Brainchild PC-W User manual

1
User Manual
Ethernet to Wireless Client
Adaptor, PC-W
Brainchild Electronic Co., Ltd.
UMPCWA, 06/200

2
Important Announcement
The information contained in this document is the property of Brainchild Electronic and is supplied for the
sole purpose of operation and maintenance of products of Brainchild Electronic. No part of this publication
is to be used for any other purposes, and it is not to be reproduced, copied, disclosed, transmitted, stored
in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language, in any form, by any means, in
whole or in part, without the prior explicit written consent of Brainchild Electronic
Brainchild Electronic Co. Ltd
6F, No.20 , Chung Yang Rd, Nankang Dist
Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C
Tel: 886-2-278612 , Fax: 886-2-278613 5
Email: sales@brainchild.com.tw
Website: http://www.brainchild.com.tw
opyright © 2009 Brainchild Electronic. All rights reserved
All other product names referenced herein are registered trademarks of their respective companies.

3
FCC WARNING
Class A for this product
This product has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a lass A digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the F Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
onnect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
onsult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This product complies with Part 15 of the F Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This product complies with F radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This
model should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
IEEE 802.11b/g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmware-limited to channels 1 through 11.
UL Notice for Power supplier
All the series of P -W products are intended to be supplied by a Listed Power Unit marked with “LPS”,
“Limited Power Source” or “ lass 2” and output rate 9~48VD , 1.0A minimum. Or, use the recommended
power supply in “Optional Accessories”.

4
Contents
1.
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................... 6
1.1.
O
VERVIEW
...................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.2.
F
EATURES
....................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.
GETTING STARTED ......................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1.
P
ACKAGING
I
NCLUDE
..................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.
O
RDERING INFORMATION
............................................................................................................................... 7
2.3.
I
NTERFACES
.................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.4.
I
NSTALLATION
P
ROCEDURES
.......................................................................................................................... 8
3.
SOFTWARE SETUP ........................................................................................................................................... 8
3.1.
D
EFAULT
S
ETTINGS
........................................................................................................................................ 8
3.2.
IP
A
SSIGNMENT
.............................................................................................................................................. 9
3.2.1.
Configure IP by Serial Manager Utility .....................................................................................9
3.2.2.
Configure IP address using ARP commands ...........................................................................9
3.2.3.
Configure IP Using eb Interface..........................................................................................10
3.2.4.
Automatic IP address assignment using DHCP.....................................................................10
3.3.
TCP/IP
P
ORT
N
UMBER
................................................................................................................................. 1
4.
APPLICATION CONNECTIVITY ................................................................................................................. 11
4.1.
TCP
&
UDP
P
ROTOCOLS
.............................................................................................................................. 11
4.1.1.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) ....................................................................................11
4.1.2.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) .............................................................................................11
4.2.
C
ONNECTIVITY
T
OPOLOGY
........................................................................................................................... 11
4.3.
E
THERNET TO
WLAN
B
RIDGE
F
UNCTION
.................................................................................................... 12
4.4.
V
IRTUAL
COM
M
ODE
.................................................................................................................................. 12
4.4.1.
TCP Server in Virtual COM Mode ..........................................................................................12
4.4.2.
TCP Client in Virtual COM Mode ...........................................................................................12
4.5.
T
UNNELING
M
ODE
....................................................................................................................................... 13
4.6.
UDP
MODE
................................................................................................................................................... 14
5.
CONFIGURE PC-W BY WEB INTERFACE................................................................................................. 16
5.1.
L
OGIN TO
S
YSTEM
........................................................................................................................................ 16
5.2.
G
ENERAL
I
NFORMATION
............................................................................................................................... 16
5.2.1.
Device Information .................................................................................................................18
5.2.2.
ireless Client Adaptor Information ......................................................................................18
5.2.3.
Serial Information ...................................................................................................................19
5.3.
N
ETWORK
C
ONFIGURATIONS
........................................................................................................................ 19
5.3.1.
ireless Client Adaptor Settings............................................................................................20
5.3.2.
DNS Settings..........................................................................................................................21
5.3.3.
SNMP Settings.......................................................................................................................21
5.4.
W
IRELESS
C
ONFIGURATION
.......................................................................................................................... 22
5.4.1.
ireless Settings ...................................................................................................................23
5.4.2.
Sample ireless Application Cases ......................................................................................23
5.5.
COM
P
ORT
C
ONFIGURATION
........................................................................................................................ 25
5.5.1.
TCP Server Mode ..................................................................................................................25

5
5.5.2.
TCP Client Mode....................................................................................................................25
5.5.3.
UDP Mode..............................................................................................................................27
5.5.4.
Serial Settings ........................................................................................................................27
5.5.5.
Packet delimiter......................................................................................................................28
5.6.
C
ONFIGURE
S
YSTEM
..................................................................................................................................... 28
5.6.1.
Configure Time by NTP Service.............................................................................................28
5.6.2.
LAN Region ........................................................................................................................29
5.6.3.
Security (Password Change) .................................................................................................29
5.6.4.
Restoring Factory Default Configurations ..............................................................................30
5.6.5.
Restart System.......................................................................................................................30
5.7.
A
PPLICATIONS
.............................................................................................................................................. 31
5.7.1.
Paperless Recorder VR18 (Ethernet port) to ireless Ethernet ...........................................31
5.7.2.
Paperless Recorder VR18 (Serial port) to ireless Ethernet................................................37
5.7.3.
Paperless Recorder VR18 to PC via ireless Ethernet (Using 2 PC- devices) ................46
APPENDIX A.
USING VIRTUAL CO ........................................................................................................... 48
A.1.
P
RE
-
INSTALLATION
R
EQUIREMENTS
............................................................................................................. 48
A.2.
