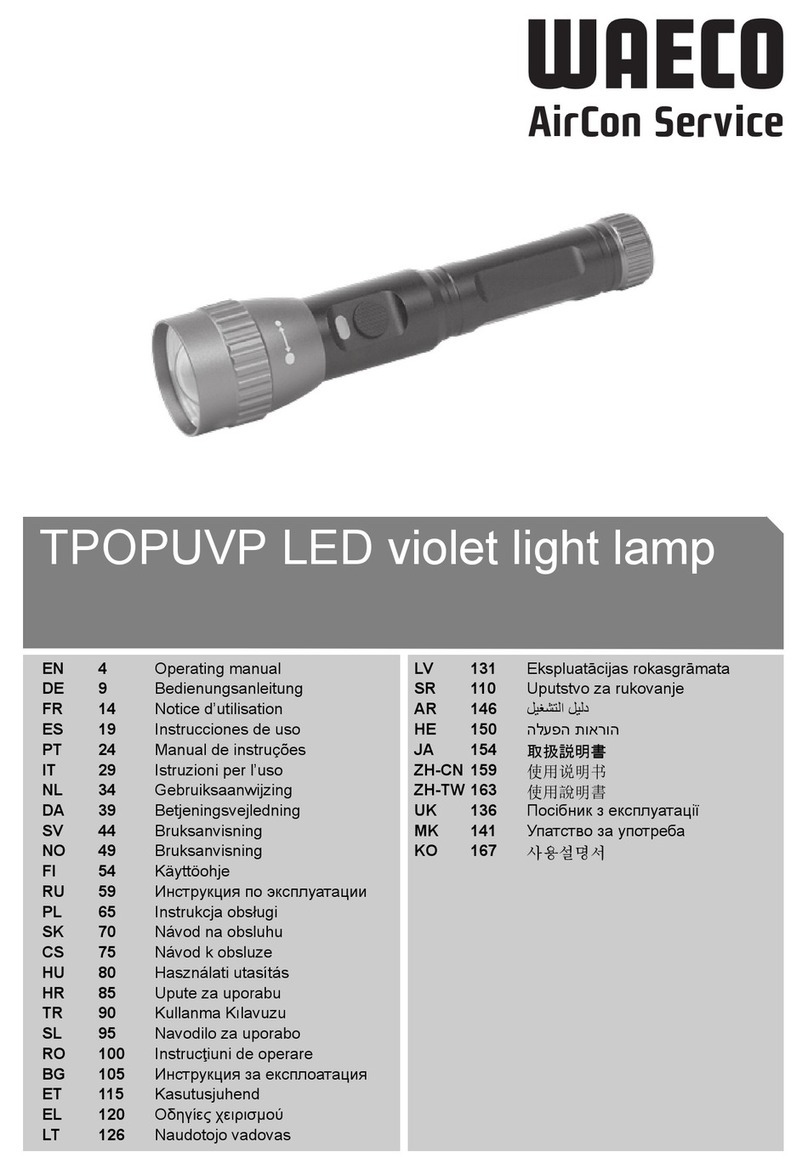
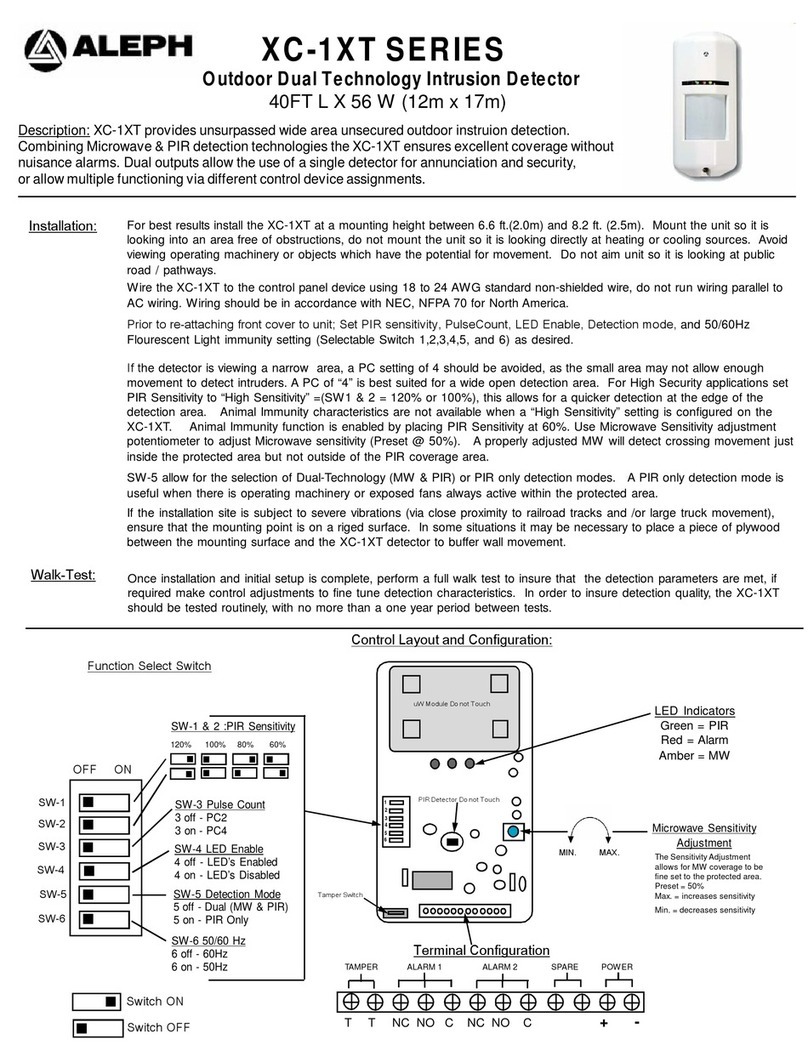
LIMITED WARRANTY AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
Each Fluke Networks product is warranted to be free from defects in material and
workmanship under normal use and service. The warranty period for the mainframe is
one year and begins on the date of purchase. Parts, accessories, product repairs and
services are warranted for 90 days, unless otherwise stated. Ni-Cad, Ni-MH and Li-Ion
batteries, cables or other peripherals are all considered parts or accessories. The
warranty extends only to the original buyer or end user customer of a Fluke Networks
authorized reseller, and does not apply to any product which, in Fluke Networks’
opinion, has been misused, abused, altered, neglected, contaminated, or damaged by
accident or abnormal conditions of operation or handling. Fluke Networks warrants
that software will operate substantially in accordance with its functional specifications
for 90 days and that it has been properly recorded on non-defective media. Fluke
Networks does not warrant that software will be error free or operate without
interruption.
Fluke Networks authorized resellers shall extend this warranty on new and unused
products to end-user customers only but have no authority to extend a greater or
different warranty on behalf of Fluke Networks. Warranty support is available only if
product is purchased through a Fluke Networks authorized sales outlet or Buyer has
paid the applicable international price. Fluke Networks reserves the right to invoice
Buyer for importation costs of repair/replacement parts when product purchased in
one country is submitted for repair in another country.
Fluke Networks warranty obligation is limited, at Fluke Networks option, to refund of
