9
4.3 Installation and commissioning
Preparatory stages for the machine installation and commissioning:
-Identify an area suitable for food-processing that is completely accessible for cleaning in which collocate
the machine.
-It is not necessary to provide floor anchors but the floor must be well leveled because SP401,601 and
SP801 models do not have leveling feet, whereas the SP801 Gold model comes with frontal legs.
-Check that the power line is properly connected by means of a suitable outlet.
-Check that any command and removable safety protections work properly.
4.3.1 Installation
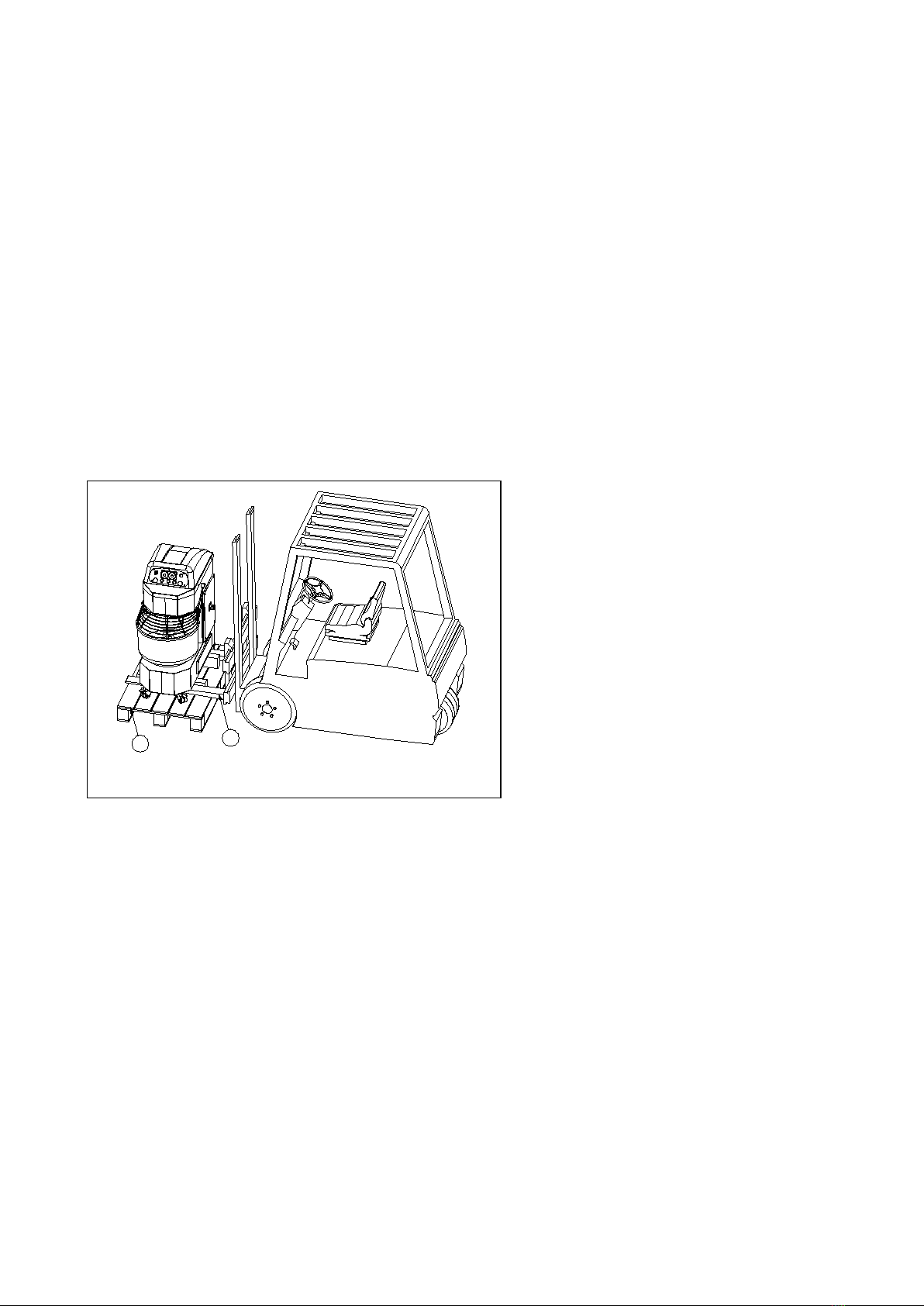
Once the machine has been transported to the chosen location, the installation is carried out following the
stages outlined below (see figs.3/4):
a) For SP401, SP601 and SP801 models, lock
the wheels by pressing on the lever with the
foot Pos.1 Fig.3a, until the lever remains
locked. For the SP801 Gold model the
positioning of the machine is done by
adjusting the front legs Pos.51 fig.3b through
the hand wheel Pos.53 and subsequently
blocking by tightening the nut, Pos.52.
b) Connect the machine to the power outlet,
turn the knob on Pos.3 and check that the ON
lights up, Pos. 4, Fig.4/5.
c) Check that the bowl protection is turned
down, Pos. 4, Figg.3a/3b.
d) Push on Start button, Pos. 5 Fig. 4/5
If the tank turns clockwise, ie opposite to the
one indicated by the arrow on the side of the
tank, the phases on the engine are incorrect,
then swap two of the three phases in the
socket.
The control panel Pos.2, figs.3/4/5 is
composed of:
Fig.3b : SP801- Gold Installation
Fig.3a : SP401/601-SP801 Installation