L
IMITATION AND
I
NSTALLATION
................................................................................................................... 48
A.3.
V
IRTUAL
COM
C
OMMUNICATION
................................................................................................................ 49
APPENDIX B.
CONFIGURATION UTILITY ................................................................................................. 52
B.1.
S
ERIAL
M
ANAGER UTILITY
I
NTRODUCTION
.................................................................................................. 52
B.2.
I
NTERFACE
.................................................................................................................................................... 52
B.3.
F
UNCTIONS
................................................................................................................................................... 52
B.3.1.
Device Search........................................................................................................................52
B.3.2.
Firmware ................................................................................................................................54
B.3.3.
Configuration..........................................................................................................................56
B.3.4.
Security ..................................................................................................................................57
B.3.5.
View........................................................................................................................................58
B.3.6.
About......................................................................................................................................58
APPENDIX C.
UPGRADING SYSTE SOFTWARE .................................................................................... 58
APPENDIX D.
SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................................... 59
D.1.
H
ARDWARE
S
PECIFICATIONS
........................................................................................................................ 59
D.2.
S
OFTWARE
S
PECIFICATIONS
.......................................................................................................................... 6
D.3.
P
IN
A
SSIGNMENTS
........................................................................................................................................ 6
D.3.1.
DB9 male connector pin assignments for Serial port.............................................................60
D.4.
B
EEP
&
LED
S
TATUS
.................................................................................................................................... 6
D.4.1.
Startup status .........................................................................................................................60
D.4.2.
ireless Signal Strength status .............................................................................................61
D.4.3.
LAN LED Message .............................................................................................................61
D.4.4.
COM Port LED Message .......................................................................................................61
D.4.5.
RUN LED Message................................................................................................................61
6
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
P -W Wireless lient Adaptor is a bridge between RS-232, RS422, RS-485, Ethernet based devices and
wireless LAN. It allows almost any Ethernet and serial devices to be connected to a new or existing wireless
network. The information transmitted by Wireless lient Adaptor is transparent to both host computers (IP
network over wireless LAN) and devices (Ethernet/RS-232/RS-422/ RS-485). Data from the wireless LAN is
transmitted to the designated Ethernet/ RS-232/ RS-422/ RS-485 port and data from Ethernet/ RS-232/
RS-422/ RS-485 port is transmitted to the Wireless (T P/IP) transparently.
In the computer integration manufacturing or industrial automation area, Wireless lient Adaptor is used for
field devices to direct connect to network.
Many control devices provide the ability to communicate with hosts through Ethernet/RS-232/RS-485
however RS-232/RS-485 serial communication has its limitations. For instance, it is hard to transfer data
through Wireless or long distance. With P -W, it is possible to communicate with a remote device in the
Intranet environment and thus, increases the communication distance dramatically.
Flexible configuration options enable this unit to be setup remotely over IP network by Web browser, or
Window utility. Packed in a rugged DIN Rail mountable case and 9~48V D power input range, P -W is
ideal for almost any industrial and manufacturing automation.
1.2. Features
Features
2 Nos. serial ports
Selectable RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 serial mode by software
Transparent between Ethernet to Wireless networking
Support UDP, T P server and client protocols for Virtual OM mode and pair connection
onfigurable via built-in web server and Windows-based utilities
Metal housing and IP50 standard with DIN-Rail mounting.
15KV ESD protection for serial ports
IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps wireless network connectivity
Standard 2.4GHz High-gain antenna

7
2. Getting Started
2.1. Packaging Include
P -W Wireless lient Adaptor x 1
4 dBi Antenna x 1
Wall mount kits x 2
P -W Wireless lient Adaptor quick start guide x 1
Product D containing configuration utility x 1
NOTE: Notify your sales representative if any of the above items is missing or damaged.
2.2. Ordering information
The P -W can be ordered using the following codes.
PC-W Wireless lient Adaptor plus 2-ports with D-Sub 9pin serial
connector
Optional Accessories and their ordering codes
AH1812-B
AH1812-E
1GP-240
1PG-24001
1CB-0025
A 100~240V US plug / D 12V D – Jack, Power adapter
A 100~240V EU plug / D 12V D - Jack, Power adapter
9.0 dBi Omni directional antenna,
N female connector (Max. line of sight distance: 800 mtr)
9.0 dBi directional panel antenna
External RF able, RG58 SMA to N Male 3 m to be used with antenna
2.3. Interfaces
The interfaces of P -W on the front panel are shown in Fig. 1.
DB Model (9 pin D-Sub onnectors)
Fig. 1. PC-W Front Panel and Interfaces
8
2.4. Installation Procedures
Prepare necessary cables, D power adaptor and RS-232/RS-485 connector.
Install Serial Manager software in your P from Product D
Place P -W under the access point signal coverage area. onnect P -W to your P via Ethernet
using RJ45 connector.
If you wish to connect serial device to P -W, connect it. Please make sure the connector and
wiring of RS-232 or RS422 or RS-485 is correct. If you just wish to connect Ethernet device to
P -W, then first complete checking of P -W status from omputer, then connect Ethernet device
to P -W
Plug in P -W to D -9-48V power source (with D -jack), buzzer will beep and the RUN LED will
blink if P -W functions normally. For LED Status see Appendix D.4
Use Serial Manager, configuration utility to check the status of P -W. If it starts up successfully, users shall
find the IP and MA addresses of P -W. Users can also change IP address, gateway IP address and
subnet mask networking parameters of P -W according to user networking configurations.
3. Software Setup
Now the P -W hardware is installed and the power is on, network IP configuration will be set in this section.