the purchase price, free of charge repair, or replacement of a defective product which
is returned to a Fluke Networks authorized service center within the warranty period.
To obtain warranty service, contact your nearest Fluke Networks authorized service
center to obtain return authorization information, then send the product to that
service center, with a description of the difficulty, postage and insurance prepaid (FOB
destination). Fluke Networks assumes no risk for damage in transit. Following
warranty repair, the product will be returned to Buyer, transportation prepaid (FOB
destination). If Fluke Networks determines that failure was caused by neglect, misuse,
contamination, alteration, accident or abnormal condition of operation or handling,
or normal wear and tear of mechanical components, Fluke Networks will provide an
estimate of repair costs and obtain authorization before commencing the work.
Following repair, the product will be returned to the Buyer transportation prepaid
and the Buyer will be billed for the repair and return transportation charges (FOB
Shipping point).
THIS WARRANTY IS BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OR MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. FLUKE NETWORKS SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LOSSES, INCLUDING LOSS OF DATA,
ARISING FROM ANY CAUSE OR THEORY.
Since some countries or states do not allow limitation of the term of an implied
warranty, or exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, the
limitations and exclusions of this warranty may not apply to every buyer. If any
provision of this Warranty is held invalid or unenforceable by a court or other
decision-maker of competent jurisdiction, such holding will not affect the validity or
enforceability of any other provision.
4/04
Fluke Networks
PO Box 777
Everett, WA 98206-0777
USA