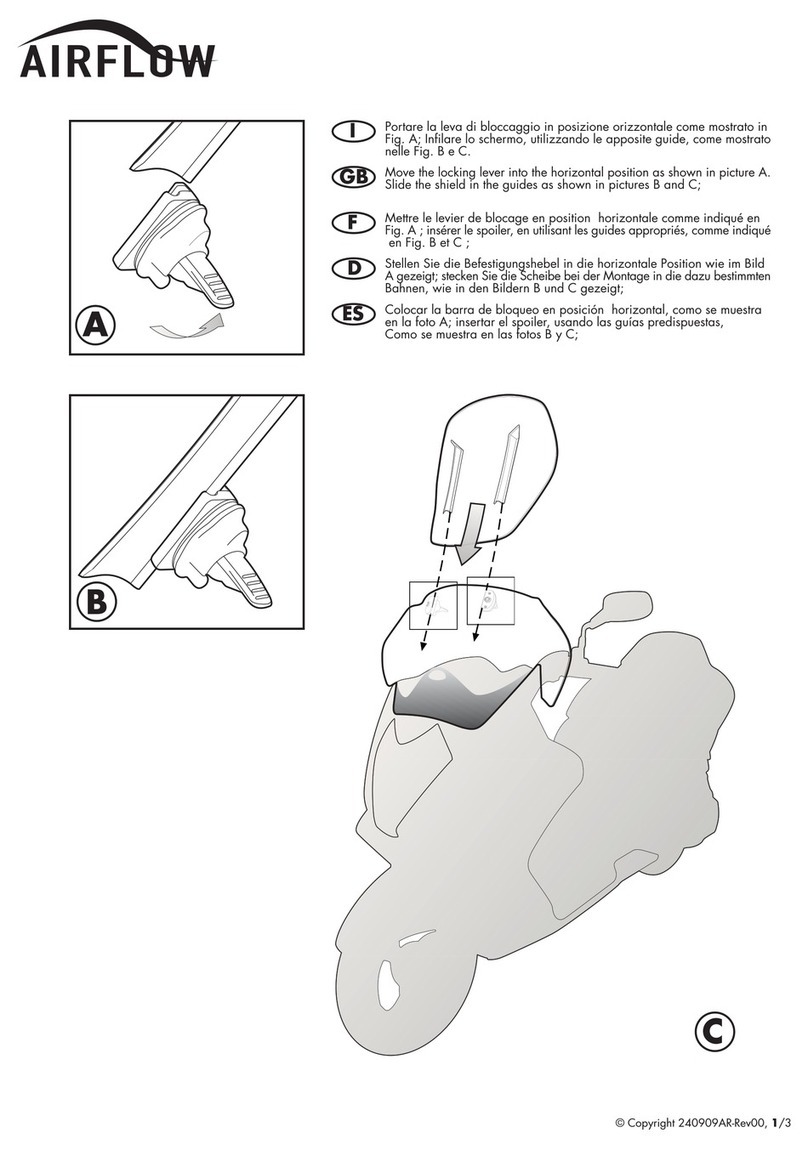
EME VR-ExtAdj Guide

1
Adjustable Electronic Voltage Regulator
Installation, Adjustment and Recommendations
Special Tools Required; Digital Voltmeter.
External Solid State Transitorized Voltage Regulator with Adjustable Voltage
Application
BMW R Airhead 1970-1995 and Moto Guzzi 1970-on
(with Bosch Alternator)
Euro MotoElectrics Part # VR-ExtAdj
Background
The function of a voltage regulator in a charging system is to limit the voltage produced by the
alternator to a set limit. In other words, it regulates or limits the voltage to a pre-determined set
point coming from the alternator to the battery. The voltage regulator has no ability to increase the
amperage output of the alternator. It simply regulates voltage below a range that is safe for the
battery and other electrical components in the vehicle’s electrical system.