3.1. Default Settings
The P -W has two IP addresses one for Ethernet interface and another one for
wireless network interface. These default settings are shown below
Property Default Value
Wireless Client Adaptor IP
IP Address 10.0.50.100
Gateway 10.0.0.254
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Security
User Name Admin
Password Null (Leave it blank)
Serial
OM 9600/None/ 8/1,No flow control, packet delimiter disabled
Link Mode T P Server, Listen port 4660/4661,No Filter, Virtual OM disabled
SNMP
SysName of SNMP Name
SysLocation of SNMP Location
Sys ontact of SNMP ontact
Table 1. Factory default settings of the PC-W
Reset procedure: Push Reset button for 5 seconds and then release to restart PC-W with the
factory default settings.
Warning: Please avoid setting LAN and WLAN IP addresses in the same subnet. This may create
unexpected networking problems.
9
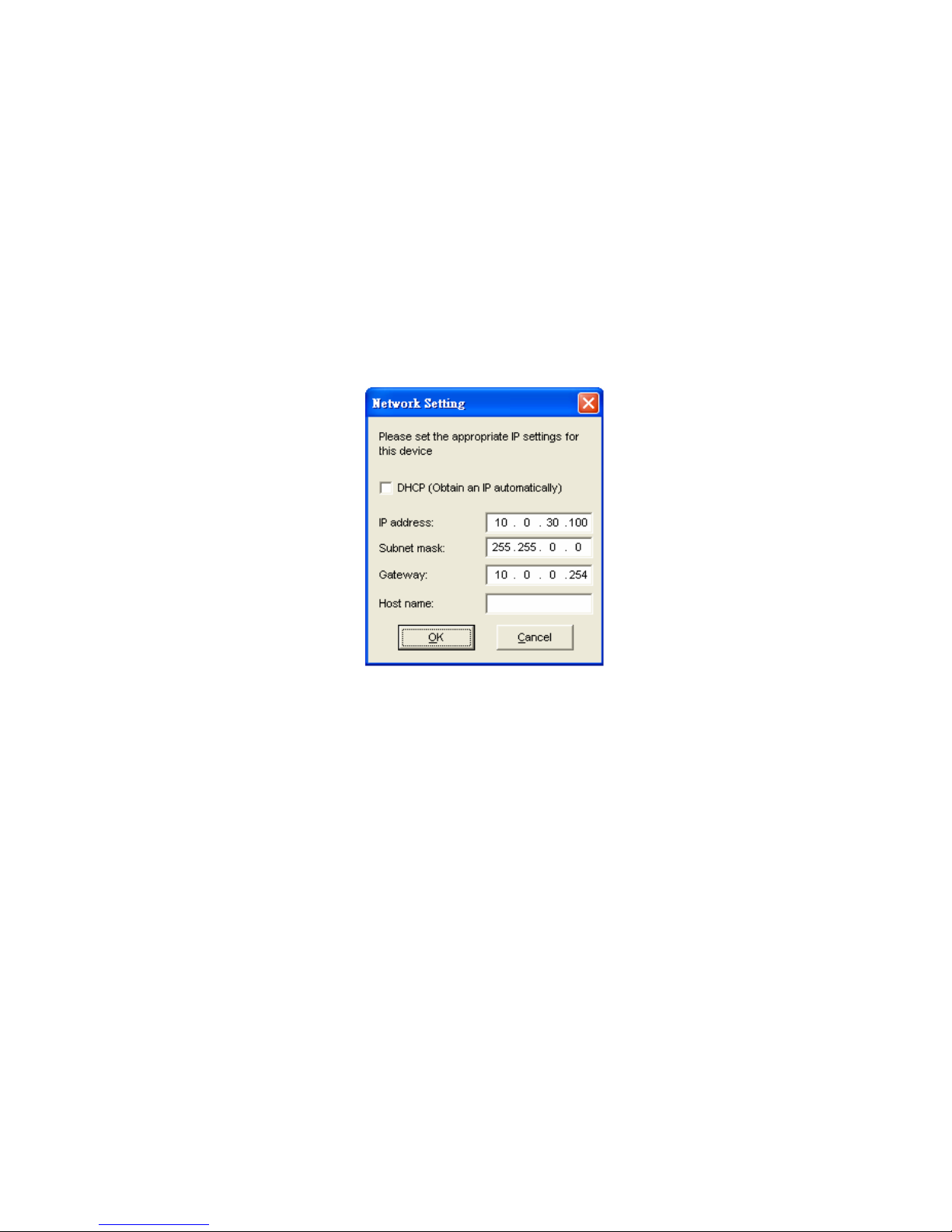
3.2. IP Assignment
3.2.1. Configure IP by Serial Manager Utility
Use Serial Manager, configuration utility that comes with Product D-ROM to configure the network
parameters. For more details, please refer to Appendix B1.
Find a new device and IP assignment
Use Serial Manager Utility to find the new device IP address or to get the device’s current IP
address as shown in Fig. 2.
If needed, use Serial Manager Utility to re-assign a new IP address, Network Mask and Gateway
address to the new device.
Users can also configure User ID, Password and Host Name using Serial Manager Utility.
Fig. 2. IP Settings using Serial Manager Utility software
Note: All settings will NOT be changed if User ID or Password was incorrect.
If there is more than one device using the same IP address in the same subnet, users need to correct the
mapping between MA address and IP address using ARP commands as explained in the next section.
