipo eléctrico más allá
a lo descrito en las instrucciones de operación. Todo otro servicio deberá ser
referido a personal de servicio calificado.
9. El aparato eléctrico debe ser situado de tal manera que su posición no
interfiera su uso. La colocación del aparato eléctrico sobre una cama, sofá,
alfombra o superficie similar puede bloquea la ventilación, no se debe colocar
en libreros o gabinetes que impidan el flujo de aire por los orificios de
ventilación.
10. El equipo eléctrico deber ser situado fuera del alcance de fuentes de calor
como radiadores, registros de calor, estufas u otros aparatos (incluyendo
amplificadores) que producen calor.
11. El aparato eléctrico deberá ser connectado a una fuente de poder sólo del
tipo descrito en el instructivo de operación, o como se indique en el aparato.