Compu Pool C-CPP Commercial Series Manual 10
7.3.2 The ideal salt level is 3500 ppm. A low salt level will reduce efficiency of the
chlorinator and result in low chlorine production. A high salt level can cause a salty
taste to the pool. In addition, operating the unit outside the recommended salt
range will rapidly reduce the longevity of the cell. The salt in the pool/spa is
constantly recycled and the loss of salt throughout the swimming season should be
small. This loss is due primarily to the addition of extra water to replace water lost
from splashing, backwashing, and draining (because of rain). Salt is not lost due to
evaporation.
7.3.3 If salt content is too high you will need to reduce the level of water in the pool/spa
and refill the pool/spa with fresh water that has not been diluted with salt.
7.3.4 To initially start a pool with the correct amount of salt, add salt to the pool at a rate
of 0.03 pounds of salt for every 1 gallon of water.
8.0 INSTALLATION
8.1 Positioning
8.1.1 The C-CPP series chlorinator must be installed in a room or area that is protected
from the environment and weather. The chlorinator must not be installed into a
location that is used for chemical storage as this will void the warranty.
8.1.2 Water leaks, no matter how small should be attended to immediately. If there is
water in the vicinity of the chlorinator, condensation may form on the internal
electrical components which can result in malfunction. The warranty will not cover
malfunction due to condensation or weather.
8.1.3 The chlorinator must be positioned downstream from the filtration plant and
upstream from any heating equipment.
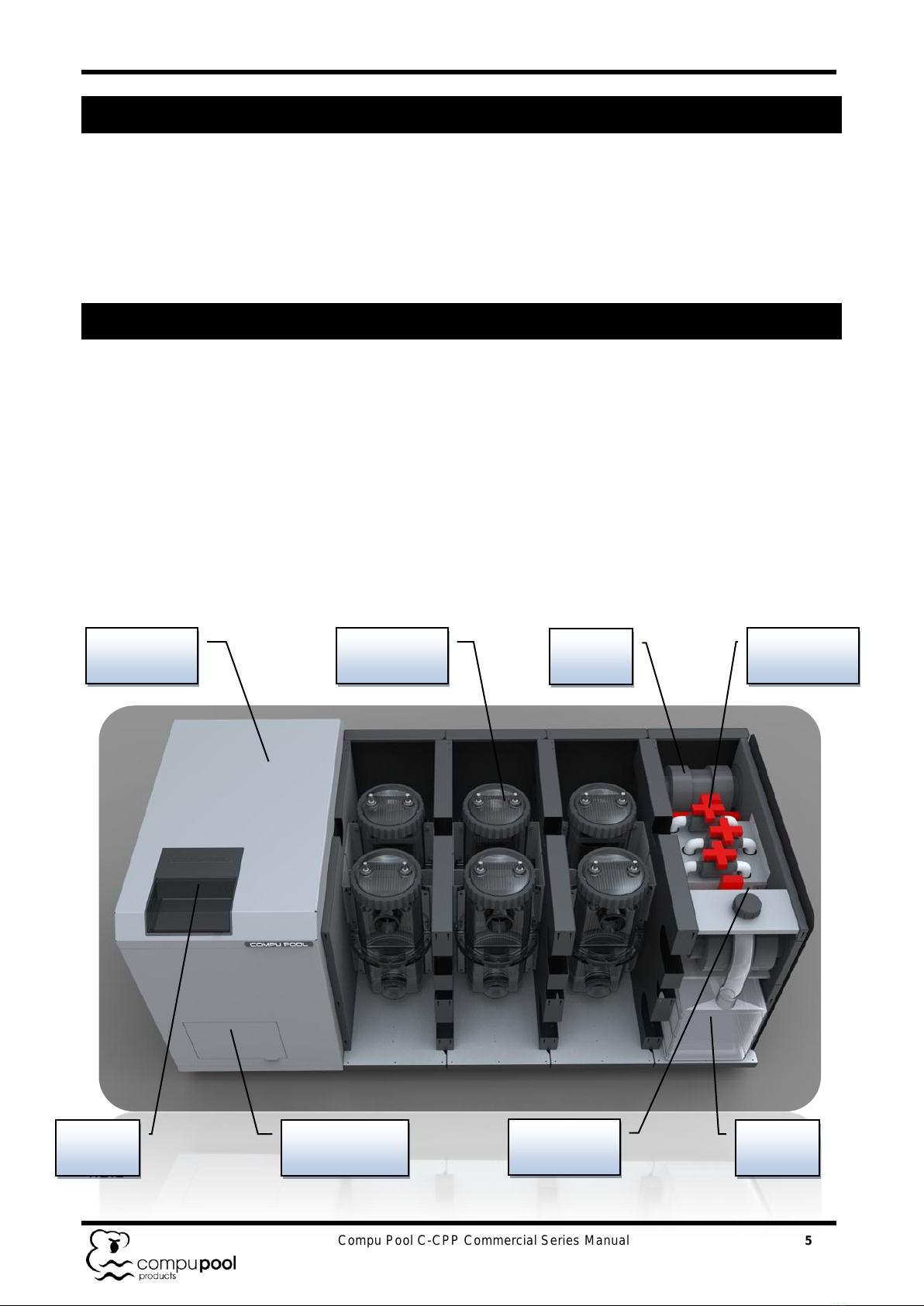
8.1.4 Positioning should allow for easy access to the electronics module door, control
panel, cell bays and valves.
8.1.5 The chlorinator can be moved into position with either a forklift or pallet jack(s).
8.2 Plumbing
8.2.1 The C-CPP series chlorinator must be plumbed to the main return pipe of the pool
after the filtration system.
8.2.2 A branch line needs to be taken from the main filtration return line and diverted
through the Chlorinator to create a bypass installation. This must be done in the
manner shown in the plumbing diagram in the following section (Figure 1). Installing
the Chlorinator in this manner avoids excessive pressure on the Chlorinator and
filtration system. Additionally the Chlorinator can be isolated from the main flow
return line to enable uninterrupted filtration.