3.2.2. Configure IP address using ARP commands
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) commands can be used to assign a static IP address on P -W using its
hardware MA (Media Access ontrol) address. The MA address "0060E9-xxxxxx" is printed on the rear
side of P -W. The following procedure show how to use ARP commands on MS-DOS ommand Prompt
Window
Example: Set the IP address 10.0.50.101 to the MA address 00-60-E9-00-79-F8
C:\> arp –s 10.0.50.101 00-60-E -00-7 -F8
arp –a command shows the current mapping IP and MA addresses
arp –s “IP address” “MA address” maps the IP address to a specific MA address
Note: ARP commands can only be used to set a static IP address of PC-W

10
Fig. 3. Mapping IP address to MAC address using ARP Command
3.2.3. Configure IP Using Web Interface
Use common web browsers, e.g. Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox, to configure the network
parameters of P -W.
Open a Web browser, type in the IP address (default IP: 10.0.50.100) of the P -W to be
configured. The default user name is admin and the default password is null (leave it blank).
From the Web Network links page, please configure IP address, subnet mask, and gateway
address, and then click “Save Configuration” to save all settings.
lick Restart button to reboot the device to make the changes effective.
Please refer to contents of Web onfiguration section for more details of the settings.
3.2.4. Automatic IP address assignment using DHCP
DH P server can automatically supply an IP address, gateway address, and subnet mask to P -W device
if its DH P client function is enabled. By default, the DH P client function is disabled, users can activate
the DH P function by following these steps
Execute Serial Manager Utility
lick on the IP address of P -W (This can be the default IP address if it was never set before).
lick Config to pop-up the static IP Dialog Window.
heck on Auto IP
lick Config Now. (The P -W will restart and obtain an IP from DH P server automatically)
Note: You need to have a DHCP Server running in your subnet to automatically supply an IP
address. Please consult your network administrator if you are not sure.
3.3. TCP/IP Port Number
Default T P Port numbers of P -W are 4660 (1st port) and 4661 (2nd Port) that are associated with the
Serial port COM1 and COM2, respectively. After the application program connects to the T P port 4660
(or 4661) on the P -W, data of user’s application program are transparently transmitted to Serial port
OM1 (or OM2) of P -W.

11
4. Application Connectivity
The P -W is designed to transmit data between one or more Ethernet/serial devices to/from one or more
T P/IP devices through wireless Ethernet interface. P -W can enhance the accessibility of the serial
device through T P/IP based Ethernet as well as Wireless Ethernet. The connection distance limit is
overcome by P -W. Examples of these devices are PL controllers, card readers, display signs, security
controls, N controller, etc.
4.1. TCP & UDP Protocols
P -W can operate in two most common transportation protocols, T P and UDP.
4.1.1. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
T P provides a connection and a byte oriented data stream with control parameters such as flow control,
multiple ports option, and order delivery notification. Once the connection is established, data can be
transmitted in both directions. T P guarantees data is transmitted from one node to the other node(s) in
orderly. The protocol also distinguishes the transmitted data for different applications (such as a Web server
or an Email server) on the same computer.
For redundant or dual-network connectivity purposes, P -W offers two T P operation modes so users may
choose for their specific application, T P Server Mode and T P lient Mode.
4.1.2. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP is a faster datagram delivery protocol. User can configure P -W to work in the UDP mode. UDP is
connectionless protocol and can transmit multicast data to/from a serial device to one/multiple host
computer. Because UDP is the connectionless protocol, UDP does not guarantee the reliability and orderly
data streams like T P protocol. Datagram may arrive out of order or lose without notice. But the advantage
of UDP is the speed. UDP is faster and hence more attractive in time-sensitive applications.
4.2. Connectivity Topology
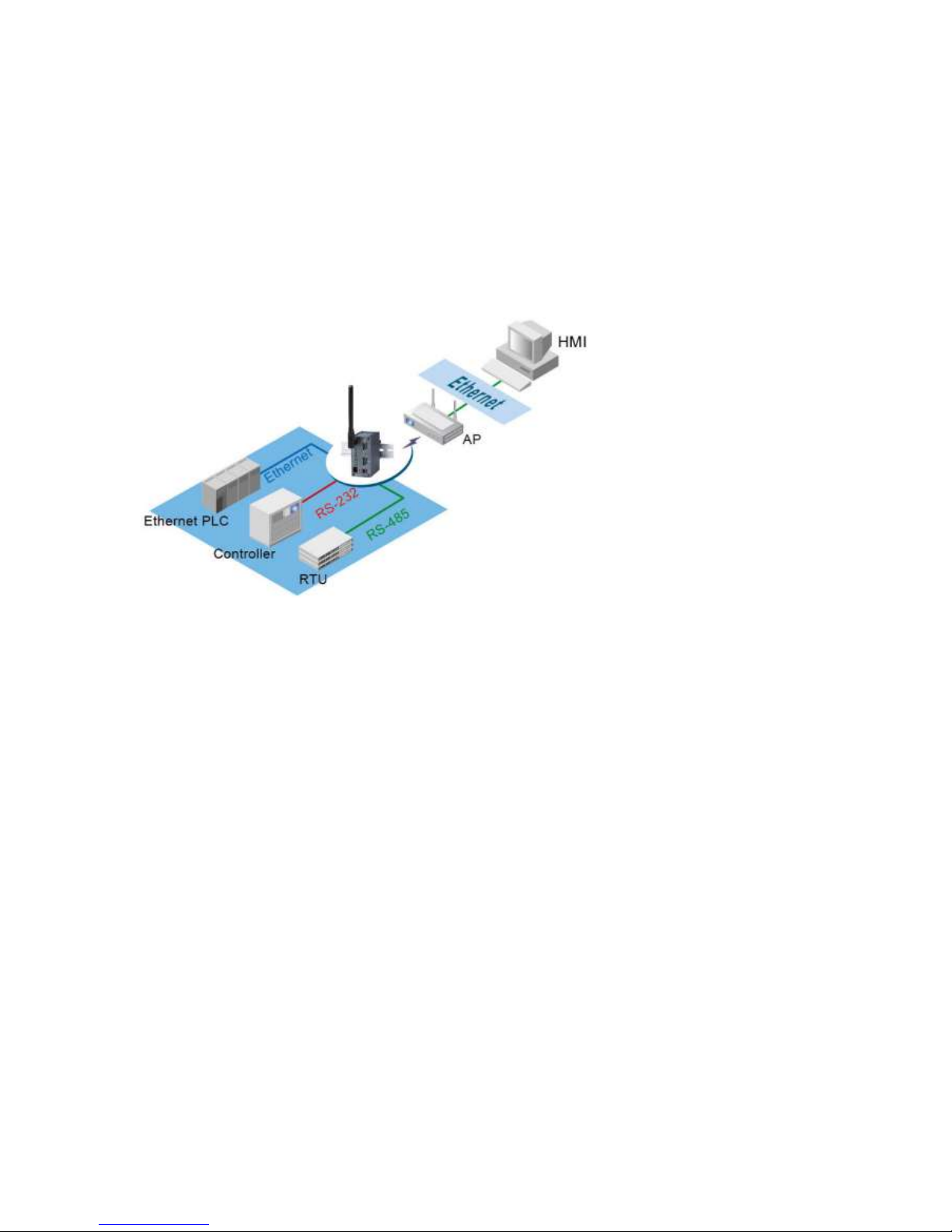
P -W is also equipped with Tunneling and Virtual OM operation modes. It is designed to transmit data
to/from multiple serial devices and from/to multiple T P/IP devices on Ethernet, so it can enhance the
accessibility of the serial devices immensely. The example of P -W connection topology is shown in Fig. 4.
