8
- Cutting blades are available in two basic designs; abrasive blades and diamond blades.
- High-quality blades are often most economical. Lower quality blades often have inferior cutting
capacity and a shorter service life, which results in a higher cost in relation to the quantity of mate-
rial that is cut.
- Make sure that the right bushing is used for the cutting blade to be tted on the machine. See the
instructions under the heading Fitting the cutting blade.
Suitable cutting blades
For more information, see the '"Technical data" section.
*Without water
**See instructions under the heading "Toothed blades, carbide tipped blades and emergency situa-
tions".
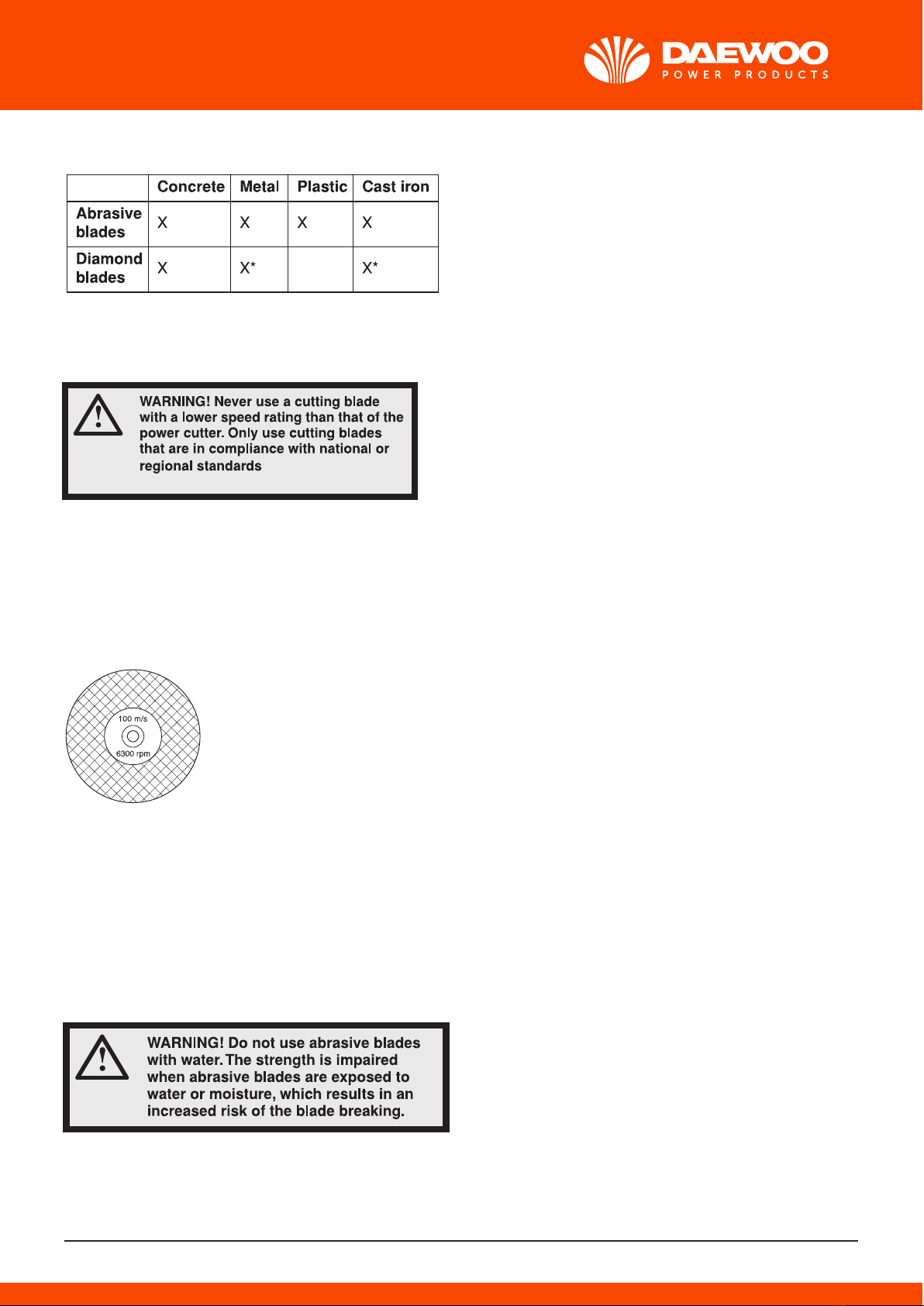
Cutting blades for different materials
Follow the instructions supplied with the culling blade concerning the suitability of the blade for
various applications, or consult your dealer in case of doubts.
- Diamond blades consist of a steel core provided with segments that contain industrial diamonds.
- Diamond blades ensure lower costs per cutting operation, fewer blade changes and a constant
cutting depth.
- When using diamond blades make sure that it rotates in the direction indicated by the arrow on the
blade.
Diamond blades for different materials
- Diamond blades are ideal for masonry, reinforced concrete and other composite materials.
- Diamond blades are available in several hardness classes.
- Special blades should be used when cutting metal. Ask your dealer for help in choosing the right
product.
Sharpening diamond blades
- Always use a sharp diamond blade.
- Diamond blades can become dull when the wrong feeding pressure is used or when cutting
certain materials such as heavily reinforced concrete.
- Working with a dull diamond blade causes overheating, which can result in the diamond segments
coming loose.
- Sharpen the blade by cutting in a soft material such as sandstone or brick.
Diamond blades and cooling
- During culling the friction in the cut causes the diamond blade to be heated up. If the blade is
allowed to get too hot this can result in loss of blade tensioning or core cracking.
Diamond blades for dry cutting
- Although no water is required for cooling, dry cutting blades must be cooled with air ow around
the blades. For this reason dry cutting blades are recommended only for intermittent cutting. Every
few seconds of cutting the blade should be allowed to run 'free" with no load to allow the air ow
around the blade to dissipate the heat.
Diamond blades for wet cutting
- Wet cutting diamond blades must be used with water to keep the blade core and segments cool
during sawing.
- Wet cutting blades should NOT be used dry.
- Using wet cutting blades without water can cause excessive heat build-up, resulting in poor
performance, severe blade damage and is a safety hazard.
Diamond hlade - side clearance
Water cools the blade and increases its service life while also reducing the formation of dust
Toothed blades, carbide tipped blades and emergency situations