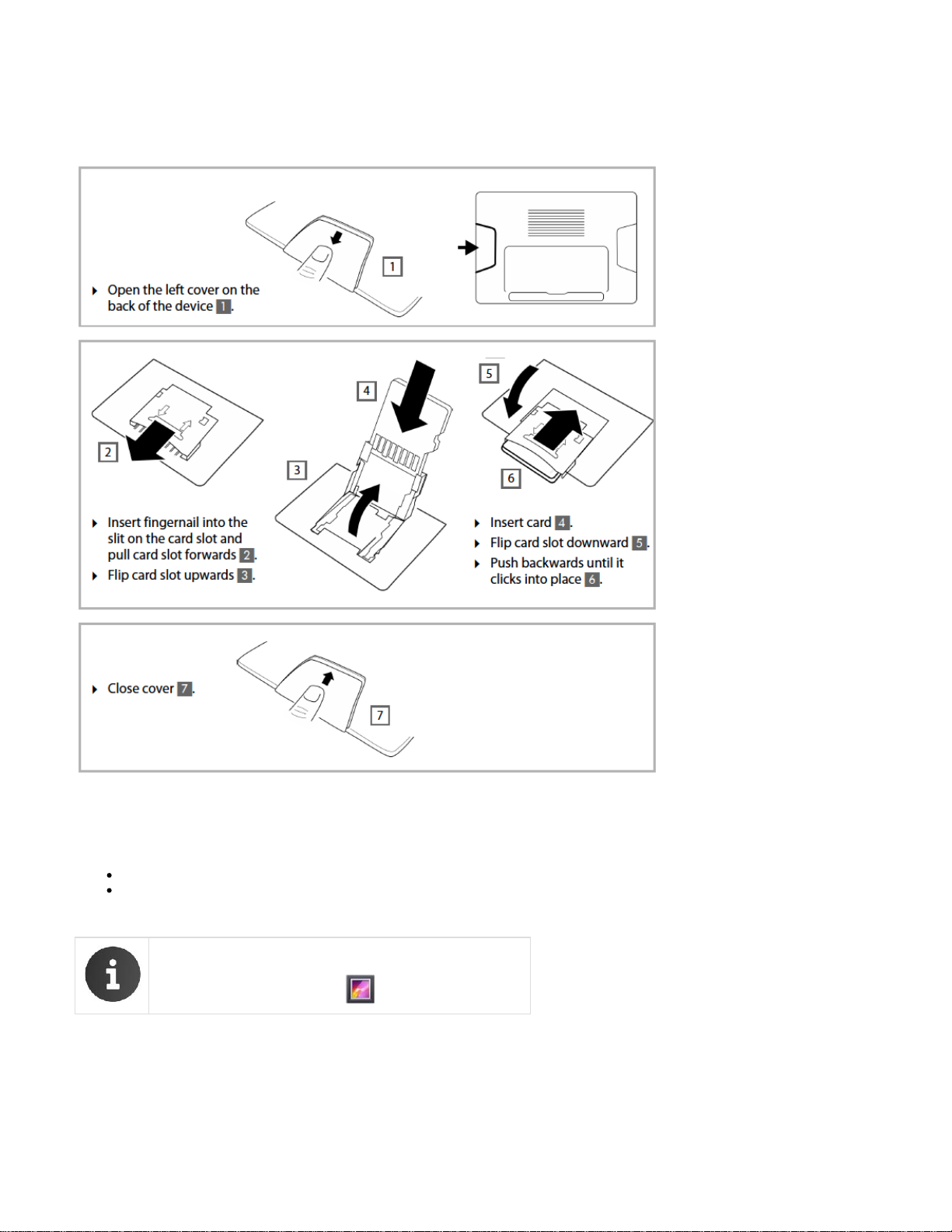
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Using the phone in different scenarios
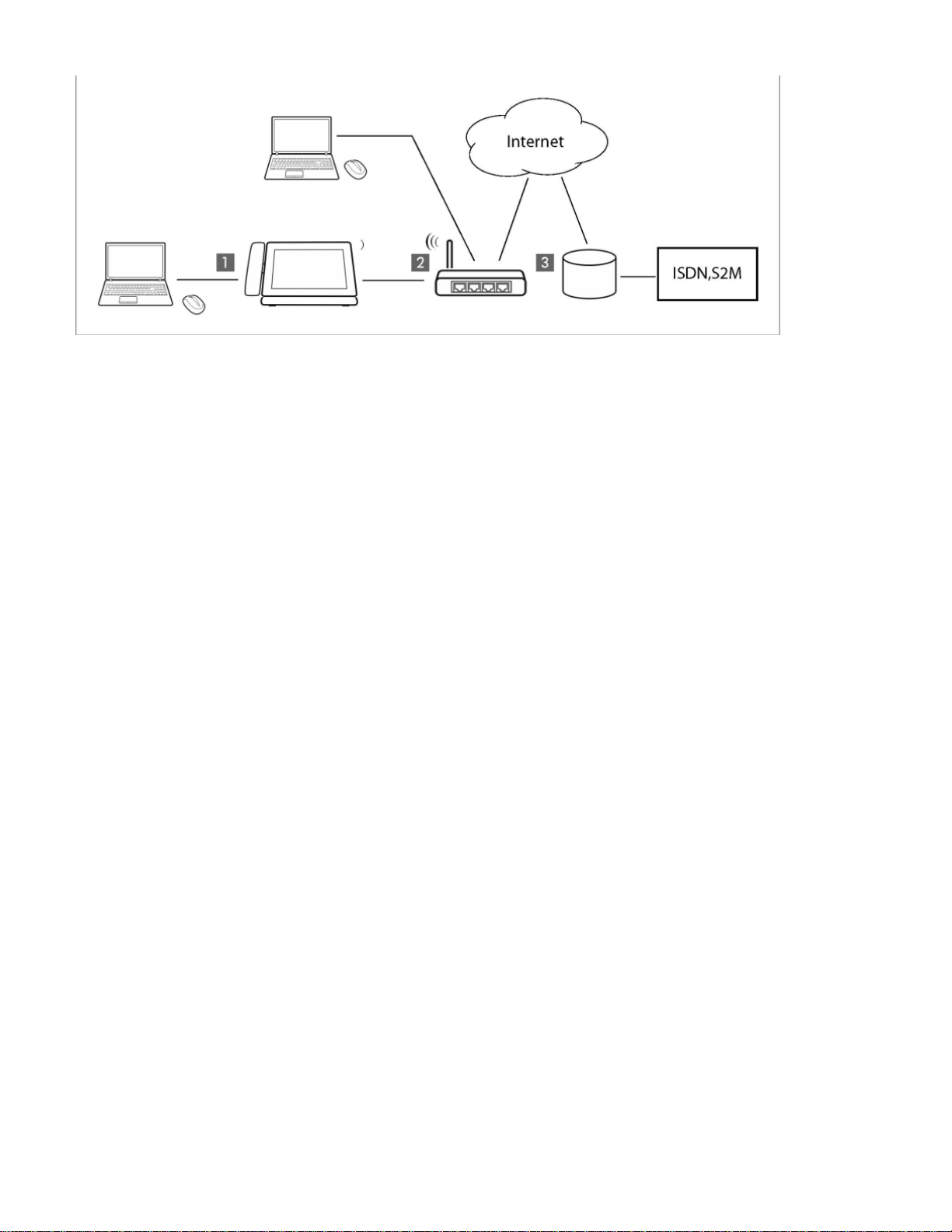
Using your phone in a professional environment with phone system and server structure
If you use your Maxwell 10 in a corporate network with a telephone infrastructure, your phone incor porates functions and data from the phone
system and servers.
In a corporate environment, the VoIP accounts and most of the settings are configured centrally by the phone system.
Gigaset IP telephone
Gigaset IP telephone with integrated gigabit switch (Maxwell 10). Your PC is connected directly to the phone, providing you with an
additional LAN connection in your network.
DECT Multicell System for connetion to up to 100 DECT handsets.
DECT base for connection to DECT handsets.
Ethernet switchSupports Quality of Service (QoS), Gigabit Ethernet and PoE (Power over Ethernet).
Phone system (e.g., Gigaset T500 PRO)Forms Internet telephony, ISDN or S2M connections. Analogue devices can be connected. A net
work connection is established using Ethernet.
Gateway to the Internet for all connected devices. Routes VoIP calls from the phone system to the Internet.
File, e-mail and workgroup servers, or NAS systems, can be wirelessly integrated into the phone system architecture. As a result:
- Invitations to conference calls can be organised via the phone system
- The phone system can be backed up to a server or the system can be started via the network
- Online directories (LDAP) can be managed centrally
Using your phone in a simplified environment without a phone system
You can also use your Maxwell 10 without a phone system.