Note: Please do not connect more then one device on Ethernet port
Fig. 4. Typical Topology of PC-W Connection
12
4.3. Ethernet to WLAN Bridge Function
The P -W can also work as a network bridge between Ethernet to WLAN. Packets from WLAN to Ethernet
or from Ethernet to WLAN are transferred transparently. This will let the Ethernet devices can be accessed
from wireless networks over the wireless interface.
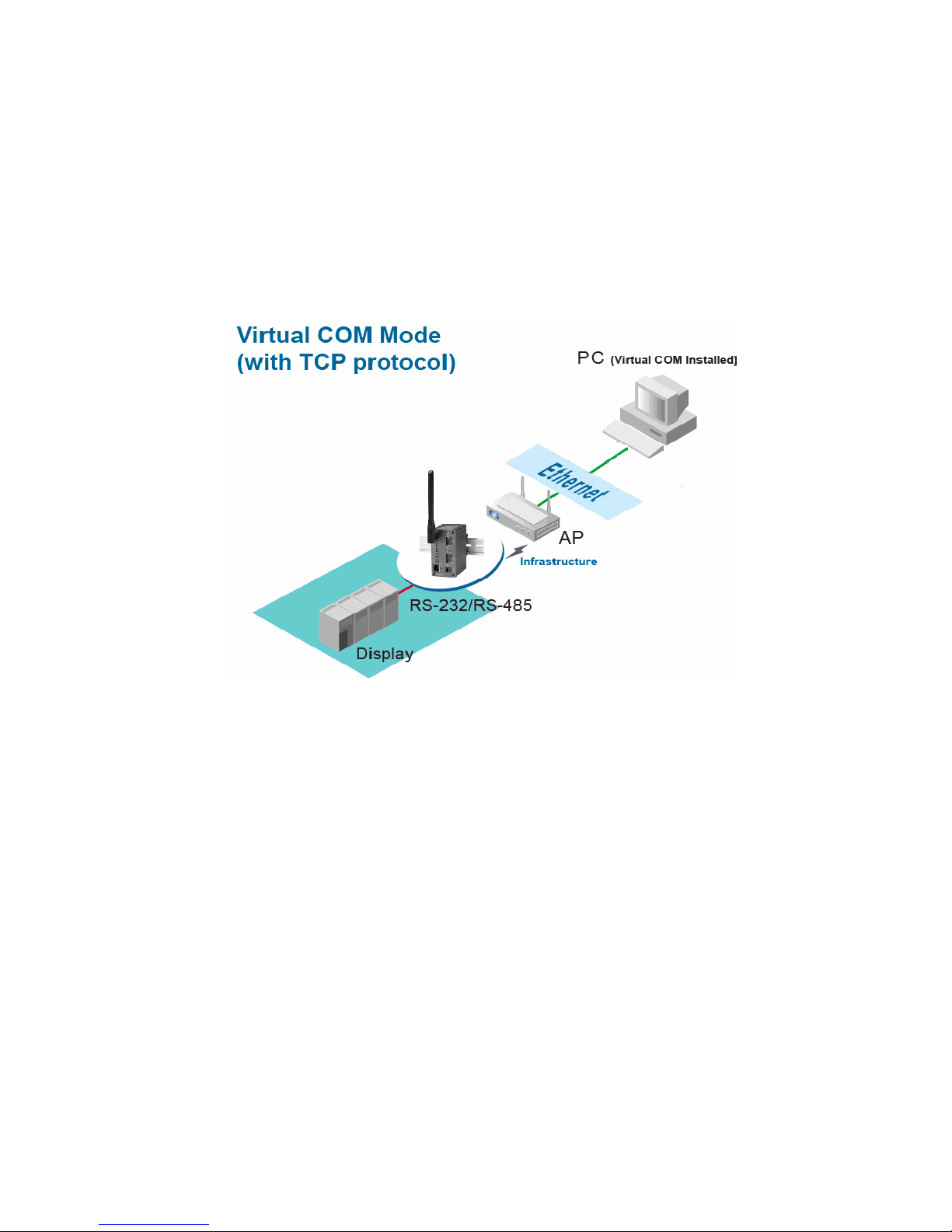
4.4. Virtual COM Mode
The Virtual COM software emulates a serial port in LAN topology. In the Virtual OM Mode, OM port data
is encapsulated with Ethernet data format. By creating a virtual OM port on a P , the Virtual OM driver
redirects communications from the virtual OM port to the destination IP address (and the designated port
number) by encapsulating OM data into IP packet format. Fig. 5 illustrates a Virtual OM connection
diagram.
