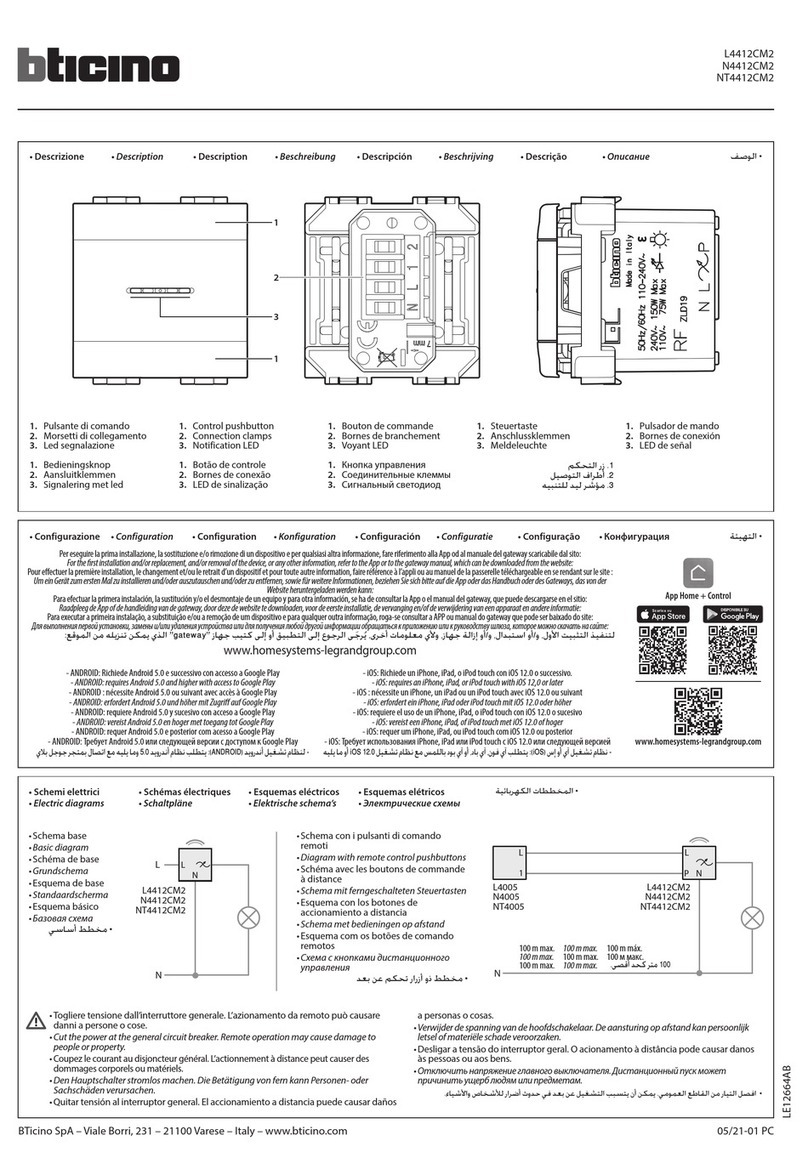
GTE SYLVANIA SSPB 800 User manual
Other GTE SYLVANIA Circuit Breaker manuals
Popular Circuit Breaker manuals by other brands

