e. When operating a power tool outdoors,
use an extension cord suitable for outdoor
use. Use of a cord suitable for outdoor use
reduces the risk of electric shock.
f. If operating a power tool in a damp
location is unavoidable, use a residual
current device (RCD) protected supply.
Use of an RCD reduces the risk of electric
shock.
3. Personal safety
a. Stay alert, watch what you are doing
and use common sense when operating
a power tool. Do not use a power tool
while you are tired or under the influence of
drugs, alcohol or medication. A moment of
inattention while operating power tools may
result in serious personal injury.
b. Use safety equipment. Always wear
eye protection. Safety equipment such as
dust mask, non-skid safety shoes, hard hat,
or hearing protection used for appropriate
conditions will reduce personal injuries.
c. Avoid accidental starting. Ensure the
switch is in the off-position before plugging
in. Carrying power tools with your finger on
the switch or plugging in power tools that
have the switch on invites accidents.
d. Remove any adjusting key or spanner
before turning the power tool on. A
spanner or a key left attached to a rotating
part of the power tool may result in personal
injury.
e. Do not overreach. Keep proper footing
and balance at all times. This enables better
control of the power tool in unexpected
situations.
f. Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing
or jewellery. Keep your hair, clothing and
gloves away from moving parts. Loose
clothes, jewellery or long hair can be caught
in moving parts.
g. If devices are provided for the connection
of dust extraction and collection facilities,
ensure these are connected and properly
used. Use of these devices can reduce dust
related hazards.
4. Power tool use and care
a. Do not force the power tool. Use the
correct power tool for your application.
The correct power tool will do the job better
and safer when used at the rate for which it
was designed.
b. Do not use the power tool if the switch
does not turn it on and off. Any power tool