Fig. 5. TCP Connection in Virtual COM Mode
4.4.1. TCP Server in Virtual COM Mode
P -W can be configured in the T P server mode (P acts as a client) with a unique IP and Port number,
and P -W waits passively for the P to establish a connection. After the connection is established, P can
communicate to serial devices through P -W.
Configure PC-W to be TCP server
Using one of the two configuration methods, by Web-based and by Windows-based Serial Manager utility,
Users can configure P -W to be a T P Server as follows.
Disabled the IP filter (default)
Set the port number (default port is 4660 for OM1, 4661 for OM2).
If IP filter is enabled, only the assigned source IP is allowed to be connected to P -W.
4.4.2. TCP Client in Virtual COM Mode
P -W can also be configured in T P lient mode (P as a server) to establish a T P connection to an
application server on P , or the Remote ontrol Host. Once the connection is established, P or Remote
ontrol Host can exchange data with several serial devices at the same time through P -W as shown in Fig.
6.
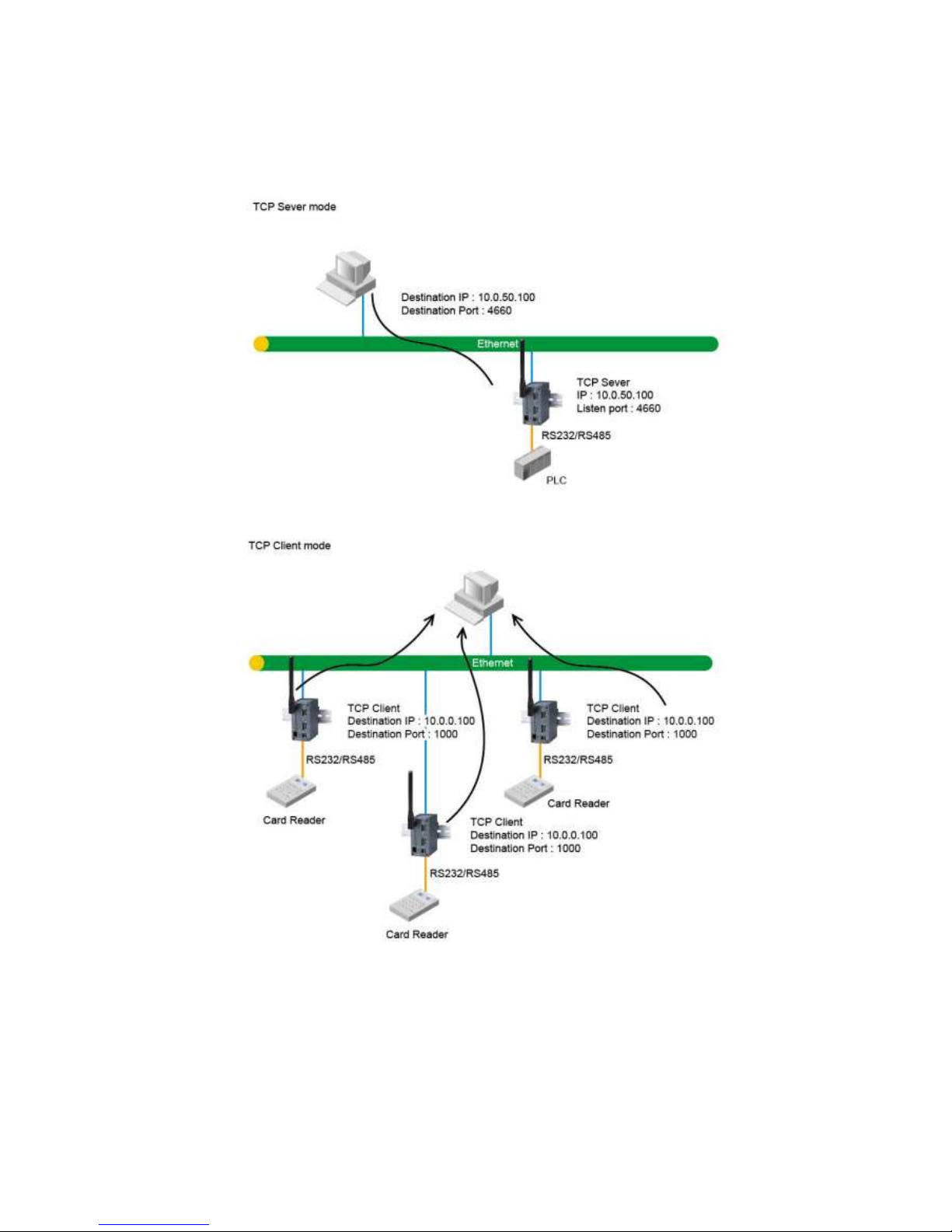
13
Configuring PC-W to be TCP client
User can configure P -W to be as a T P client, for example, from Fig. 7, P , as a server, has IP address
10.0.0.100 and listening on port 1000. Each P -W, connected with serial device, configured as T P client
mode with destination IP address 10.0.0.100 and the destination port 1000, and the IP filter is disabled (by
default).
