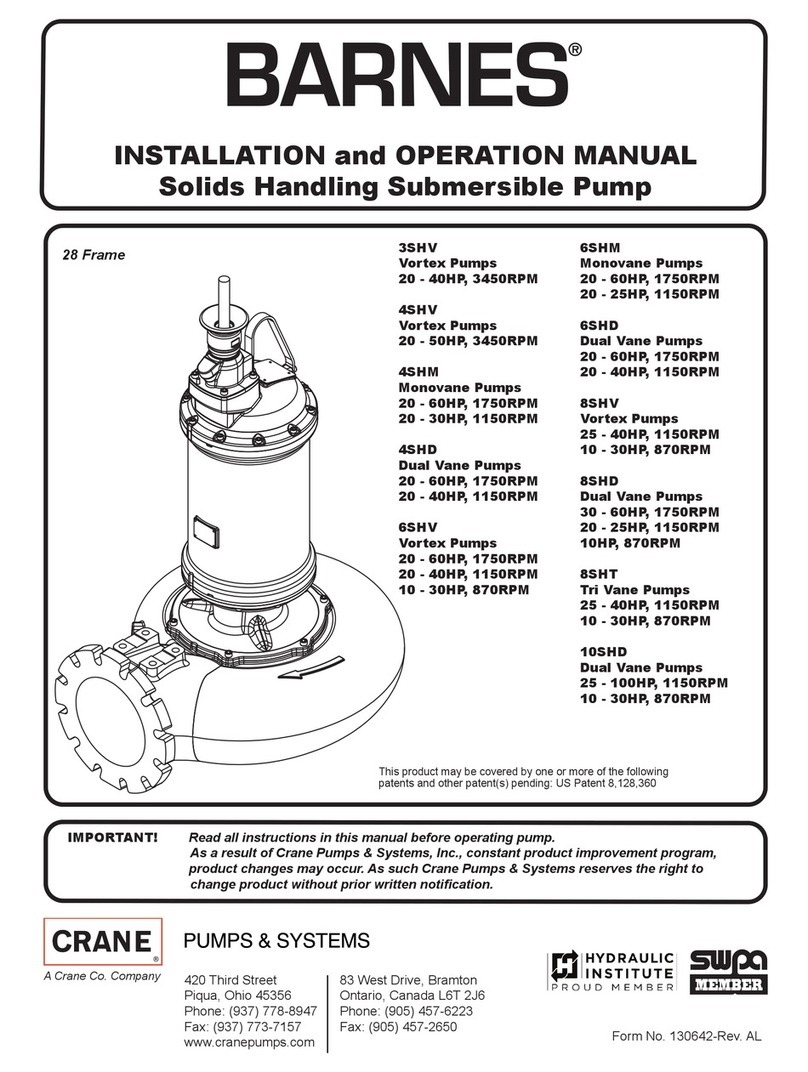
6
5. PIPING
The pump suction and discharge connections are not
intended to indicate the required suction and discharge
pipe sizes. The pipe diameter must be selected according
to the requirements of the pumping system and
recommended friction losses for the liquid being pumped.
Usually, it is advisable to increase the size of both the
suction and discharge pipes at the pump nozzles to have
minimum acceptable friction loss, suction pipe should
never be smaller in diameter than the pump suction
nozzle. When suction pipe is of larger diameter than the
pump suction nozzle, an eccentric reducer is required to
eliminate possible air or vapor pockets at the pump suction
inlet.
Both suction and discharge pipes must be supported
independently near the pump, so that when piping is
connected to the pump, no strain will be transmitted to the
pump. Piping should be arranged with as few bends as
possible, and, preferably, with long radius elbow whenever
possible.
SUCTION PIPING
A horizontal suction line must have a gradual rise to the
pump. Any high point in the suction pipe can become fi lled
with air and prevent proper operation of the pump and may
cause loss of prime. The pipe and fi ttings must be free of
all air leaks.
Any valves or fi ttings should located at a distance equal
to 5 to 10 times the diameter of the suction pipe from the
pump suction nozzle. If an elbow must be installed at the
pump suction, it should be installed in a vertical position
to reduce unequal fl ow into the pump, which may cause
cavitation in the pump.
NOTE: A gate valve in the suction piping should not be
used as a throttling device, as this may cause the liquid to
overheat during operation.
6. WIRING
For electric motor drives, connect power supply to conform
with national and local codes. Line voltage and wire capacity
must match the ratings stamped on the motor nameplate.
7. ROTATION
Before starting the pump, check the required direction
of rotation of the pump. The proper direction is indicated
by a direction arrow on the pump casing. Separate the
coupling halves, then start motor to see that it rotates in
the direction required by the pump. If it does not, reverse
any two main leads of the 3-phase wiring to the motor.
The coupling halves can be reconnected and the pump
primed for starting.
C - OPERATION
1. PRIMING
CAUTION: Before starting the pump, the casing and
suction line must be fi lled with liquid, and air-vented
through the vent pipe plugs. The pump must not be run
until it is completely fi lled with liquid, because of danger of
injuring some of the parts of the pump which depend upon
liquid for lubrication. The discharge gate vale should be
closed during priming. Be sure the mechanical seal and
power frame are supplied with the proper lubrication.
See LUBRICATION.
PRIMING BY SUCTION PRESSURE
When operating with suction pressure (fl ooded suction),
remove the pipe plug at the top of the casing and when
pump is fi lled with liquid, replace plug.
PRIMlNG WITH FOOT VALVE AND STRAINER
A foot valve and strainer may be installed on the lower end of
the suction pipe to keep pump fi lled with liquid. Incorporate
fi ller pipe in discharge pipe between pump and check valve.
Remove pipe plug at top of casing, then fi ll suction pipe and
pump with liquid. When pump is full of liquid, replace plug
and close fi ller pipe.
CAUTION: When a foot valve and strainer are in stalled on
the suction pipe, a spring loaded type check valve MUST be
installed next to the pump in the discharge piping to prevent
pump rupture from water hammer shock.
Priming by means of primer pump or ejector, attached to
the pump, will also remove air from suction pipe and pump
casing. When pump is fi lled with liquid, start motor and
slowly open discharge gate valve.
2. STARTING THE PUMP
On initial start up, the gate valve in the discharge piping
should be closed and slowly opened after pump is up to
speed and pressure developed. DO NOT operate pump for
any appreciable length of time against a closed discharge
valve, as this may heat trapped liquid excessively and
damage the pump or seal.
The following important items should be checked as pump
is started and placed in operation.
a. Pump and driver securely bolted
b. Coupling properly aligned
c. Piping complete
d. Correct pump rotation
e. Pump shaft turns freely
f. Discharge valve closed
g. Suction valve open (if used)
h. Coupling Guard installed
i. Pump fully primed
j. Pump and driver properly lubricated
Only after these items have been checked should the
pump be started.