that cannot be controlled with the switch is
dangerous and must be repaired.
c. Disconnect the plug from the power
source before making any adjustments,
changing accessories, or storing power
tools. Such preventive safety measures
reduce the risk of starting the power tool
accidentally.
d. Store idle power tools out of the reach
of children and do not allow persons
unfamiliar with the power tool or these
instructions to operate the power tool.
Power tools are dangerous in the hands of
untrained users.
e. Maintain power tools. Check for
misalignment or binding of moving parts,
breakage of parts and any other condition
that may affect the power tools operation.
If damaged, have the power tool repaired
before use. Many accidents are caused by
poorly maintained power tools.
f. Keep cutting tools sharp and clean.
Properly maintained cutting tools with sharp
cutting edges are less likely to bind and are
easier to control.
g. Use the power tool, accessories and
tool bits etc., in accordance with these
instructions and in the manner intended
for the particular type of power tool, taking
into account the working conditions and
the work to be performed. Use of the
power tool for operations different from
intended could result in a hazardous situation.
5. Service
Have your power tool serviced by a
qualified repair person using only genuine
replacement parts. This will ensure that
the safety of the power tool is properly
maintained.
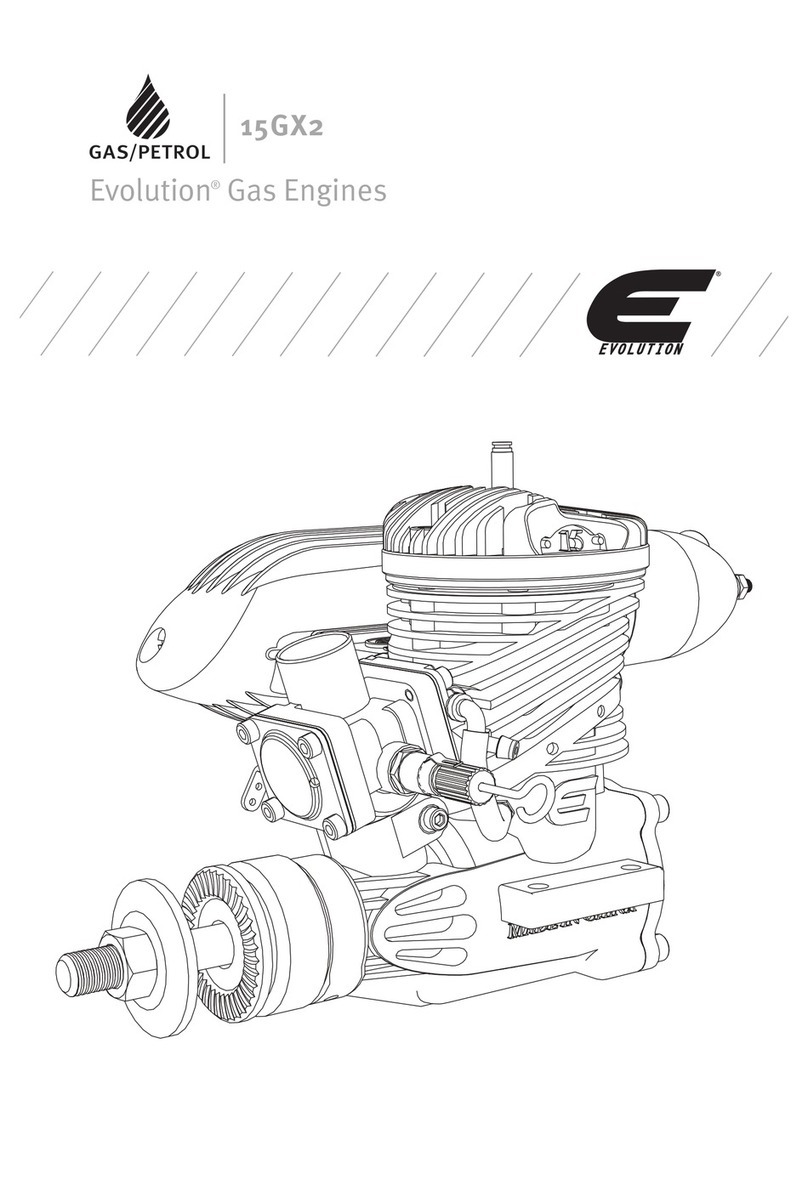
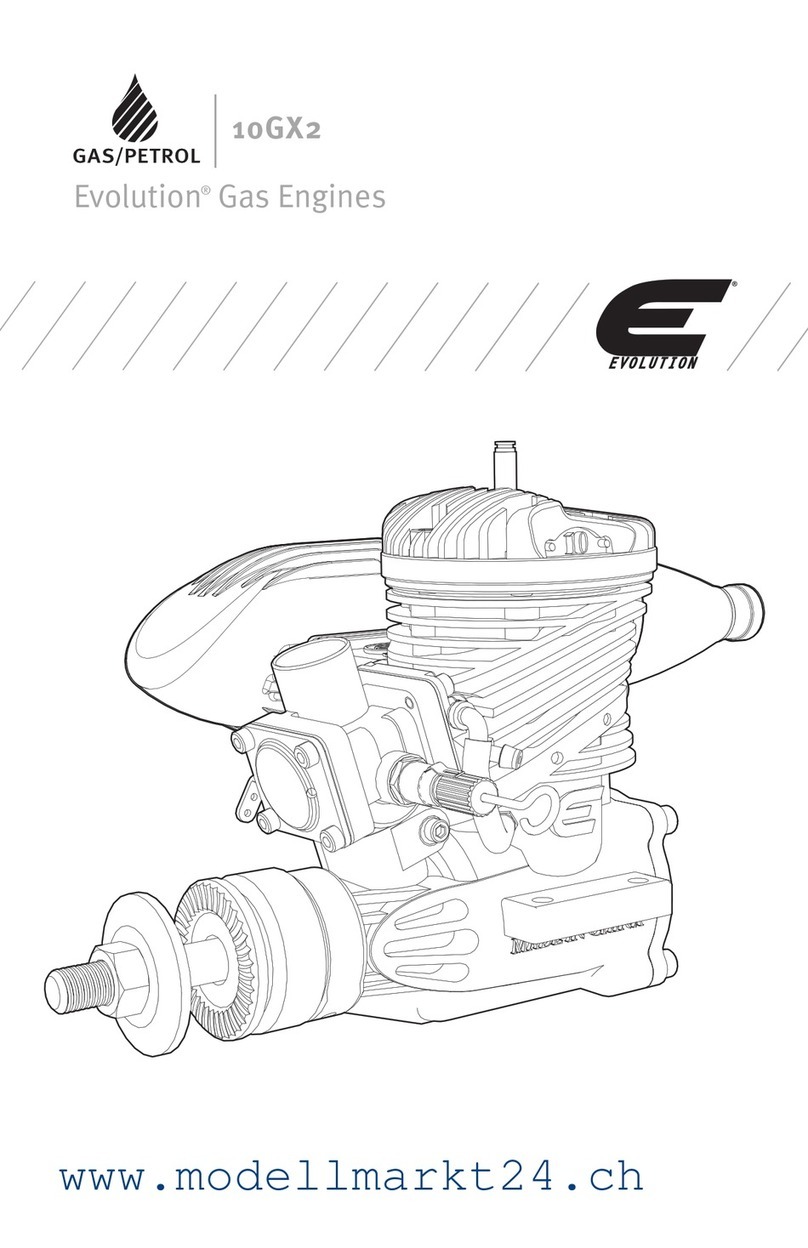
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
FOR EVOLUTION ENGINE
a. Petrol or diesel powered engines must
never be used in unventilated closed
spaces. The exhaust fumes produced are
highly toxic and can cause ‘Carbon Monoxide
Poisoning’ which will cause drowsiness and
ultimately death. It is only permissible to run
a petrol engine indoors if the building can be
very well ventilated and the exhaust fumes
can be captured and ducted to the outside
through an exhaust extraction/scavenger
system.