Fig. 6. TCP Server in Virtual COM Mode
Fig. 7. TCP Client in Virtual COM Mode
4.5. Tunneling Mode
Tunneling Mode is used for multiple serial devices to “talk” among one another through P -W’s wireless
LAN or wired Ethernet interface. This mode is particularly useful when two or more serial devices are far
away. This mode can be used to extend the normal RS-232 serial communication distance of 15 m to 100 m
or longer as shown in Fig. 8.

14
One P -W can be configured to be the T P Server Mode with serial device connected and also another
P -W is configured as T P client with serial device connected. After the connection is established, both
serial devices can exchange data to each other transparently. For example, users can implement P -W
tunneling mode for Master /Slave mode PL ’s or between other serial devices.
Fig. 8. TCP Link in Tunneling mode
Configuring PC-W to Tunneling Mode
Using one of two configuration methods (Web-based or Windows-based Serial Manager utility), users can
configure P -W to T P Server mode with a desired IP address and port, and with other P -W is configured
as T P lients mode with Server IP and port as destination IP and port respectively as shown as an
example in Fig. 9.
Note: TCP client has to assign the destination IP and the destination port corresponding to TCP
server’s IP and listening port (example: TCP 4660 port).
Fig. . TCP Tunneling Mode
4.6. UDP mode
In UDP mode, users may exchange Multicast data from one P -W with multiple P -W devices as shown in
Fig. 10.

15
Fig. 10. UDP Link in Tunneling mode
Configure PC-W in UDP Mode
Use one of the two configuration methods (Web-based or Windows-based Serial Manager Utility). Users
can configure P -W to UDP mode. In UDP mode, P -W can be configured to communicate to more than
one node (Multicasting). Note that the Multicast IP address is limited by the lass of IP address and subnet
mask. As an example, for a network of lass of subnet 192.168.1.X and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0,
the maximum Multicast IP address to be configured is four destinations IP’s.
Fig. 11. Multi-UDP Link in Tunneling Mode
16
5. Configure PC-W by Web Interface
Users need to assign an IP address to P -W before working on the web configuration operations. Please
refer to Section 3.2 for IP address assignment.
5.1. Login to System
Open one of the web browsers, ex. Microsoft IE or Firefox etc. Enter the IP address of P -W on the URL.
Example: http://10.0.50.100 or http://your-device-IP-address.
The following authentication screen shall appear. Enter User Name and Password then click on “OK”. The
default user name is “admin” and password is null (leave it blank).
Fig. 12. Authentication request for system security
5.2. General Information
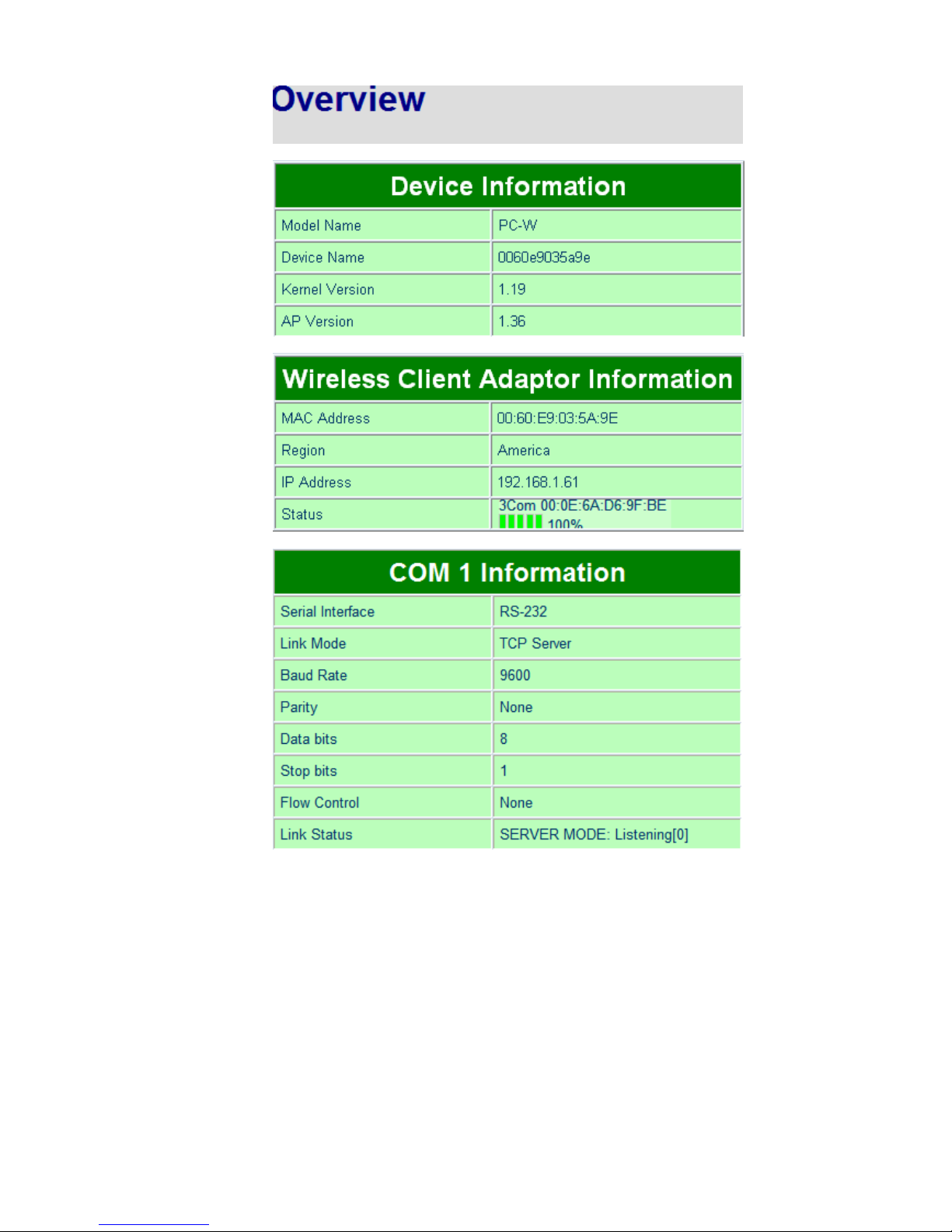
Once the login is successful, an Overview window gives the general information of P -W, included Network,
and Serial information as shown in Fig. 13.
