8
Section 3: System Operation
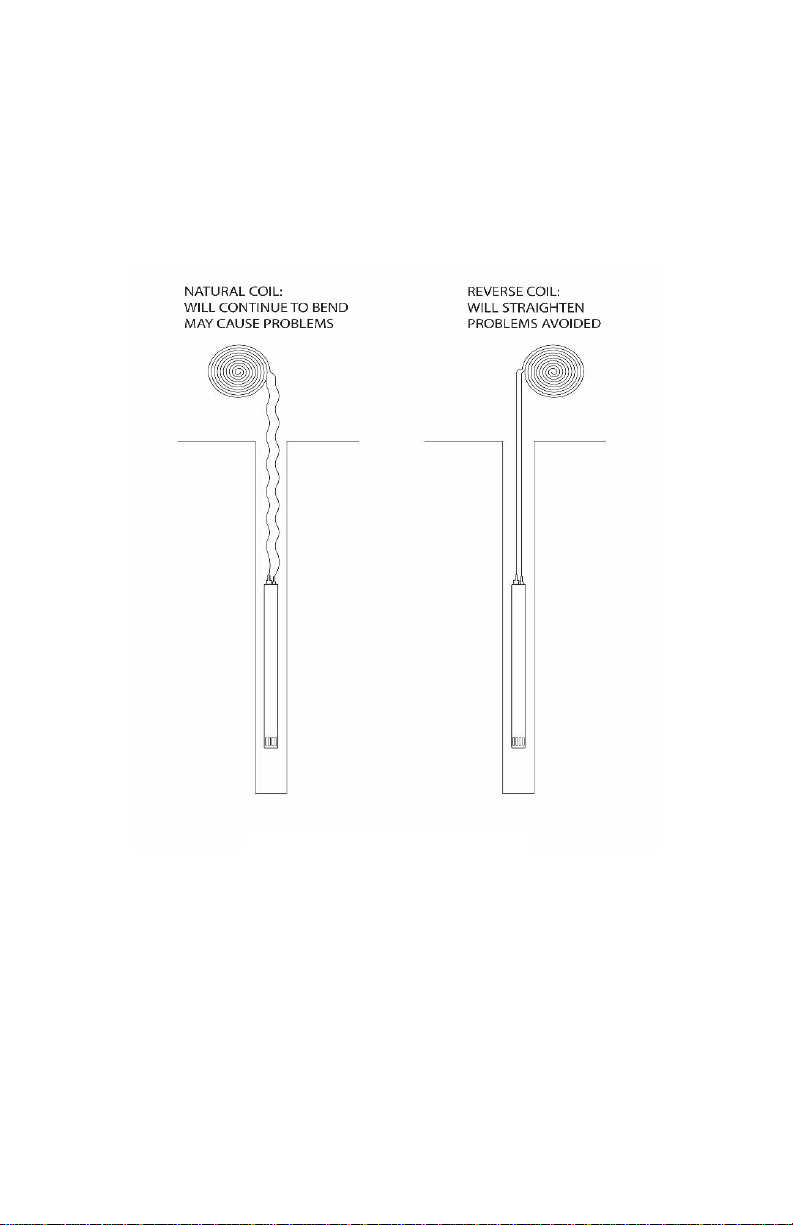
Once tubing and safety cable are connected, slowly deploy the pump into the well. If depth
to water is known, a mark can be placed on the tubing to indicate when the pump has
reached the desired level.
The pump must be fully submerged. Optimal pump performance is achieved with
submergence of greater than 10’ (3m) of water column. Less submergence could result in
reduced pump performance and physical damage to the bladder. Worn bladders can
develop a shape memory and may not be able to fill completely without sufficient
submergence. Pumping will still be achieved and the sampling event can be completed.
Once the pump is at the desired level within the well, set the controller DISCHARGE and
FILL timers. These settings should be such that the bladder is never over compressed.
Set the pressure cycle so the fluid stream exiting the fluid line starts to fall off when the
DISCHARGE timer expires. If the controller being used has a pressure gauge, you will
notice the pressure level will climb and then stabilize during pumping and start to increase
after all of the water has been evacuated from the pump. If you notice the pressure
increasing after a pump cycle, reduce the pressurization/discharge time.
Using the Example Flow Rates, set the FILL TIME to optimize the amount of fluid
discharged during the pressure cycle.
Both FILL TIME and DISCHARGE TIME vary depending on submergence, depth to water,
tubing size, and overall tubing length.
More information can be found in the user manual specific to the controller you are using.
Flowrates
Bladder Pump flow rates are influenced by pump size (diameter and length), pump depth
and submergance, as well as controller selection (i.e. compressor performance, valve flow
coefficient). A large pump at shallow depths will produce the most flow, and a small pump
at maximum depths will produce the least amount of flow.
Factors that increase flow:
increased submergance (depth of pump below water line).
a strong compressor, like the Geocontrol PRO, will enable fast pressure build up
in the airline tubing and pump cavity.
a clean intake screen will maximize the amount of water entering into the pump.