The Bosch alternator and charging system used in the BMW and Moto Guzzi has the voltage
regulator monitor the voltage across the battery indirectly through diodes in the rectifier / diode
board. Therefore a direct method of reading the charging system voltage is to attach the positive
lead of the voltmeter to the B+ lead (large male spade terminal) of the rectifier. Due to indirect
voltage through the other charging system components, the adjustable voltage regulator allows to
compensate for these variations (reductions) and to maximize the voltage arriving to the battery.
Feature
This voltage regulator has the feature of allowing the properly informed technician to select the
maximum voltage to maximize your BMW or Moto Guzzi charging system.
NOTE: It will not compensate for damaged batteries due to sulfation etc. or other electrical system
deficiencies, such as poor or intermittent grounding.
It will not increase amperage output.
“Tuning up”the electrical system
Battery
The battery must be in good condition for the voltage to pass through the battery.
A 12 volt battery requires usually a minimum of 13.8 to 14.4 volts to achieve a complete charge.
This range depends on climactic conditions (temperature) and also the design and overall sulfation
state of your battery. An old sulfated battery with shorted cells will not re-charge to ~14.0 Volts !
Therefore the battery is the basic foundation to begin “tuning-up” the charging system’s to it’s
optimum performance.
Inspecting Wiring
The entire electrical system should be inspected for solid, clean connections, especially the battery
cables and all grounds. Clean and tight contacts should be the standard, and it is especially
important to focus on all the ground returns. All connections tend to deteriorate over the years due

2
to corrosion, oxidation, etc. on older motorcycles. When in doubt, remove the connection, clean
with emery cloth and retighten, replacing loose eyelets, grommets, frayed wires, etc.
Optimizing the “Tune-up”
If most of your riding is done in urban Stop-&-Go, you may need to set your voltage as high as 14.4
volts. In no case set the voltage over 14.4 volts ! Doing so will boil off water from the battery,
eventually damaging the battery, and will probably damage other electrical components as well.
For operation where longer duration, higher RPM engine speeds are being used, you may be able
to maintain battery charge voltage with as low as 14.1 volts.
Installation and Adjustment of the Adjustable Voltage Regulator
TURN SCREW ON REGULATOR CLOCKWISE TO INCREASE VOLTAGE AND COUNTER TO
DECREASE VOLTAGE.
The battery must be fully charged; charge up the battery to ensure voltage saturation.
Charging may be accomplished by utilizing a battery charger or running the engine during a ride.
(Idling the engine will not produce enough volts / amps to charge the battery; higher RPM’s such as
during a ride, would be required.)
Check with digital voltmeter across the + and –battery posts; should read 12.5 volts.
Turn off the engine.
Gain access to the voltage regulator. Gas tank removal may be required.
Remove the old regulator and unplug connector,
Plug connector into new regulator.
Bolting the new voltage regulator back into place is not necessary at this time as access to the
voltage setting screw is required.
The voltage regulator is grounded through the connector plug (-)
Start the engine with the headlamp turned off (or bulb removed).
Increase engine speed to ~ 2500 RPM.
The voltage should increase and stabilize.
When the voltage has stabilized, use a small screwdriver to adjust
the voltage. Turn the small adjustment screw on the back of the
voltage regulator clockwise to increase voltage, and counter
clockwise to decrease the voltage until the desired voltage is obtained.
The voltage should restabilize.
If voltage does continue to slowly increase, it probably means the battery was not fully charged and
or could be fully charged due to it’s condition, and / or due to the charging system’s previous
condition.
Eventually the voltage must stabilize. This needs to be monitored until the voltage is not increasing,
especially past 14.4 volts.
There should be enough gasoline in the carburetor bowls to complete the above voltage
stabilization adjustment. However. if required, re-install gas tank / gas lines, and perform / repeat
with fuel supply in place.
Upon satisfactory voltage stabilization, re-install the voltage regulator with original bolts, replace
fuel tank, etc.
Start the engine and re-verify voltage stability.
Check voltage reading often soon after installation, especially after long rides.
Also check battery fluid level. Ensure your maximum voltage has stability.
Table of contents