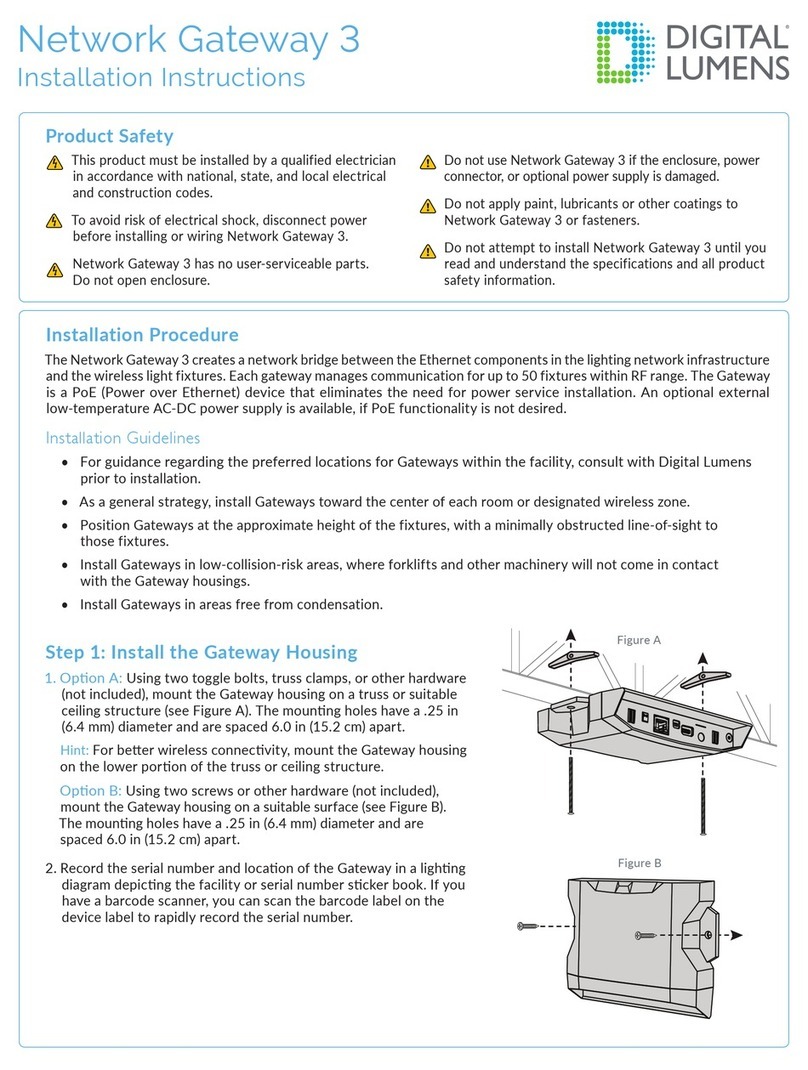
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
12-20-2002 Figure Sheet 1-853-A Page 5
SBPC-21-EN/IP Error Codes
The 7-segment LED digit on the SBPC-21-EN/IP main board is used to indicate errors or other
potential problems. See page 2 of this manual for the location of this LED. The error codes are
divided into the categories listed below. Since there is only a single-digit display and the error codes
are 3 digits in length, the error codes are displayed in three parts. The most significant digit will appear
first followed by the second and third digits. The display will go blank for a moment and the cycle
repeats unless the SBPC-21-EN/IP has been configured to attempt to restart after an error. If this is
the case, the error will only cycle once. All state machine errors 5XX are considered nonfatal and only
cycle once. Here are the error codes and their meanings.
Table 1-2
SBPC PROCESSOR ERRORS
F01 Processor attempted to execute and undefined instruction.
F02 Software interrupt vector occurred.
F03 Attempt to fetch instruction from invalid memory.
F04 Attempt to read data from invalid memory.
F05 Reserved exception vector.
F06 FLASH memory checksum fault.
F07 Pool memory allocation error.
F08 Byte memory allocation error.
F09 Unable to create thread.
F0A Unable to create event.
F0B Unable to create semaphore.
F0C Unable to create mutex.
F0D Unable to create queue.
F0E Unable to write to queue.
F0F Console I/O error.
Errors that begin with ‘F’
are unrecoverable faults.
The SBPC cannot
participate in FifeNet or
Ethernet operations. In
the default configuration,
the SBPC will attempt to
restart.
COMMUNICATION MODULE ERRORS
E01 The configuration matrix is corrupted.
E02 No HMS Anybus module detected.
E03 Anybus module failed to initialize (no interrupt received).
E04 Anybus module failed to initialize (interrupt stuck).
E05 Anybus module failed to initialize (mailbox not ready).
E06 Anybus mailbox timeout.
E07 Anybus mailbox response indicated error.
E08 Anybus mailbox response timeout.
E09 Anybus dual-port RAM fault.
E0A Anybus output area release timeout.
E0B Anybus initialization timeout.
Errors that begin with ‘E’
are associated with the
Ethernet interface. In
the default configuration,
the SBPC will attempt to
restart. With the
exception of error ‘E01,’
FifeNet is functional;
however, the default
configuration will attempt
to restart which will
interrupt FifeNet.
STATE MACHINE ERRORS
501 State machine file is corrupted.
502 State machine is disabled.
503 State machine started in shutdown mode.
504 Bad state machine instruction encountered.
505 State machine instruction fetch from address is out of range.
506 State machine stack error (too many nested calls).
507 State machine stack error (too many returns).
508 State machine attempted divide by zero.
509 State machine tried to access more than four timers.
50A State machine variable address is out of range.
Errors that begin with ‘5’
are related to the state
machine capability of the
SBPC. These errors are
cycled only once and do
not cause the SBPC to
restart.