DS2154
071498 10/71
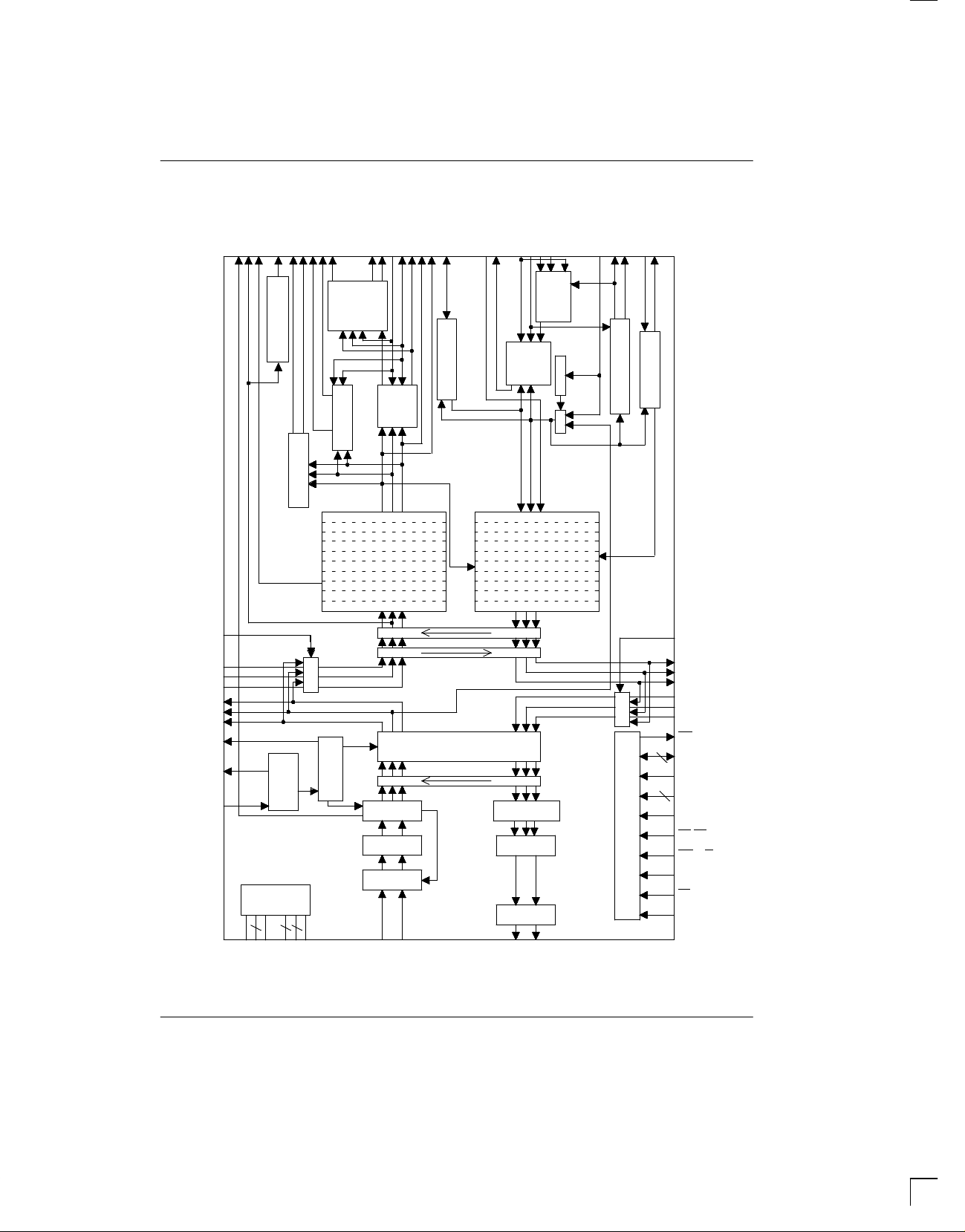
enabled. Useful for blocking clocks to a serial UART or
LAPD controller in applications where not all E1 chan-
nels are used such as Fractional E1, 384 Kbps (H0),
768 Kbps, 1920 Kbps (H12) or ISDN–PRI. Also useful
for locating individual channels in drop–and–insert
applications,forexternalper–channelloopback,andfor
per–channel conditioning. See Section 9 for details.
Transmit System Clock [TSYSCLK]. 1.544 MHz or
2.048 MHz clock. Only used when the transmit side
elastic store function is enabled. Should be tied low in
applications that do not use the transmit side elastic
store. Can be burst at rates up to 8.192 MHz.
Transmit Link Clock [TLCLK]. 4 KHz to 20 KHz
demandclock(Sabits)fortheTLINKinput. SeeSection
11 for details.
TransmitLinkData[TLINK]. Ifenabled,thispinwillbe
sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data insertion
into any combination of the Sa bit positions (Sa4 to
Sa8). See Section 11 for details.
Transmit Sync [TSYNC]. Apulseat this pinwill estab-
lisheitherframe or multiframe boundaries for the trans-
mit side. This pin can also be programmed to output
eitheraframeormultiframepulse. Alwayssynchronous
with TCLK.
TransmitFrameSync[TSSYNC]. Onlyusedwhenthe
transmitsideelasticstoreisenabled. Apulse atthispin
will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for
thetransmitside. Shouldbetiedlowinapplicationsthat
do not use the transmit side elastic store. Always syn-
chronous with TSYSCLK.
Transmit Signaling Input [TSIG]. When enabled, this
input will be sample signaling bits for insertion into out-
going PCM E1 data stream. Sampled on the falling
edgeofTCLKwhenthetransmitsideelasticstoreisdis-
abled. Sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when
the transmit side elastic store is enabled. See Section
13 for timing examples.
Transmit Elastic Store Data Output [TESO].
Updatedon therising edge ofTCLK with dataoutof the
the transmit side elastic store whether the elastic store
is enabled or not. This pin is normally tied to TDATA.
Transmit Data [TDATA]. Sampled on the falling edge
of TCLK with data to be clocked through the transmit
side formatter. This pin is normally tied to TESO.
TransmitPositiveDataOutput[TPOSO]. Updatedon
therisingedgeofTCLKOwiththebipolardataoutofthe
transmit side formatter. Can be programmed to source
NRZ data via the Output Data Format (TCR1.7) control
bit. This pin is normally tied to TPOSI.
Transmit Negative Data Output [TNEGO]. Updated
onthe risingedgeof TCLKO withthe bipolar dataout of
the transmit side formatter. This pin is normally tied to
TNEGI.
Transmit Clock Output [TCLKO]. Buffered clock that
isused toclockdata throughthetransmit sideformatter
(i.e.either TCLK orRCLKO if Loss OfTransmitClock is
enabled and in effect or RCLKI if remote loopback is
enabled). This pin is normally tied to TCLKI.
Transmit Positive Data Input [TPOSI]. Sampled on
the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out
ontotheE1line. CanbeinternallyconnectedtoTPOSO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Negative Data Input [TNEGI]. Sampled on
the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out
ontotheE1line. CanbeinternallyconnectedtoTNEGO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Clock Input [TCLKI]. Line interfacetransmit
clock. Can be internally connected to TCLKO by tying
the LIUC pin high.
RECEIVE SIDE DIGITAL PINS
Receive Link Data [RLINK]. Updated with the full
recovered E1 data stream on the rising edge of RCLK.
Receive Link Clock [RLCLK]. 4 KHz to 20 KHz clock
(Sa bits) for the RLINK output. See Section 11 for
details.
Receive Clock [RCLK]. 2.048 MHz clock that is used
to clock data through the receive side framer.