b. The engine should be positioned on
a firm level surface. The wheels should
be locked, so that the engine cannot move
during operation.
c. The engine should not be run at speeds
that exceed the maximum speed on
the rating plate. Operating an engine at
excessive speeds increases the likelihood of
component failure and consequent accidents.
d. Do not tamper with components that
regulate the engines speed. You may alter
the factory set running parameters.
e. Use only the type of fuel listed in this
Instruction Manual. Using fuel with an
octane rating less than that specified can
lead to excessive engine wear and premature
engine failure.
f. Keep the area around the engine clear,
clean and tidy. Never allow any combustible
material (timber, plastic, cardboard, canvas
etc) near a running engine.
g. Do not use in or near to potentially
explosive atmospheres. Dust laden
atmospheres as can be found in some
industrial buildings (Flour Mills, Timber Mills)
have an explosive potential.
h. Regularly check the fuel system for
leaks. Hoses and unions should be checked
for deterioration or chafing. Check the fuel
tank for damage or for a poorly fitting or worn
fuel cap. Any defects must be rectified before
the engine is used.
i. Always stop the engine and allow it to
cool down before refuelling. Try to avoid any
fuel spillage (often caused by ‘overfilling’ the
tank) and clean up any spilt fuel immediately.
The application of dry sand is an effective
way of neutralising fuel spills.
Do not allow sand to come into contact with
any part of the engine
k. Do not allow the engine to run out
of fuel while a generator under load is
attached. Surging of the engine as it uses
the last of the fuel could cause damage to
connected electrical equipment.
l. When transporting the engine in a
vehicle ensure that the fuel tap is turned
off. To minimise the risk of fuel spillage the
engine should be secured by ropes etc to the
load area of the vehicle so that it cannot move
during transportation. The engine should be
secured in as level an attitude as possible.
m. For long term storage we recommend
that the fuel system of the engine is
drained. During long term storage additives
in modern fuels can precipitate from the fuel
and block jets and valves in the fuel system.
n. Store the machine in a secure and well
ventilated area. Unauthorised personnel
should not have access to this machine.
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
FOR FUEL FILLING
a. Select level bare ground, remote from
any buildings as a refuelling station.
Ensure that there is no combustible material
in the immediate vicinity.
b. Smoking, using a naked flame or
producing sparks is strictly forbidden
whilst refuelling. Petrol is highly flammable
and its vapours are combustible.
c. Ensure that the fuel tap is turned ‘off’.
This will ensure that fresh fuel does not
‘flood’ the engines carburettor.
d. The engine must be turned ‘off’ and
allowed to cool before refuelling is
attempted. Inadvertent fuel spillage onto a
hot engine can result in the risk of fire.
e. Any fuel spills must be dealt with
immediately. If petrol contaminates any
clothing the operator must change clothes.
Do not rely on the fuel evaporating from the
clothes. Wash or launder the clothing when
the fuel has evaporated from the material.
f. The use of a funnel during refuelling is
recommended. Use of a funnel will minimise
the risk of fuel spillage.