Siemens
Siemens Sentron 3VA9157-0PK1 Series operating instructions
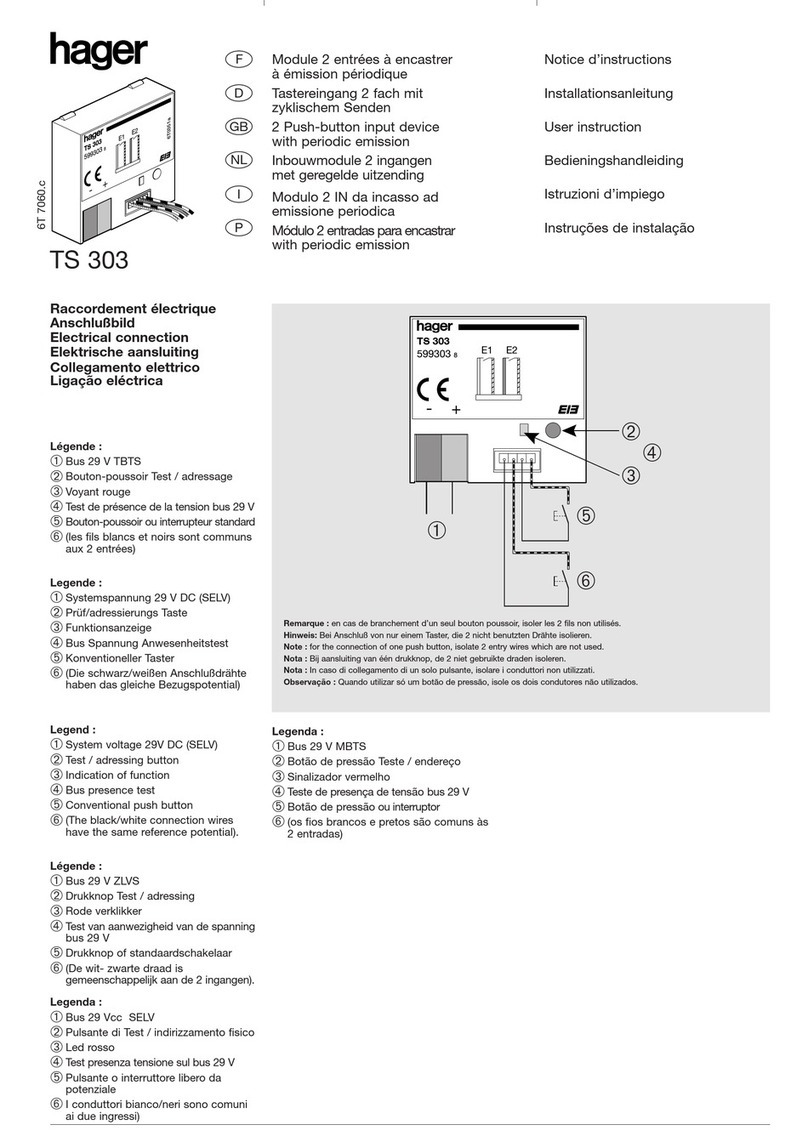
hager
hager TS 303 User instruction
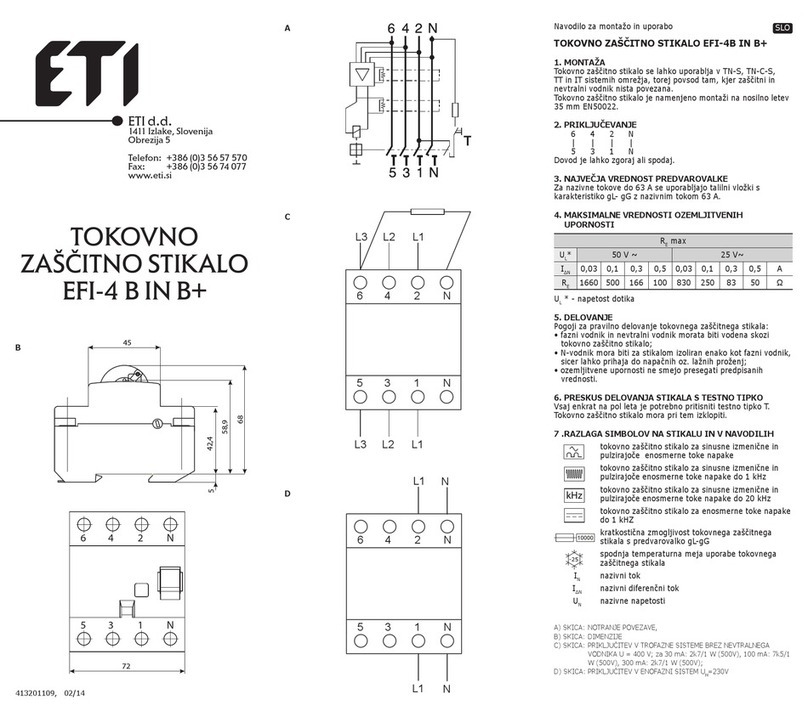
ETI
ETI EFI-4B Instructions for mounting

nader
nader NDM3EU-225 operating instructions
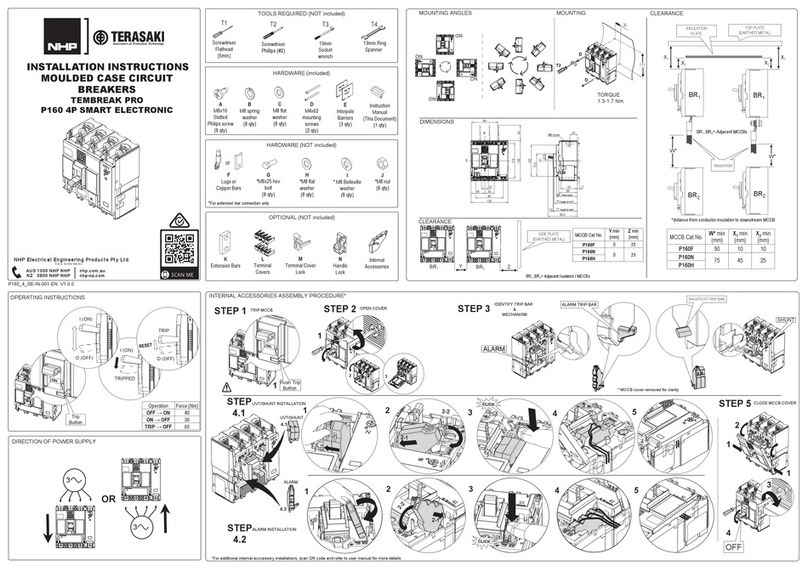
TERASAKI
TERASAKI NHP TemBreak PRO P160 Series installation instructions

Gladiator
Gladiator GCB150 Installation instruction