17

18
Fig. 13. Overview of system information on a Web Interface
5.2.1. Device Information
P -W’s system information includes Model Name, Device Name, Kernel Version, and AP version. The
information is read only and is attributed from setting page or system status.
Fig. 14. Device Information from Overview web page
5.2.2. Wireless Client Adaptor Information
Wireless lient Adaptor Information fields display both LAN & Wireless LAN (WLAN) information. The
information provided are LAN MA address, Region for Regulation, LAN IP address, WLAN MA address,
WLAN IP address, and Link status.
19
Fig. 15. Wireless Client Adaptor Information from Overview web page
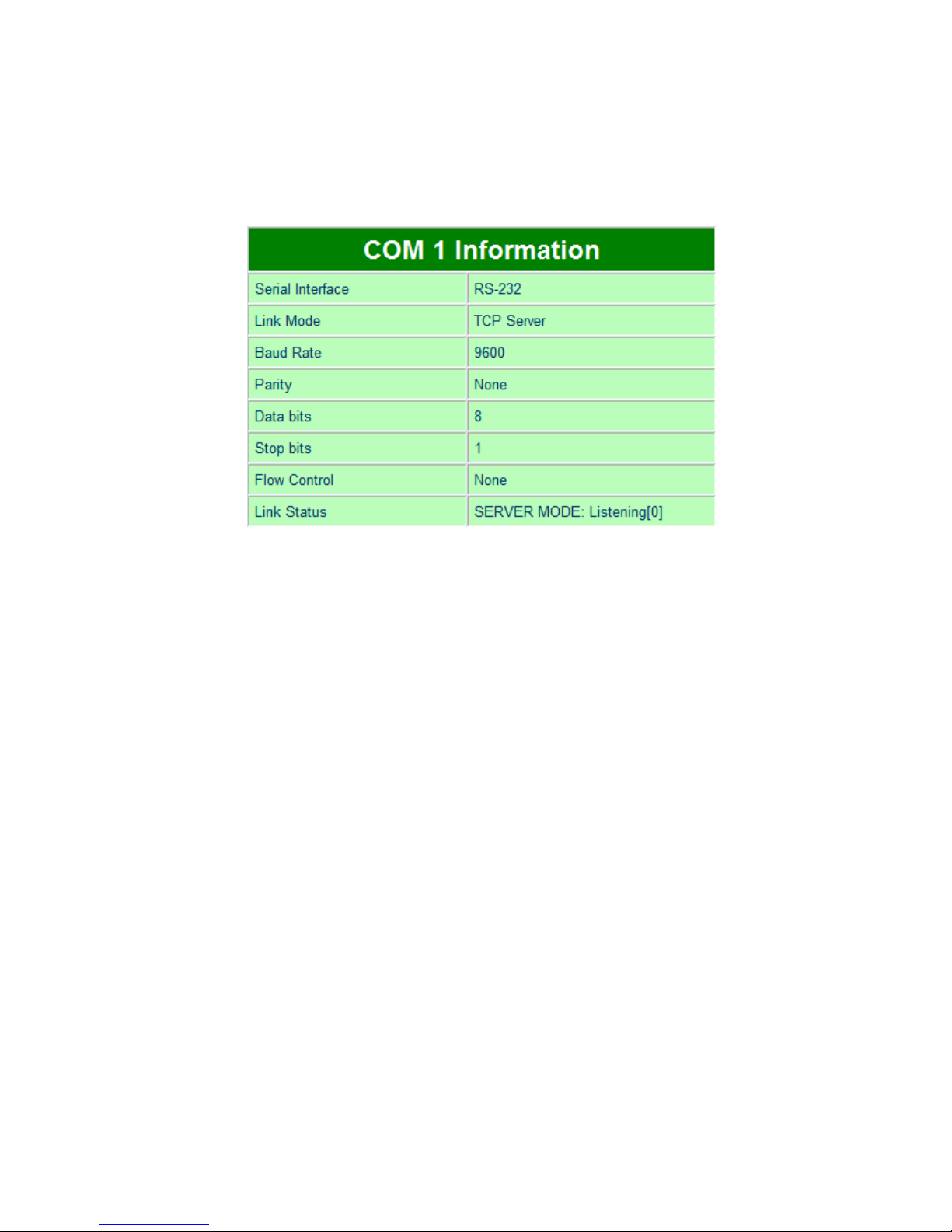
5.2.3. Serial Information
P -W OM1 ( OM2) information includes UART mode, link mode, baud rate, parity, data bits, stop bits,
flow control and link status. The OM1 ( OM2) information is read only and is attributed from Serial
settings of OM1 or OM2 Port of P -W.
Fig. 16. Serial Information from Overview web page
5.3. Network Configurations
There are three items allowed to change on Networking page, included Wireless lient Adaptor Settings,
DNS Setting and SNMP Settings.

20
Fig. 17. Network information by Web page
5.3.1. Wireless Client Adaptor Settings
lick on the “Network” link and the following screen shall appear. Fill in network information on WLAN
interface including IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway. Alternatively, User may activate DH P
client function by checking on “Obtain an IP automatically” field to automatically obtain IP Address, Subnet
mask and Default gateway from a DH P server.
Table of contents
Other Brainchild Media Converter manuals